TIDUD61E October 2020 – April 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 3.1.1 Hardware
- 3.1.2
Software
- 3.1.2.1 Opening Project Inside CCS
- 3.1.2.2 Project Structure
- 3.1.2.3 Using CLA on C2000 MCU to Alleviate CPU Burden
- 3.1.2.4 CPU and CLA Utilization and Memory Allocation
- 3.1.2.5
Running the Project
- 3.1.2.5.1 Lab 1: Open Loop, DC (PFC Mode)
- 3.1.2.5.2 Lab 2: Closed Current Loop DC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.3 Lab 3: Closed Current Loop, AC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.4 Lab 4: Closed Voltage and Current Loop (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.5 Lab 5: Open loop, DC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.6 Lab 6: Open loop, AC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.7 Lab 7: Closed Current Loop, DC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.8 Lab 8: Closed Current Loop, AC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.9 Lab 9: Closed Current Loop (Grid Connected Inverter)
- 3.1.2.6 Running Code on CLA
- 3.1.2.7
Advanced Options
- 3.1.2.7.1 Input Cap Compensation for PF Improvement Under Light Load
- 3.1.2.7.2 83
- 3.1.2.7.3 Adaptive Dead Time for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.4 Phase Shedding for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.5 Non-Linear Voltage Loop for Transient Reduction
- 3.1.2.7.6 Software Phase Locked Loop Methods: SOGI - FLL
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
3.1.2.1 Opening Project Inside CCS
To start:
- Install CCS from the Code Composer Studio (CCS) Integrated Development Environment (IDE) tools folder, CCSV9.3 or above is recommended.
- Install C2000Ware DigitalPower SDK at the C2000Ware Digital Power SDK tools folder.
- Note: powerSUITE is installed with the SDK in the default install.
- Go to View → Resource Explorer. Below the TI Resource Explorer, go to C2000Ware DigitalPower SDK.
To open the reference design software as it is (opens firmware as it was run on this design and hardware, requires the board to be exactly the same as this reference design).
- Under C2000Ware DigitalPower SDK, select Development Kits → CCM Totem Pole PFC TIDM-02008, and click on Run <Import> Project.
- These steps import the project, and the development kit or designs page show up. This page can be used to browse all the information on the design including this user guide, test reports, hardware design files, and so forth.
- Click Import <device_name> Project.
- This action imports the project into the workspace environment, and a main.syscfg page with a GUI similar to Figure 3-3shows up.
Open reference design software for adaptation. The user can modify power stage parameters, which are then used to create the model of the power stage in Compensation Designer and can also modify scaling values for voltages and currents for a custom design.
- UnderC2000Ware Digital Power SDKclick on powerSUITE →Solution Adapter Tool (
 ).
). - Select Single Phase CCM Totem Pole PFC from the list of solutions presented.
- Select the device this solution must run on the next page.
- Once the icon is clicked, a pop-up window shows up asking for a location to create the project. One can also save the project inside the workspace itself. Once the location is specified, a project is created, and a GUI page appears with modifiable options for the solution (Figure 3-3).
- This GUI can be used to change the parameters for an adapted solution, like power rating, inductance, capacitance, sensing circuit parameters, and so forth.
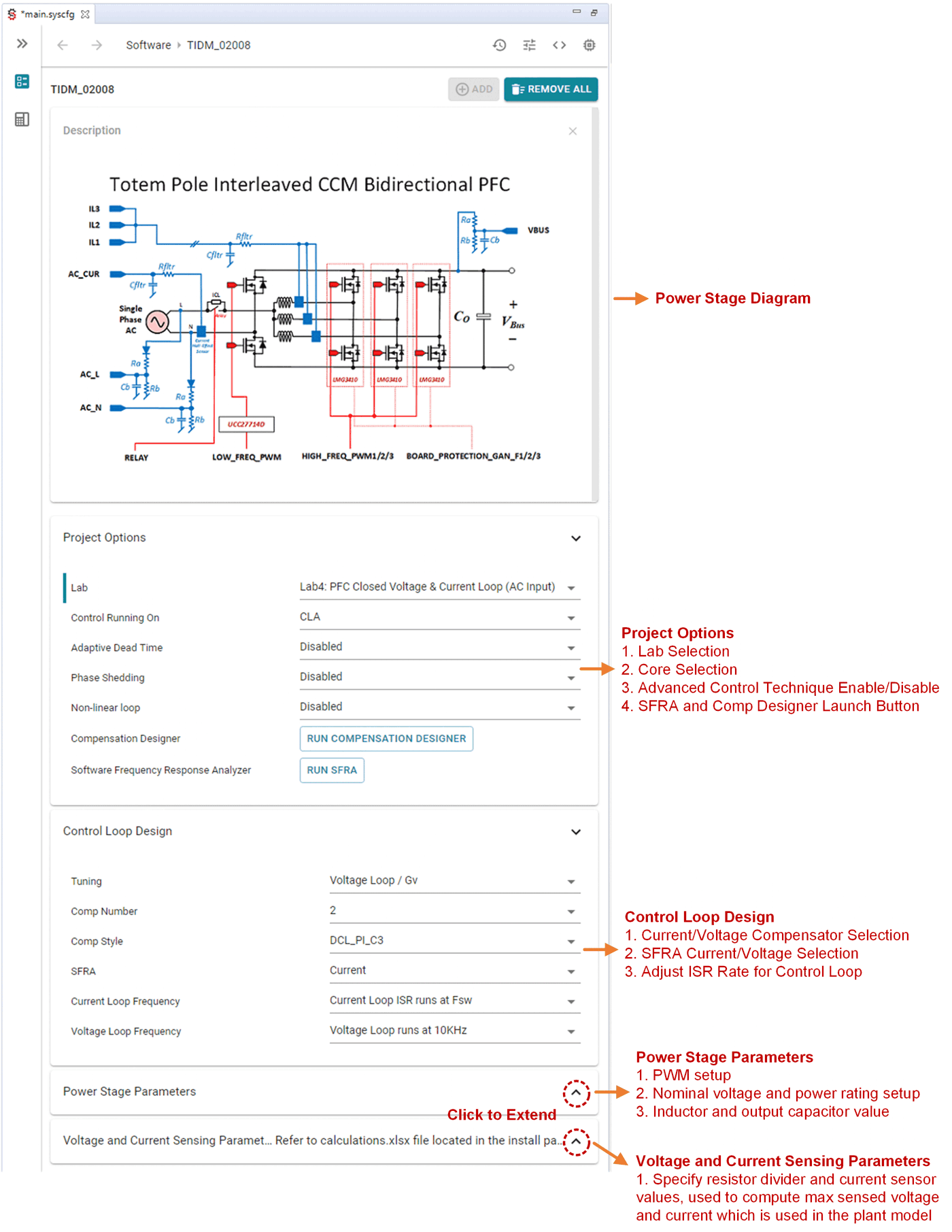 Figure 3-3 powerSUITE Page for CCM TTPL PFC Solution
Figure 3-3 powerSUITE Page for CCM TTPL PFC Solution