SLUUCC4A October 2020 – September 2021 TPS92520-Q1
- Trademarks
- General Texas Instruments High Voltage Evaluation (TI HV EMV) User Safety Guidelines
- 1Description
- 2Performance Specifications
- 3Performance Data and Typical Characteristic Curves
- 4Schematic, PCB Layout, and Bill of Materials
- 5Software
- 6TPS92520EVM-133 Power Up and Operation
- 7Revision History
6.5.1 Channel 1 or 2 Sub-Window: Settings, Measurements, and Faults
The Channel Sub-Window is broken down into basic features and settings set by selecting boxes or slide, measurements of VIN and LED, and fault status boxes (see Figure 6-20).
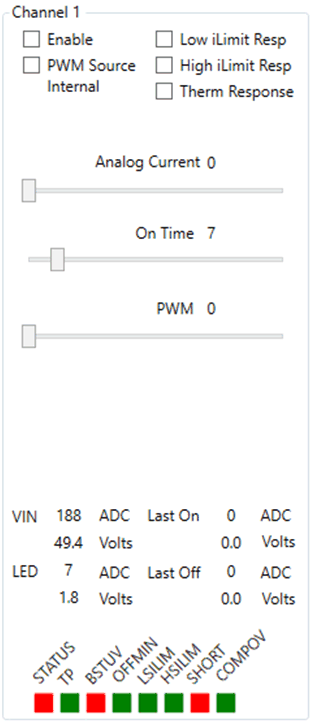 Figure 6-20 Channel 1 Window -
Configurations, Measurement, and Fault Window.
Figure 6-20 Channel 1 Window -
Configurations, Measurement, and Fault Window. 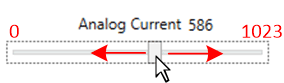 Figure 6-21 Analog Current Slide Bar.
Figure 6-21 Analog Current Slide Bar. The On Time slide adjust CHxTON registers which controls the switching frequency of the constant current LED buck driver, see Figure 6-22. The default value is 7 (decimal) which coincides with a 437-kHz switching frequency. The switching frequency ranges from 100 kHz to 2,200 kHz, see the Switching Frequency and Adaptive On-Time Control section of the TPS92520-Q1 data sheet for detailed calculations. The EVM is optimized to operate at the default switching frequency.
 Figure 6-22 On Time Slide Bar for Changing Switching Frequency.
Figure 6-22 On Time Slide Bar for Changing Switching Frequency. The PWM slide adjusts the internal 10 bit PWM duty cycle (CHxPWM registers) from 0 to 1023, which coincides with 0 (off) and 1023 (full ON), see Figure 6-23. For example, if you want to operate at a 50% duty cycle slide the bar to 512 (decimal value), which is half of the full scale of 1024 or 50%. The PWM Source Internal box much be selected for the PWM slide bar setting to be implemented. The PWM Source Internal box sets the CHxINTPWM bit high and enables the use of the internal PWM registers to generate the PWM function for that channel.
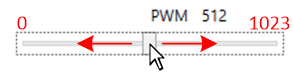 Figure 6-23 Internal PWM Duty Cycle Slide Bar.
Figure 6-23 Internal PWM Duty Cycle Slide Bar. The Enable box set the CHxEN bit to 1 for that channel, which means the associated channel is turned on, see Figure 6-24.
 Figure 6-24 Channel Feature Selection Boxes.
Figure 6-24 Channel Feature Selection Boxes. The Low iLimit Resp, High iLimit Resp, and Therm Response buttons coincide with setting the device to auto-restart after a fault time (IFT register setting) has elapsed or if it will latch off when the fault occurs. If box is selected then the device will latch off when the fault occurs and then reset the EN bit to the default of 0 (off) and will only continue to run when the EN bit is set to 1 (enabled).
Each channel window also reads the input voltage (VIN) and the output LED voltage (LED) at the CSNx pin for each respective channel using the internal ADC of the device. VIN is a reading of the CHxVIN registers and LED is a reading of CHxVLED registers, see Figure 6-25.
 Figure 6-25 VIN and LED Voltage Measurements From Internal ADC.
Figure 6-25 VIN and LED Voltage Measurements From Internal ADC. 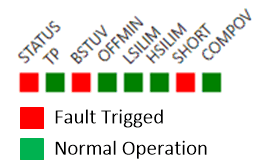 Figure 6-26 Status Indicators for Channels.
Figure 6-26 Status Indicators for Channels.