SWRU546E October 2018 – May 2022 AWR6843 , AWR6843AOP , IWR6443 , IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP
- Trademarks
- 1Getting Started
-
2MMWAVEICBOOST
- 2.1 Hardware
- 2.2 Block Diagram and Features
- 2.3 Muxing Scheme for Multiple Sources
- 2.4 Using the MMWAVEICBOOST With the Starter Kit
- 2.5 Interfacing with the DCA1000EVM
- 2.6 Power Connections
- 2.7
Connectors
- 2.7.1 20-Pin LaunchPad and Booster Pack Connectors (J5, J6)
- 2.7.2 60-Pin High Density (HD) Connector (J4 and J17)
- 2.7.3 60-Pin High Density (HD) Connector (J10)
- 2.7.4 MIPI 60-Pin Connector (J9)
- 2.7.5 TI 14-Pin JTAG Connector (J19)
- 2.7.6 CAN Connector (J1 and J2)
- 2.7.7 Ultra-Miniature Coaxial Connector (J3)
- 2.8 Jumpers, Switches and LEDs
- 3xWR6843ISK / IWR6843ISK-ODS REV C
-
4xWR6843AOPEVM Rev G
- 4.1 Hardware
- 4.2 Block Diagram
- 4.3 PCB Storage and Handling Recommendations
- 4.4 Heat Sink and Temperature
- 4.5 xWR6843AOPEVM Antenna
- 4.6 Switch Settings
- 4.7 xWR6843AOPEVM Muxing Scheme
- 4.8 Modular, DCA1000EVM and MMWAVEICBOOST Mode
- 4.9 Known Issues: Spurious Performance
- 4.10 PC Connection
- 4.11 REACH Compliance
- 4.12 Regulatory Statements with Respect to the xWR6843AOPEVM Rev G
- 5xWR6843AOPEVM Rev F
- 6IWR6843ISK / IWR6843ISK-ODS (deprecated)
- 7IWR6843AOPEVM (Deprecated)
- 8TI E2E Community
- 9Certification Related Information
- Revision History
2.7.6 CAN Connector (J1 and J2)
The J1 and J2 connectors shown in Table 2-8 provide the CAN_L and CAN_H signals from the onboard CAND-FD transceiver (TCAN1042HGVDRQ1) and CAN transceiver (SN65HVDA540QDR) independently, as shown in Figure 2-22. These signals are wired to the CAN bus after muxing with the SPI interface signals; one of the two paths must be selected. Two CANs are selected by closing the switch S1 (1st position of switch to be ON).
Table 2-8 CAN Connectivity
| Pin Description | Device Interface | Connector on Board |
|---|---|---|
| SPI_CS1 SPI_CLK1 | CAN2_TX CAN2_RX | J2 pin 1 (CAN2 corresponds to Regular CAN) J2 pin 3 |
| MISO_1 MOSI_1 | CAN1_TX CAN1_RX | J1 pin 1 (CAN1 corresponds to CANFD) J1 pin 3 |
Figure 2-22 shows the CAN connectors.
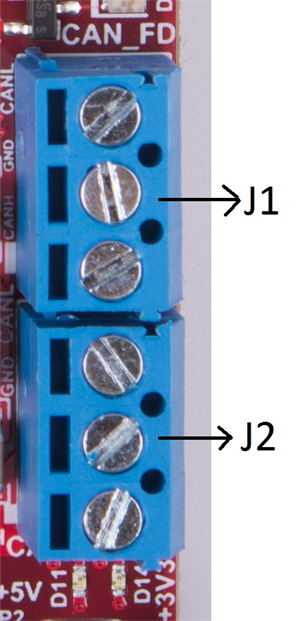 Figure 2-22 CAN Connectors
Figure 2-22 CAN Connectors