SWRA705 August 2021 AWR1243 , AWR1443 , AWR1642 , AWR1843 , AWR1843AOP , AWR2243 , AWR2944 , AWR6443 , AWR6843 , AWR6843AOP , AWRL1432 , AWRL6432 , IWR1443 , IWR1642 , IWR1843 , IWR2243 , IWR2944 , IWR6243 , IWR6443 , IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP , IWRL6432 , IWRL6432AOP
4.2 Spherical Radome Angle Dependent Error
Figure 4-2 shows the distance traveled through a curved shaped spherical radome. In this case, at different grazing angles, the radome performance can be shown to be similar to the boresight.
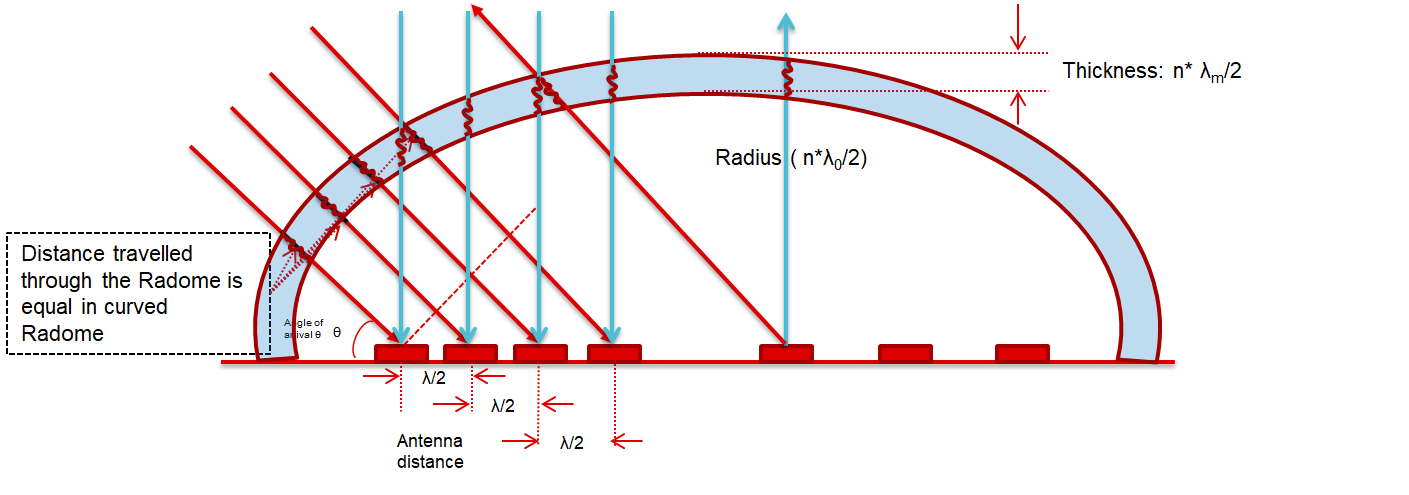 Figure 4-2 Distance Traveled in Spherical
Radome Wall for Different Grazing Angles
Figure 4-2 Distance Traveled in Spherical
Radome Wall for Different Grazing Angles