TIDUD61E October 2020 – April 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 3.1.1 Hardware
- 3.1.2
Software
- 3.1.2.1 Opening Project Inside CCS
- 3.1.2.2 Project Structure
- 3.1.2.3 Using CLA on C2000 MCU to Alleviate CPU Burden
- 3.1.2.4 CPU and CLA Utilization and Memory Allocation
- 3.1.2.5
Running the Project
- 3.1.2.5.1 Lab 1: Open Loop, DC (PFC Mode)
- 3.1.2.5.2 Lab 2: Closed Current Loop DC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.3 Lab 3: Closed Current Loop, AC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.4 Lab 4: Closed Voltage and Current Loop (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.5 Lab 5: Open loop, DC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.6 Lab 6: Open loop, AC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.7 Lab 7: Closed Current Loop, DC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.8 Lab 8: Closed Current Loop, AC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.9 Lab 9: Closed Current Loop (Grid Connected Inverter)
- 3.1.2.6 Running Code on CLA
- 3.1.2.7
Advanced Options
- 3.1.2.7.1 Input Cap Compensation for PF Improvement Under Light Load
- 3.1.2.7.2 83
- 3.1.2.7.3 Adaptive Dead Time for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.4 Phase Shedding for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.5 Non-Linear Voltage Loop for Transient Reduction
- 3.1.2.7.6 Software Phase Locked Loop Methods: SOGI - FLL
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
2.4.5 AC Drop Test
AC drop testing requires accurate detection of ac failure and ac back event to freeze and resume PFC operation. The biggest technical challenge in ac drop test is the PLL synchronization issue when ac gets back. Typically, SW based PLL required several cycles to catch up with the grid phase and therefore it can't provide current reference in phase with the voltage during this transitional period. The ideal ac drop test waveform is shown Figure 2-14. PLL immediately catches the ac grid and resume normal PFC operation as soon as ac gets back.
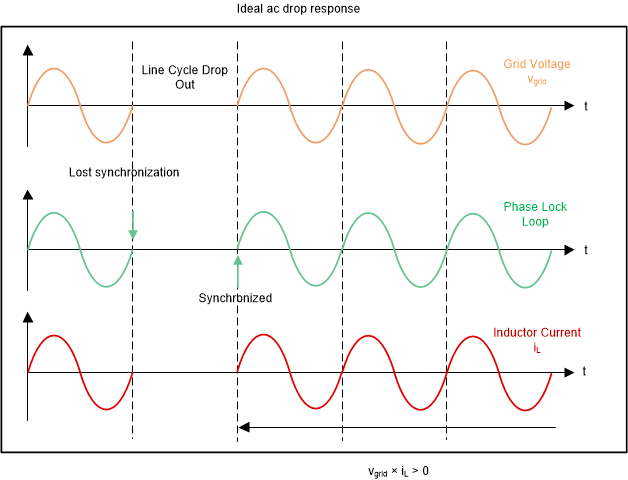 Figure 2-14 Ideal AC Drop Waveforms
Figure 2-14 Ideal AC Drop WaveformsFigure 2-15 presents the non-ideal ac drop solution. Due to the SPLL transitioning time, it requires extra time for PLL to work and does not provide fast dc bus recovery.
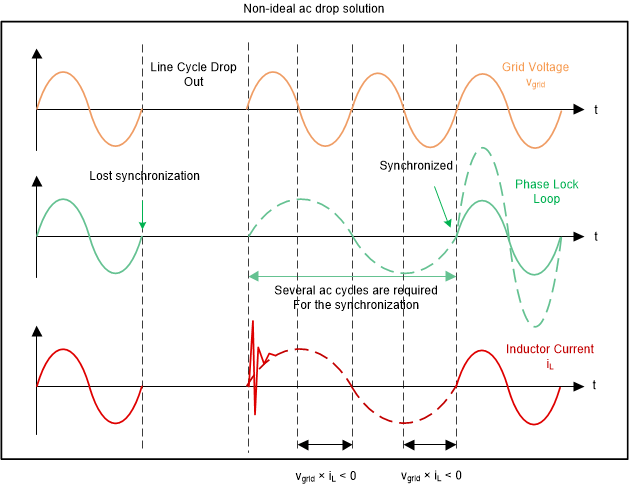 Figure 2-15 Non Ideal AC Drop Waveforms
Figure 2-15 Non Ideal AC Drop WaveformsIn TIDM-02008, a virtual ac voltage is introduced. An internal sine wave is generated inside the MCU and the magnitude and the phase angle are synchronized with the actual ac grid when it is available. Once it is synchronized, the virtual signal provides the sinusoidal signal regardless of the actual grid voltage and it can be utilized even during the ac drop period. As shown in Figure 2-16, virtual ac signal provides the current reference during the transition and once PLL catches up the ac grid, PLL provides the current reference as usual.
