SPRAC76G November 2022 – February 2024 AM5706 , AM5708 , AM5716 , AM5718 , AM5726 , AM5728 , AM5729 , AM5746 , AM5748 , AM5749 , AM620-Q1 , AM623 , AM625 , AM625-Q1 , AM625SIP , AM6411 , AM6412 , AM6421 , AM6422 , AM6441 , AM6442 , AM6526 , AM6528 , AM6546 , AM6548
- 1
- Sitara Processor Power Distribution Networks: Implementation and Analysis
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Guidelines for PCB Stack-Up
- 3Physical Layout Optimization of the PDN
- 4Static PDN Analysis (IR Drop Optimization)
- 5Dynamic Analysis of PCB PDN
- 6Checklist for PDN
- 7Implementation Examples and PDN Targets
- Revision History
7.3 AM572x
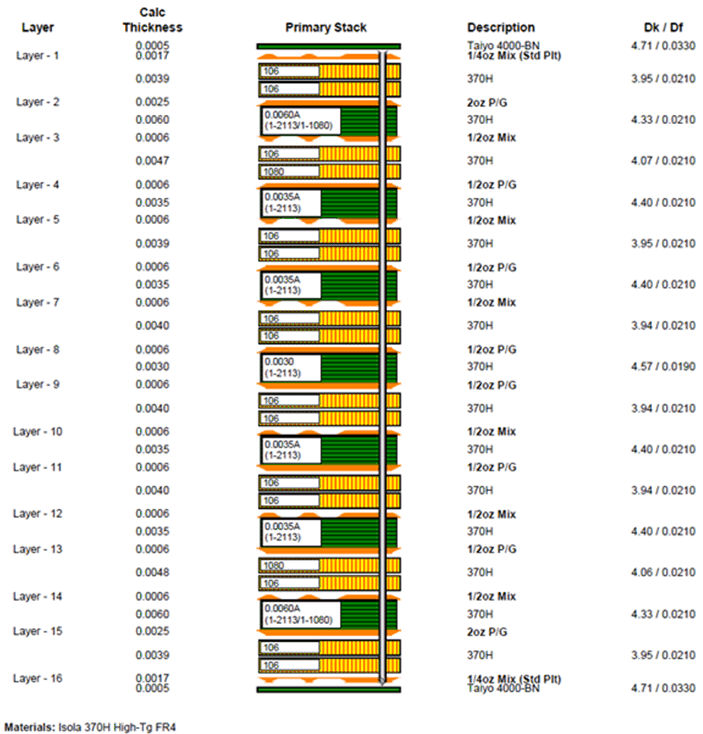
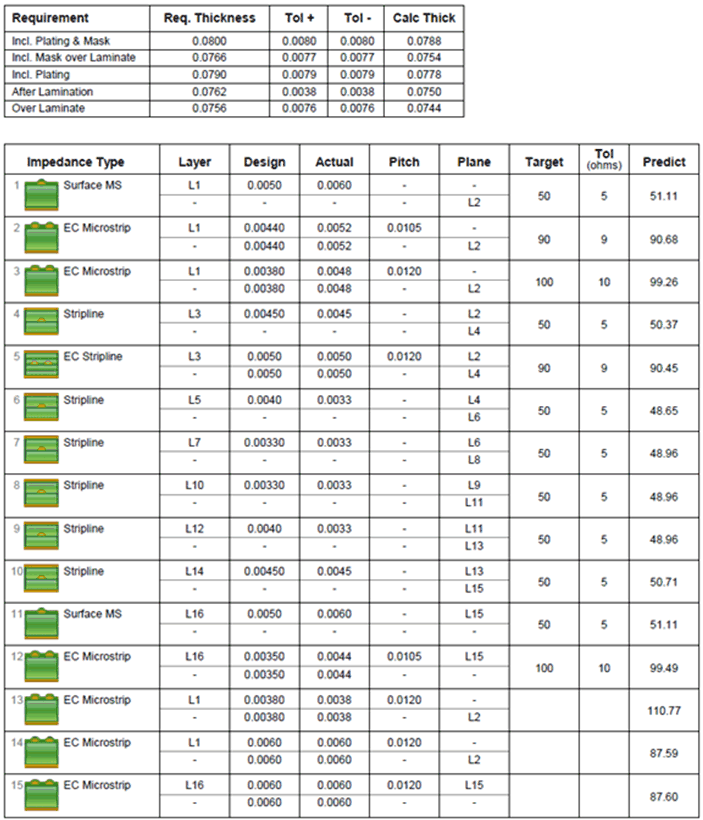
Table 7-3 AM572x PDN Targets and Decoupling Example
| Supply Name(10) | Static PDN Target | Dynamic PDN Targets | Number of Decoupling Capacitors Per Supply (1)(2)(3)(4)(5)(6) (9) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Reff (mΩ) (7) | Dec Cap Max LL (nH) (6)(8) | Max Impedance (mΩ) | Frequency of Interest (MHz) | 100 nF | 220 nF | 470 nF | 1 µF | 2.2 µF | 4.7 µF | 10 µF | 22 µF | |
| VDD_CORE | 27 | 2 | 87 | ≤50 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| VDD_MPU | 10 | 2 | 57 | ≤20 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| VDD_DSPEVE | 13 | 2.5 | 54 | ≤20 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| VDD_IVA | 48 | 2 | 800 | ≤100 | 5 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| VDD_GPU | 18 | 2.5 | 207 | ≤50 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| VDDS_DDR1 | 10 | 2.5 | 200 | ≤100 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||
| VDDS_DDR2 | 10 | 2.5 | 200 | ≤100 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||
| CAP_VBBLDO_DSPEVE | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VBBLDO_GPU | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VBBDLO_IVA | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VBBLD0_MPU | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_CORE1 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_CORE2 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_CORE3 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_CORE4 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_CORE5 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_DSPEVE1 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_DSPEVE2 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_GPU | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_IVA | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_MPU1 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | 1 | |||||||
| CAP_VDDRAM_MPU2 | N/A | 6 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
(1) For more information on peak-to-peak noise values, see the Recommended Operating Conditions table in the device-specific data manual.
(2) ESL must be as low as possible and not exceed 0.5 nH.
(3) The power delivery network (PDN) impedance characteristics are defined versus the device activity (that runs at different frequency) based on the Recommended Operating Conditions table in the Specifications chapter of the device-specific data manual.
(4) The static drop requirement drives the maximum acceptable PCB resistance between the PMIC or the external SMPS and the processor power balls.
(5) Assuming that the external SMPS (power IC) feedback sense is taken close to processor power balls.
(6) High-frequency (30 MHz – 70 MHz) PCB decoupling capacitors.
(7) Maximum Reff from VRM/SMPS/PMIC to processor.
(8) Maximum loop inductance for decoupling capacitor.
(9) Decoupling capacitor counts and values are provided as a baseline recommendation only. TI recommends that all PCB designs be simulated prior fabrication to ensure that the processor PDN requirements are met.
(10) Ganged rails must meet all requirements of each member rail.