SNVSBJ0B December 2019 – August 2021 LM5170
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Bias Supply (VCC, VCCA)
- 8.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) and Master Enable or Disable
- 8.3.3 High Voltage Input (VIN, VINX)
- 8.3.4 Current Sense Amplifier
- 8.3.5 Control Commands
- 8.3.6 Channel Current Monitor (IOUT1, IOUT2)
- 8.3.7 Cycle-by-Cycle Peak Current Limit (IPK)
- 8.3.8 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.9 Ramp Generator
- 8.3.10 Soft Start
- 8.3.11 Gate Drive Outputs, Dead Time Programming, and Adaptive Dead Time (HO1, HO2, LO1, LO2, DT)
- 8.3.12 PWM Comparator
- 8.3.13 Oscillator (OSC)
- 8.3.14 Synchronization to an External Clock (SYNCIN, SYNCOUT)
- 8.3.15 Diode Emulation
- 8.3.16 Power MOSFET Failure Detection and Failure Protection (nFAULT, BRKG, BRKS)
- 8.3.17 Overvoltage Protection (OVPA, OVPB)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
60-A, Dual-Phase, 48-V to 12-V Bidirectional Converter
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Determining the Duty Cycle
- 9.2.1.2.2 Oscillator Programming
- 9.2.1.2.3 Power Inductor, RMS and Peak Currents
- 9.2.1.2.4 Current Sense (RCS)
- 9.2.1.2.5 Current Setting Limits (ISETA or ISETD)
- 9.2.1.2.6 Peak Current Limit
- 9.2.1.2.7 Power MOSFETS
- 9.2.1.2.8 Bias Supply
- 9.2.1.2.9 Bootstrap
- 9.2.1.2.10 RAMP Generators
- 9.2.1.2.11 OVP
- 9.2.1.2.12 Dead Time
- 9.2.1.2.13 IOUT Monitors
- 9.2.1.2.14 UVLO Pin Usage
- 9.2.1.2.15 VIN Pin Configuration
- 9.2.1.2.16 Loop Compensation
- 9.2.1.2.17 Soft Start
- 9.2.1.2.18 ISET Pins
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
60-A, Dual-Phase, 48-V to 12-V Bidirectional Converter
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Orderable Information
8.3.1 Bias Supply (VCC, VCCA)
The LM5170 requires an external bias supply of 9 V to 12 V at the VCC and VCCA pins to function. If an external supply voltage is greater than 12 V, a 10-V LDO or switching regulator must be used to produce 10 V for VCC and VCCA. Figure 8-1 shows typical connections of the bias supply. The VCC voltage is directly fed to the low-side MOSFET drivers. A 1-µF to 2.2-µF ceramic capacitor must be placed between the VCC and PGND pins to bypass the driver switching currents. The VCCA pin serves as the bias supply input for the internal logic and analog circuits for which the ground reference is the AGND pin. VCCA must be connected to VCC through a 25-Ω to 50-Ω external resistor. A 0.1-µF to 1-µF bypass capacitor must be placed between the VCCA and AGND pins to filter out possible switching noise.
The internal VCC undervoltage (UV) detection circuit monitors the VCC voltage. When the VCC voltage falls below 8 V on the falling edge, the LM5170 is held in shutdown state. For normal operation, the VCC and VCCA voltages must be greater than 8.5 V on a rising edge.
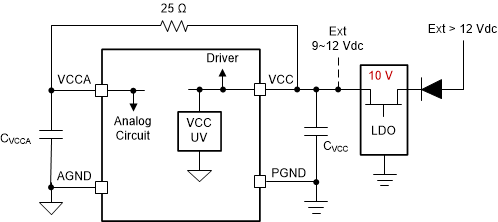 Figure 8-1 VCC Bias Supply Connections
Figure 8-1 VCC Bias Supply Connections