SBOS891C October 2018 – September 2023 TMP144
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YBK|4
- YFF|4
- YMT|4
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.6 Interrupt Functionality
The TMP144 interrupts the host by disconnecting the bus and issuing an interrupt request by holding the bus low if all of following conditions are met as shown in Figure 7-3.
- INT_EN in the configuration register is set to 1;
- The temperature result of the last conversion is greater than the value in the temperature high limit register or less than the value in the temperature low limit register (also indicated by a 1 in either FH or FL, respectively);
- The bus is logic high and idle for more than 28 ms.
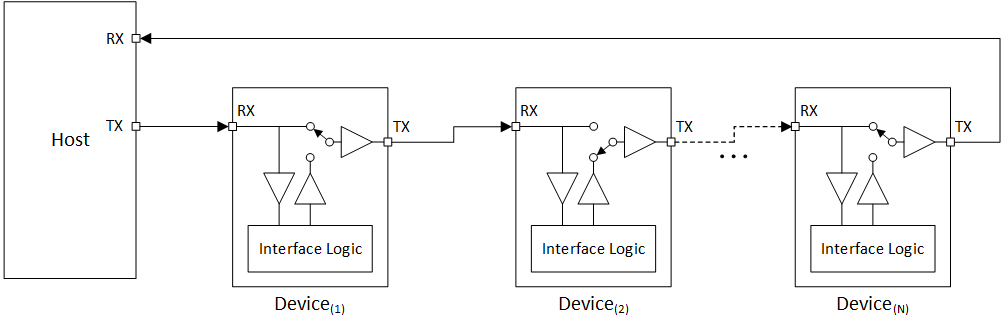 Figure 7-3 TMP144
Daisy-Chain: Bus Status During an Interrupt Request (Logic Low) From Second
Device
Figure 7-3 TMP144
Daisy-Chain: Bus Status During an Interrupt Request (Logic Low) From Second
DeviceThe interrupt on the bus is latched regardless of the status of LC. Writing a 1 to INT_EN automatically sets the LC bit. The TMP144 holds the bus low until one of the following events happen:
- Global Interrupt Clear command is received.
- Global Software Reset command is received.
- A power-on reset event occurs.
Each of these events clears the INT_EN. The TMP144 does not issue future interrupts until the host writes sets the INT_EN in the configuration register to re-enable future interrupts.
In a system with enabled interrupts, it is possible for a TMP144 on the bus to issue an interrupt at the same time that the host starts a communication sequence. To avoid this scenario, TI recommends that the host should check the status on the receiving side of the bus after transmitting the calibration byte. If it is 1, then the host can continue with the communication. If it is 0, one of the TMP144 devices on the bus is issuing an alert and the host must transmit a Global Interrupt Clear command.