SPRAD61A March 2023 – November 2023 AM2732 , AM2732 , AM2732-Q1 , AM2732-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Power
- 3 Clocking
- 4 Resets
- 5 Bootstrapping
- 6 JTAG Emulators and Trace
- 7 Multiplexed Peripherals
- 8 Digital Peripherals
- 9 Layer Stackup
- 10Vias
- 11BGA Power Fan-Out and Decoupling Placement
- 12References
- 13Revision History
11.3.1.1 3.3V Digital and Analog Layout - TMDS273GPEVM
A common step-down-converter generates a 3.3 V rail that is supplied to the PMIC on the AM273x GPEVM as well as the peripheral 3.3 V system needs and LDOs for the 2.5 V Ethernet and 1.7V VPP power rails. The PMIC generates a 3.3 V rail on the VIO_LDO output, which supplies the 3.3 V analog and digital supplies for all of the AM273x digital I/O and analog I/O loads. This is common in most designs where all 3.3 V digital level I/O share a common power supply.
On the AM273 GPEVM, the 3.3 V rail is generated by the PMIC on layer 10, but transitions to layer 6 to spread across the board. There is a current sense shunt resistor on layer 1 between the main 3.3 V plane on the board and the 3.3 V plane to the AM273 device on layer 6. Vias underneath the AM273 device connect the plane to the BGA ball pads on the top layer and the decoupling capacitors on the bottom layer.
