SBOSAK2A May 2025 – September 2025 INA187
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1.1 RSENSE and Device Gain Selection
The accuracy of any current-sense amplifier is maximized by choosing the largest current-sense resistor value possible. A larger value sense resistor maximizes the differential input signal for a given amount of current flow and reduces the error contribution of the offset voltage. However, there are practical limits as to how large the current-sense resistor value can be in a given application because of the physical dimensions of the package, package construction, and maximum power dissipation. Equation 2 gives the maximum value for the current-sense resistor for a given power dissipation budget:

where:
- PDMAX is the maximum allowable power dissipation in RSENSE.
- IMAX is the maximum current that flows through RSENSE.
An additional limitation on the size of the current-sense resistor and device gain is due to the power-supply voltage, VS, and device swing-to-rail limitations. To verify that the current-sense signal is properly passed to the output, both positive and negative output swing limitations must be examined. Equation 3 provides the maximum values of RSENSE and GAIN to keep the device from exceeding the positive swing limitation.

where:
- IMAX is the maximum current that flows through RSENSE.
- GAIN is the gain of the current-sense amplifier.
- VSP is the positive output swing of the device as specified in the Specifications.
To avoid positive output swing limitations when selecting the value of RSENSE, there is always a trade-off between the value of the sense resistor and the gain of the device under consideration. If the sense resistor selected for the maximum power dissipation is too large, then selecting a lower gain device is possible to avoid positive swing limitations.
The negative swing limitation places a limit on how small the sense resistor value can be for a given application. Equation 4 provides the limit on the minimum value of the sense resistor.
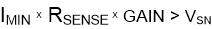
where:
- IMIN is the minimum current that flows through RSENSE.
- GAIN is the gain of the current-sense amplifier.
- VSN is the negative output swing of the device as specified in the Specifications.
Table 7-1 shows an example of the different results obtained from using five different gain versions of the INA187. From the table data, the highest gain device allows a smaller current-shunt resistor and decreased power dissipation in the element.
| PARAMETER | EQUATION | RESULTS AT VS = 5V | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 DEVICES | A2 DEVICES | A3 DEVICES | |||
| G | Gain | 20V/V | 50V/V | 100V/V | |
| VSENSE | Ideal differential input voltage | VSENSE = VOUT / G | 250mV | 100mV | 50mV |
| RSENSE | Current sense resistor value | RSENSE = VSENSE / IMAX | 25mΩ | 10mΩ | 5mΩ |
| PSENSE | Current-sense resistor power dissipation | RSENSE × IMAX2 | 2.5W | 1W | 0.5W |