JAJU732C June 2019 – July 2022
- 概要
- Resources
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Circuit Description
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5Design Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Terminology
- 8About the Author
- 9Revision History
2.3.4.4 Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor in the dual-active bridge must be designed to handle the ripple. This value impacts the output voltage specification. From Figure 2-19, Equation 15 and Equation 16 are obtained.
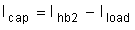
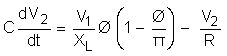
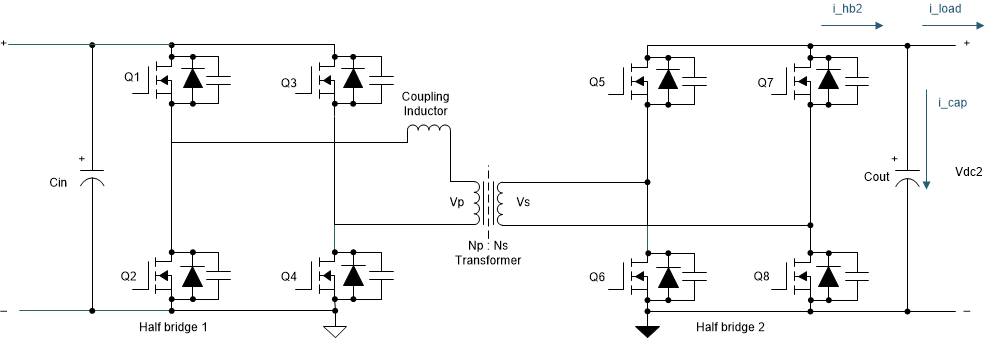 Figure 2-19 Output Current in Dual-Active Bridge
Figure 2-19 Output Current in Dual-Active BridgeFigure 2-20 shows the effect of the leakage inductor on the selection of the output capacitance. For a particular value of phase shift and inductance, capacitance required for containing the voltage ripple to a specified limit, as per the system specification, increases as the leakage inductor increases. This also means that more capacitance is needed to handle the voltage ripple. As the RMS value of capacitor current increases, more is the loss dissipated across the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of capacitance. Considering these factors, the output capacitor was chosen to keep the output voltage under 5% ripple.
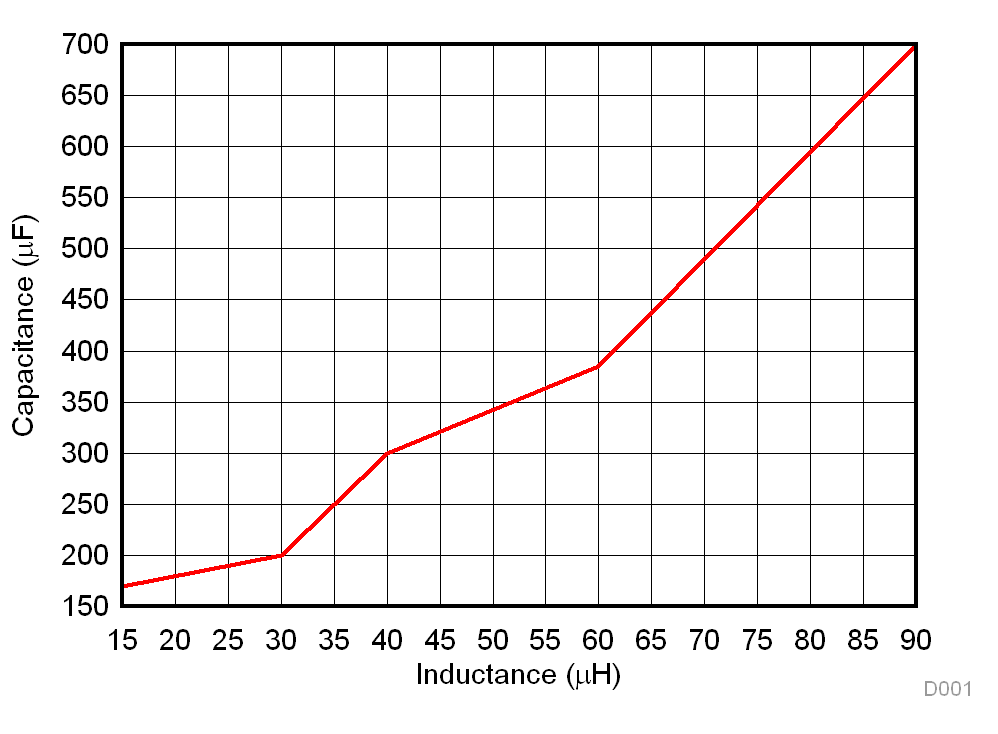 Figure 2-20 Desired Output Capacitance Versus Leakage Inductance
Figure 2-20 Desired Output Capacitance Versus Leakage Inductance