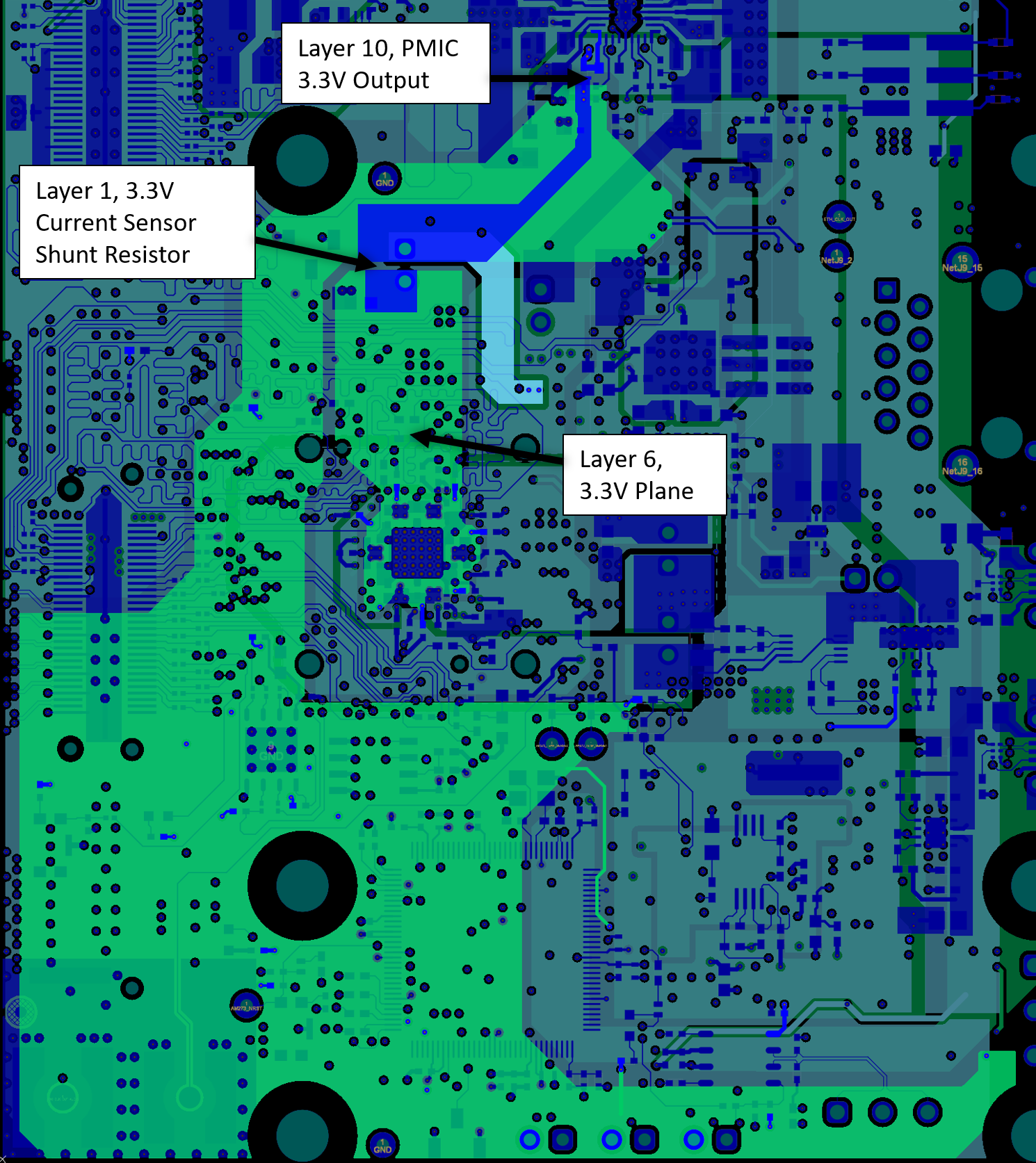 Figure 11-14 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Digital and Analog
Power Planes on Layer 6
Figure 11-14 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Digital and Analog
Power Planes on Layer 6 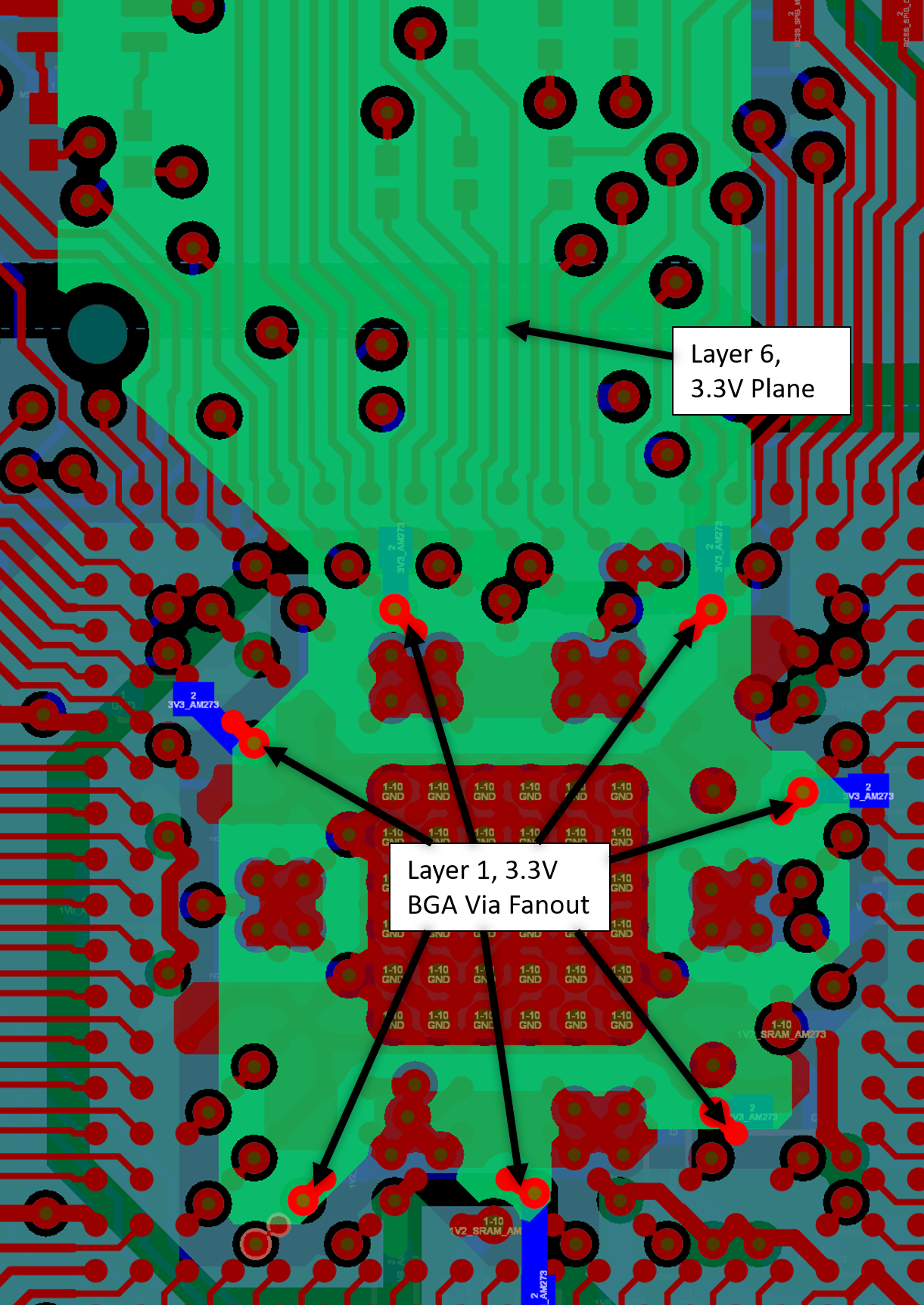 Figure 11-15 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Digital I/O and
Analog I/O BGA Pinout
Figure 11-15 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Digital I/O and
Analog I/O BGA Pinout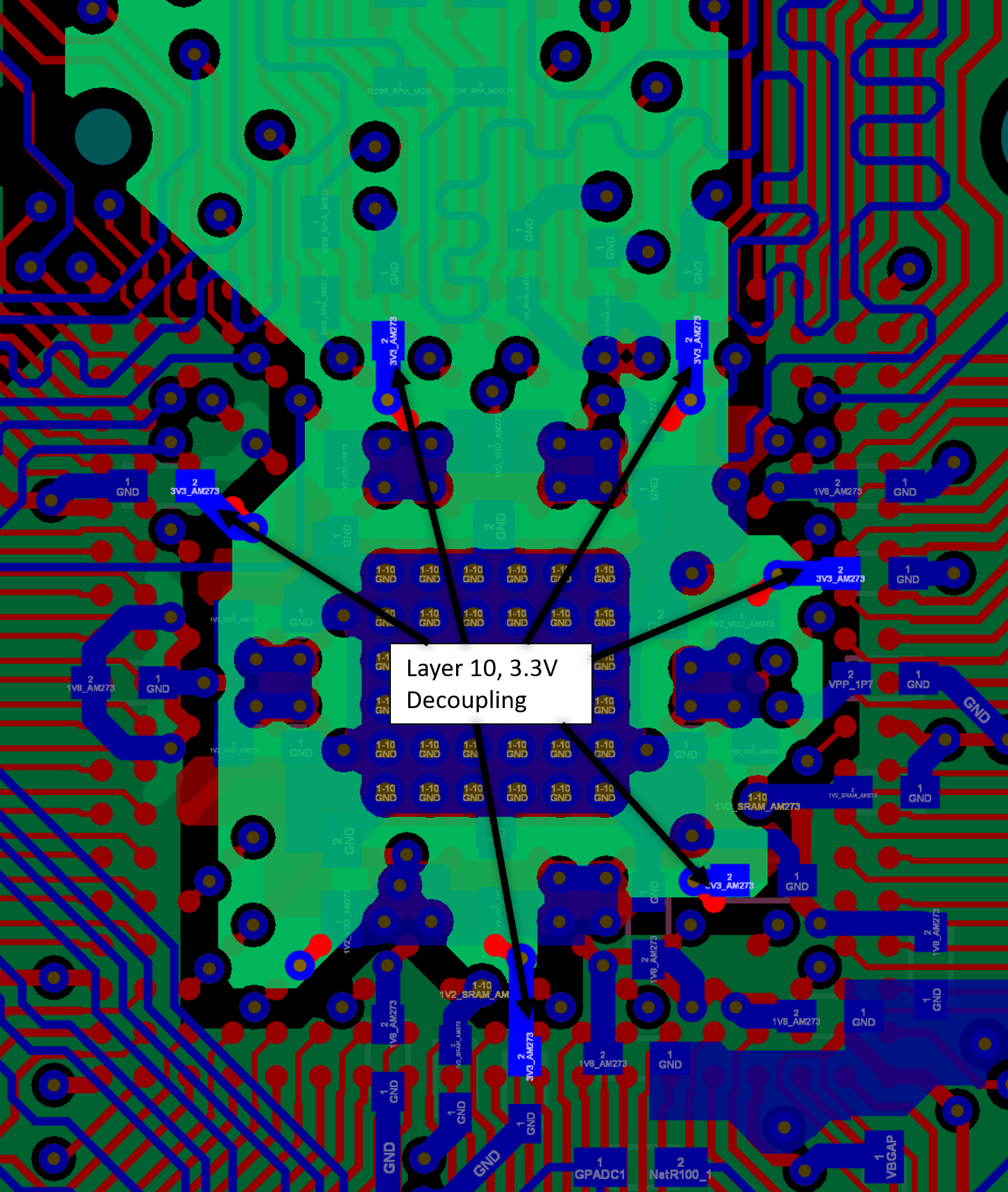 Figure 11-16 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Decoupling
Figure 11-16 AM273 GPEVM Excerpt – 3.3 V Decoupling