SWRU546E October 2018 – May 2022 AWR6843 , AWR6843AOP , IWR6443 , IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP
- Trademarks
- 1Getting Started
-
2MMWAVEICBOOST
- 2.1 Hardware
- 2.2 Block Diagram and Features
- 2.3 Muxing Scheme for Multiple Sources
- 2.4 Using the MMWAVEICBOOST With the Starter Kit
- 2.5 Interfacing with the DCA1000EVM
- 2.6 Power Connections
- 2.7
Connectors
- 2.7.1 20-Pin LaunchPad and Booster Pack Connectors (J5, J6)
- 2.7.2 60-Pin High Density (HD) Connector (J4 and J17)
- 2.7.3 60-Pin High Density (HD) Connector (J10)
- 2.7.4 MIPI 60-Pin Connector (J9)
- 2.7.5 TI 14-Pin JTAG Connector (J19)
- 2.7.6 CAN Connector (J1 and J2)
- 2.7.7 Ultra-Miniature Coaxial Connector (J3)
- 2.8 Jumpers, Switches and LEDs
- 3xWR6843ISK / IWR6843ISK-ODS REV C
-
4xWR6843AOPEVM Rev G
- 4.1 Hardware
- 4.2 Block Diagram
- 4.3 PCB Storage and Handling Recommendations
- 4.4 Heat Sink and Temperature
- 4.5 xWR6843AOPEVM Antenna
- 4.6 Switch Settings
- 4.7 xWR6843AOPEVM Muxing Scheme
- 4.8 Modular, DCA1000EVM and MMWAVEICBOOST Mode
- 4.9 Known Issues: Spurious Performance
- 4.10 PC Connection
- 4.11 REACH Compliance
- 4.12 Regulatory Statements with Respect to the xWR6843AOPEVM Rev G
- 5xWR6843AOPEVM Rev F
- 6IWR6843ISK / IWR6843ISK-ODS (deprecated)
- 7IWR6843AOPEVM (Deprecated)
- 8TI E2E Community
- 9Certification Related Information
- Revision History
5.4 Heat Sink and Temperature
