SLAAED0 March 2024 TAS2764 , TAS2780 , TAS2781
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Measurement Methodology
- 3 Introduction to Noise-gate and Pop in Class-D Amplifiers
- 4 Causes of Pop in TAS27xx family of Class-D Amplifiers
- 5 Click and Pop Using TAS27xx
-
6 Click and Pop Measurement Technique Using
AP v6.0. 2
- 6.1 Measurement Setup
- 6.2 Filter Settings
- 6.3 Data Capture Settings
- 6.4 Auto Range Settings for Pop Measurement
- 6.5 ASI or I2S Configurations for Pop Measurement
- 6.6 APx Sound Level Meter Utility
- 6.7 Data Acquisition
- 6.8 Interpreting Click and Pop Waveforms
- 6.9 Post Processing of AP Waveforms
- 6.10 A-Weighted Click and Pop Numbers
- 6.11 Exporting the A-Weighted Numbers
- 7 Noise-Gate Pop and Measurement Technique Using APx
- 8 Configuring TAS2764 for Improved Click and Pop Noise Performance
- 9 Summary
- 10References
1 Introduction
Click and pop noise refers to an undesired transient audible artifact, which gets played on the speaker, usually during power-up and shutdown of the speaker driver (in this case, the Class-D audio amplifier). Click and pop noise can occur even if the audio amplifier receives no input and isn’t playing any music at the output (idle channel condition).
Pop can occur irrespective of the type of amplifier driving the speaker. However, it is usually lower in more linear amplifiers such as Class-A or Class-AB as compared to Class-D. The Class-D amplifier outputs are pulse width modulated (PWM) based switching to achieve high efficiency at higher output powers. A settled Class-D amplifier output voltage frequency spectrum comprises of the gained-up audio input signal frequency (Fin) in audio band (20-20KHz) as well tones around switching frequency (Fsw), and the multiples.
When the device is in idle channel, the differential voltage across the speaker (in audio band), after the Class-D output is settled is just the RMS noise voltage of the amplifier. This can be the Idle channel noise of 32uV A-weighted on TAS2780/81 (Refer Electrical Characteristics in data sheet).
However, during start of the PWM from shutdown state, the differential error pulses start to build at Class-D output from zero error voltage hence resulting in a spectral energy that leaks into audio band. A similar scenario occurs due to stop of PWM pulses. Click and pop can occur at the output of the Class-D amplifier irrespective of the modulation scheme due to amplifier output differential offset (Output offset voltage Vos as per data sheet) and amplifier output settling related artifacts.
Figure 1-1 shows a sample start and stop of an LSR modulated Class-D PWM switching waveform.
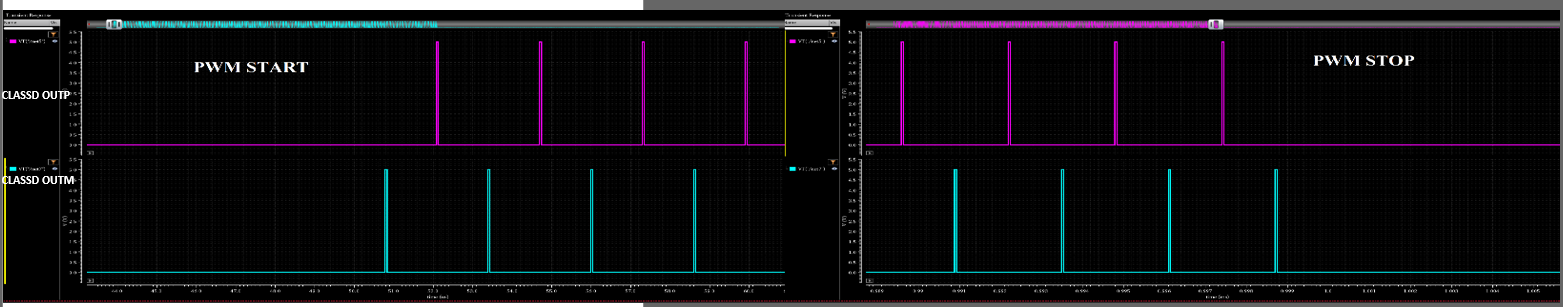 Figure 1-1 Sample LSR Modulated Class-D PWM
Output Switching Waveforms at the Start and Stop
Figure 1-1 Sample LSR Modulated Class-D PWM
Output Switching Waveforms at the Start and Stop