SNVSAU8A June 2017 – February 2024 TPS549B22
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
-
7 Register Maps
- 7.1 OPERATION Register (address = 1h)
- 7.2 ON_OFF_CONFIG Register (address = 2h)
- 7.3 CLEAR FAULTS (address = 3h)
- 7.4 WRITE PROTECT (address = 10h)
- 7.5 STORE_DEFAULT_ALL (address = 11h)
- 7.6 RESTORE_DEFAULT_ALL (address = 12h)
- 7.7 CAPABILITY (address = 19h)
- 7.8 VOUT_MODE (address = 20h)
- 7.9 VOUT_COMMAND (address = 21h)
- 7.10 VOUT_MARGIN_HIGH (address = 25h) ®
- 7.11 VOUT_MARGIN_LOW (address = 26h)
- 7.12 STATUS_BYTE (address = 78h)
- 7.13 STATUS_WORD (High Byte) (address = 79h)
- 7.14 STATUS_VOUT (address = 7Ah)
- 7.15 STATUS_IOUT (address = 7Bh)
- 7.16 STATUS_CML (address = 7Eh)
- 7.17 MFR_SPECIFIC_00 (address = D0h)
- 7.18 MFR_SPECIFIC_01 (address = D1h)
- 7.19 MFR_SPECIFIC_02 (address = D2h)
- 7.20 MFR_SPECIFIC_03 (address = D3h)
- 7.21 MFR_SPECIFIC_04 (address = D4h)
- 7.22 MFR_SPECIFIC_06 (address = D6h)
- 7.23 MFR_SPECIFIC_07 (address = D7h)
- 7.24 MFR_SPECIFIC_44 (address = FCh)
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 TPS549B22 1.5-V to 18-V Input, 1-V Output, 25-A Converter
- 8.2.2 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.3.2 Switching Frequency Selection
- 8.2.3.3 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.3.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.7 BP Pin
- 8.2.3.8 R-C Snubber and VIN Pin High-Frequency Bypass
- 8.2.3.9 Optimize Reference Voltage (VSEL)
- 8.2.3.10 MODE Pin Selection
- 8.2.3.11 ADDR Pin Selection
- 8.2.3.12 Overcurrent Limit Design
- 8.2.4 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVF|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVF|40
Orderable Information
6.3.7.1 Current Limit (ILIM) Functionality
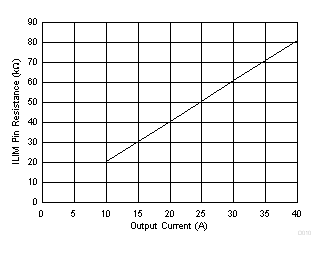 Figure 6-4 Current Limit Resistance vs OCP Valley Overcurrent Limit
Figure 6-4 Current Limit Resistance vs OCP Valley Overcurrent LimitThe ILIM pin sets the OCP level. Connect the ILIM pin to GND through the voltage setting resistor, RILIM. To provide both good accuracy and a cost-effective solution, the TPS549B22 device supports temperature compensated internal MOSFET RDS(on) sensing.
Also, the TPS549B22 device performs both positive and negative inductor current limiting with the same magnitudes. The positive current limit normally protects the inductor from saturation that causes damage to the high-side FET and low-side FET. The negative current limit protects the low-side FET during OVP discharge.
The voltage between GND pin and SW pin during the OFF time monitors the inductor current. The current limit has 1200 ppm/°C temperature slope to compensate the temperature dependency of the on-resistance (RDS(on)). The GND pin is used as the positive current sensing node.
The TPS549B22 device uses cycle-by-cycle over-current limiting control. The inductor current is monitored during the OFF-state and the controller maintains the OFF-state during the period that the inductor current is larger than the overcurrent ILIM level. VILIM sets the valley level of the inductor current.