SBOS891C October 2018 – September 2023 TMP144
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YBK|4
- YFF|4
- YMT|4
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.6 Register Maps
Figure 7-17 shows the internal register structure of the TMP144. Communications between the registers are transferred through the interface in LSB-first order. The 8-bit command register as shown in , is used to determine the address pointer for the register that the host device wants to access.
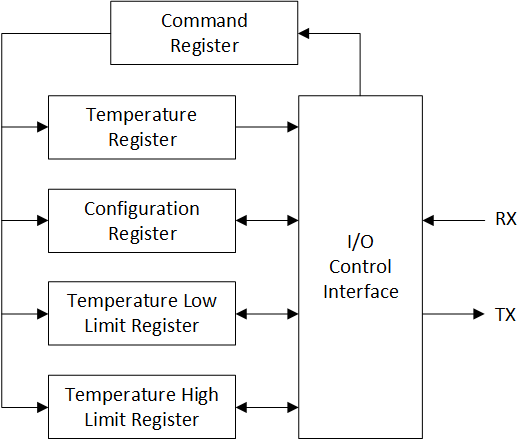 Figure 7-17 Internal Register
Structure.
Figure 7-17 Internal Register
Structure.
Table 7-4 Register Map
| ADDRESS POINTER P[1:0] | TYPE | RESET | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME | SECTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | R | 0000h | Temp_Result | Temperature result register | Go |
| 01 | R/W | 0200h | Configuration | Configuration Register | Go |
| 10 | R/W | 3C00h | Tlow_limit | Temperature low limit register | Go |
| 11 | R/W | F600h | Thigh_limit | Temperature high limit register | Go |
Table 7-5 Register Section/Block Access
Type Codes
| Access Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Read Type | ||
| R | R | Read |
| RC | R | Read |
| C | to Clear | |
| R-0 | R | Read |
| -0 | Returns 0s | |
| Write Type | ||
| W | W | Write |
| W0CP | W | W |
| 0C | 0 to clear | |
| P | Requires privileged access | |
| Reset or Default Value | ||
| -n | Value after reset or the default value | |