SBOS350B December 2006 – December 2024 OPA4830
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Related Products
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics VS = ±5V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5V
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics VS = 3V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V, Differential Configuration
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Wideband Voltage-Feedback Operation
- 8.1.2 DC Level-Shifting
- 8.1.3 AC-Coupled Output Video Line Driver
- 8.1.4 Noninverting Amplifier With Reduced Peaking
- 8.1.5 Single-Supply Active Filter
- 8.1.6 Differential Interface Applications
- 8.1.7 DC-Coupled Single-to-Differential Conversion
- 8.1.8 Low-Power, Differential I/O, 4th-Order Active Filter
- 8.1.9 Dual-Channel, Differential ADC Driver
- 8.1.10 Video Line Driving
- 8.1.11 4-Channel DAC Transimpedance Amplifier
- 8.1.12 Operating Suggestions: Optimizing Resistor Values
- 8.1.13 Bandwidth vs Gain: Noninverting Operation
- 8.1.14 Inverting Amplifier Operation
- 8.1.15 Output Current and Voltages
- 8.1.16 Driving Capacitive Loads
- 8.1.17 Distortion Performance
- 8.1.18 Noise Performance
- 8.1.19 DC Accuracy and Offset Control
- 8.2 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.3 Layout
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.2 DC Level-Shifting
Figure 8-4 shows a DC-coupled noninverting amplifier that level-shifts the input up to accommodate the desired output voltage range. Given the desired signal gain (G), and the amount VOUT needs to be shifted up (ΔVOUT) when VIN is at the center of the range, Equation 1 and Equation 2 give the resistor values that produce the desired performance. Assume that R4 is between 200Ω and 1.5kΩ.

where:

Make sure that VIN and VOUT stay within the specified input and output voltage ranges.
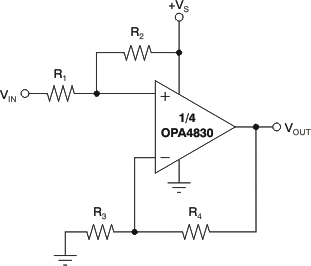 Figure 8-4 DC
Level-Shifting
Figure 8-4 DC
Level-ShiftingThe front-page circuit is a good example of this type of application. The device was designed to take VIN between 0V and 0.5V and produce VOUT between 1V and 2V when using a +3V supply. This output means G = 2.00, and ΔVOUT = 1.50V – G × 0.25V = 1.00V. Plugging these values into Equation 1 and Equation 2 (with R4 = 750Ω) gives: NG = 2.33, R1 = 375Ω, R2 = 2.25kΩ, and R3 = 563Ω. The resistors were changed to the nearest standard values for the front-page circuit.