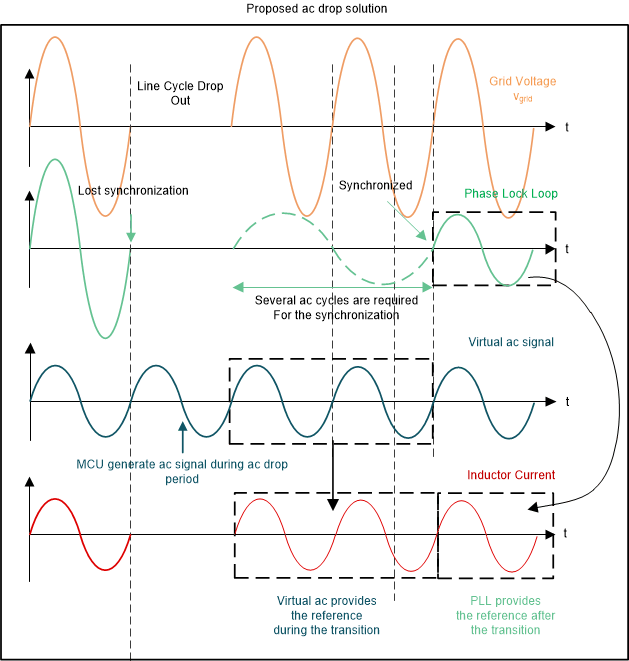 Figure 2-16 Proposed AC Drop Waveforms
Figure 2-16 Proposed AC Drop WaveformsA state machine shown in Figure 2-17 monitors ac voltage and makes a decision depending on the ac voltage status.
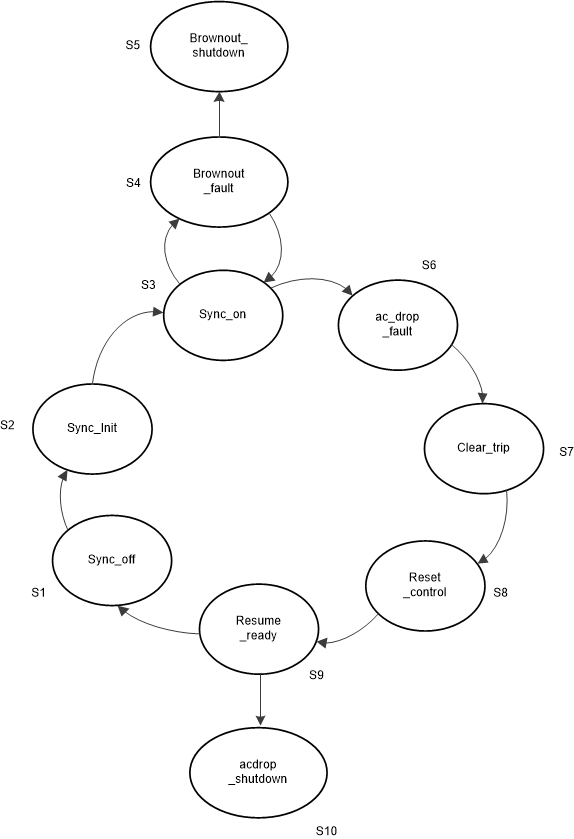 Figure 2-17 AC Drop State Machine
Figure 2-17 AC Drop State MachineThe actual AC drop test waveform is shown inFigure 2-18 It was captured under 900 w load with 120 V ac input.
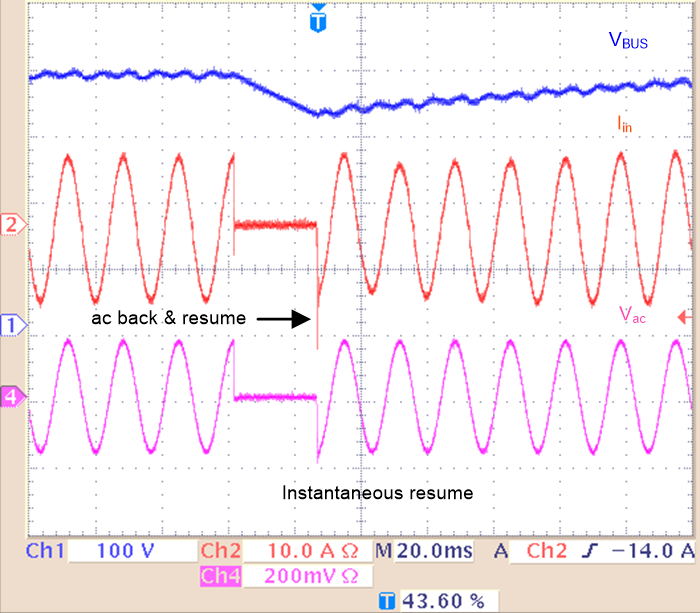 Figure 2-18 AC Drop Test Results Under 900 W
Figure 2-18 AC Drop Test Results Under 900 WThe AC drop test feature can be turned on and off by changing TTPLPFC_AC_DROP in ttplpfc_user_settings.h
#define TTPLPFC_AC_DROP 1 (1: enable, 0: disable)