SLLS732A October 2006 – November 2019 SN65LBC174A-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Revision History
- 5Description (continued)
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
- DW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.5.2 Typical Application
The following block diagram shows an MCU host connected via RS-485 to a SPI slave device. This device can be an ADC, DAC, MCU, or other SPI slave peripheral.
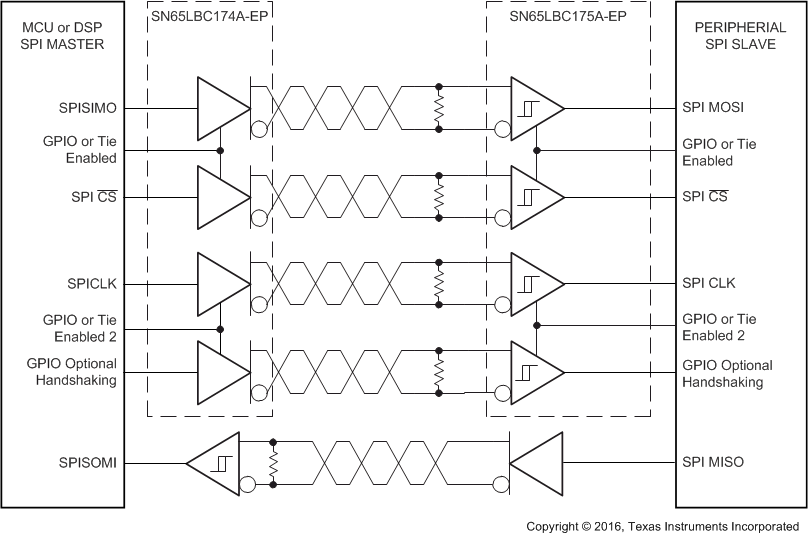 Figure 16. Typical Application Circuit, MCU Master to Slave Link Via Serial Peripheral Interface
Figure 16. Typical Application Circuit, MCU Master to Slave Link Via Serial Peripheral Interface