Users are strongly encouraged to use the xWR6843AOPEVM with the heat sink installed. Due to the smaller size of the xWR6843AOPEVM, it is likely to get warmer than other larger sized EVMs on the mmWave Radar portfolioso care must be taken to ensure the junction temperature does not exceed 105°C. Figure 5-4 shows measurement of junction temperature versus duty cycle taken with and without the heat sink. As seen in the plot, the EVM can safely operate up to 50% duty cycle with or without the heat sink. Although the heatsink is not absolutely required, usage of the heat sink provides protection against exceeding the junction temperature at higher duty cyles.
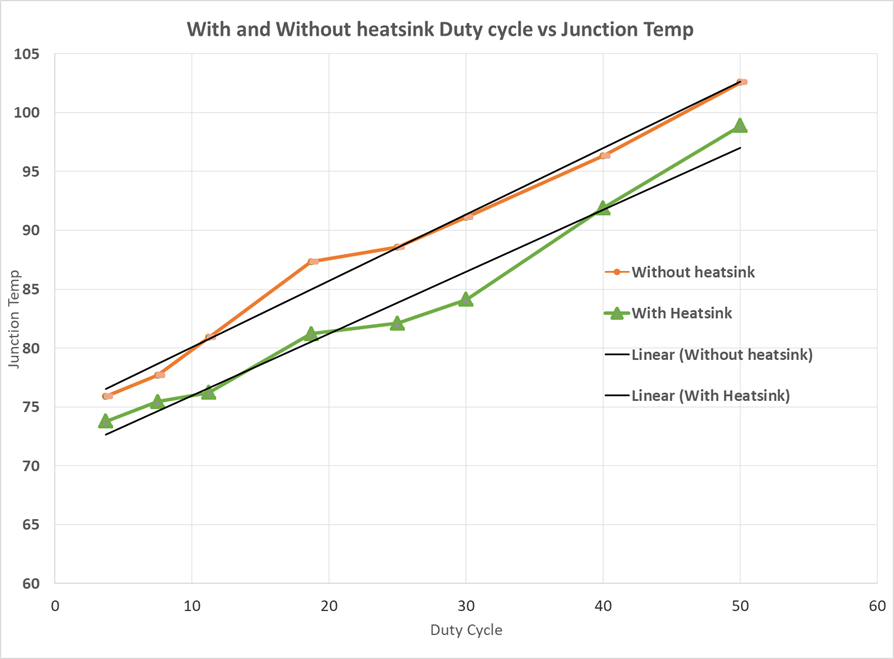 Figure 5-4 Duty Cycle versus Junction Temperature
Figure 5-4 Duty Cycle versus Junction TemperatureWhen using the EVM for custom applications, the duty cycle can be adjusted as needed, the heat sink provided with the kit can be used, customers can also design their own heat sink using better heat disippating materials or one with more surface area such as addition of fins. The CAD drawing for the heat sink is shown in Figure 5-5
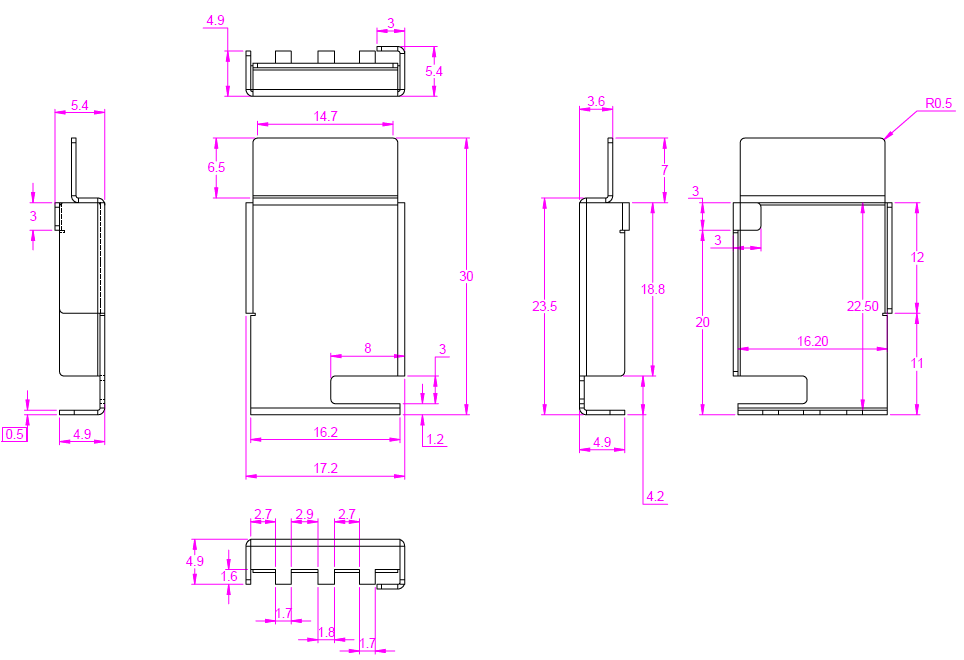 Figure 5-5 Heat sink CAD drawing
Figure 5-5 Heat sink CAD drawingApplication of the heat sink is shown in Figure 5-6
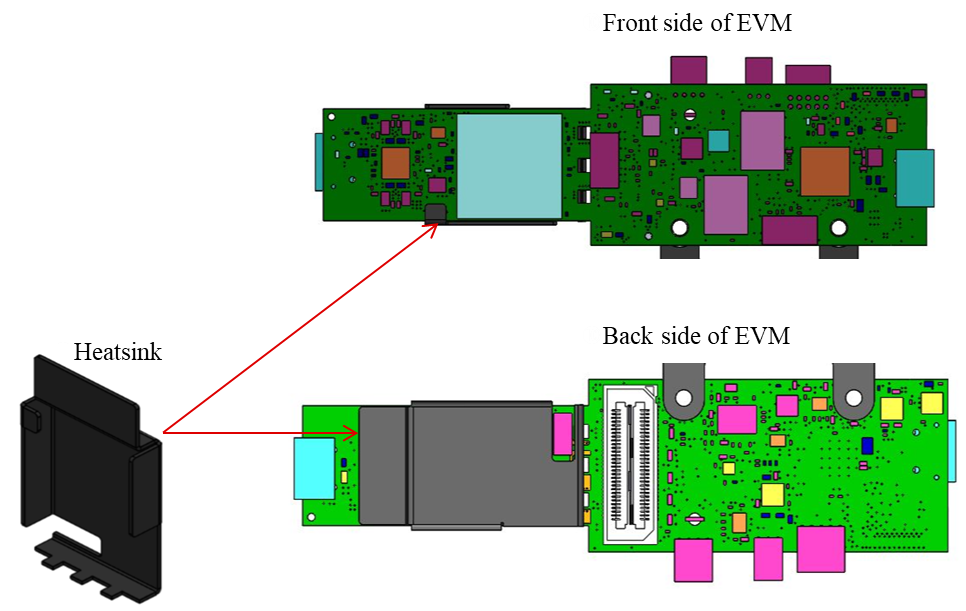 Figure 5-6 Heat sink placement
Figure 5-6 Heat sink placement