JAJU732C June 2019 – July 2022
- 概要
- Resources
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Circuit Description
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5Design Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Terminology
- 8About the Author
- 9Revision History
4.4.5 Lab 5
- Figure 4-40 shows test setup for lab 5 (Open Loop voltage - Reverse power flow).
In this setup, the DC source is connected to secondary side and the resistive load is connected to primary side.
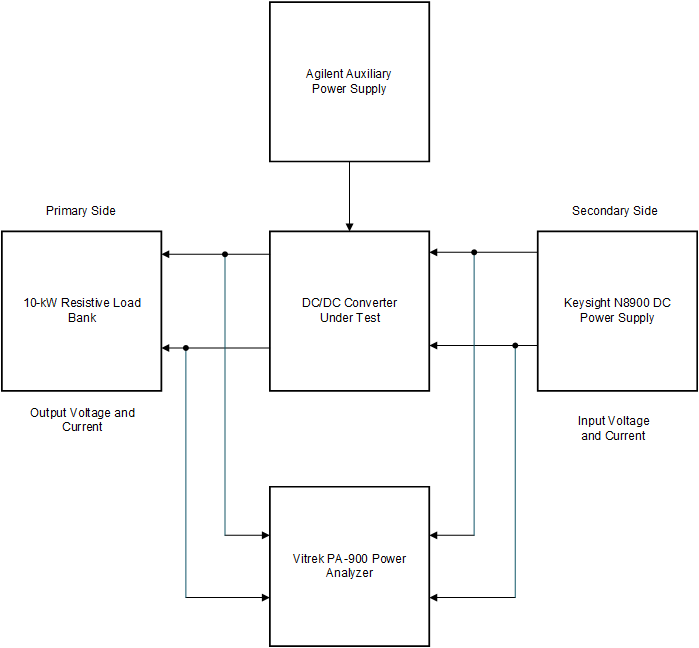
Figure 4-40 Lab 5 Test Setup - Compile the project by selecting Lab 5: Open
Loop PWM, Sec to Prim Power Flow in the drop-down menu of Project
Options from PowerSUITE GUI. Ensure current and voltage limits are set per
operating
conditions.
#if DAB_LAB == 5 #define DAB_CONTROL_RUNNING_ON C28X_CORE #define DAB_POWER_FLOW DAB_POWER_FLOW_SEC_PRI #define DAB_INCR_BUILD DAB_OPEN_LOOP_BUILD #define DAB_TEST_SETUP DAB_TEST_SETUP_RES_LOAD #define DAB_PROTECTION DAB_PROTECTION_ENABLED #define DAB_CONTROL_MODE DAB_VOLTAGE_MODE #define DAB_SFRA_TYPE 0#define DAB_SFRA_AMPLITUDE (float32_t)DAB_SFRA_INJECTION_AMPLITUDE_LEVEL2 #endif- Run the project by clicking green run button in CCS
- Populate the required
variables in the watch window by loading javascript '
setupdebugenv_lab5.js' in the scripting console
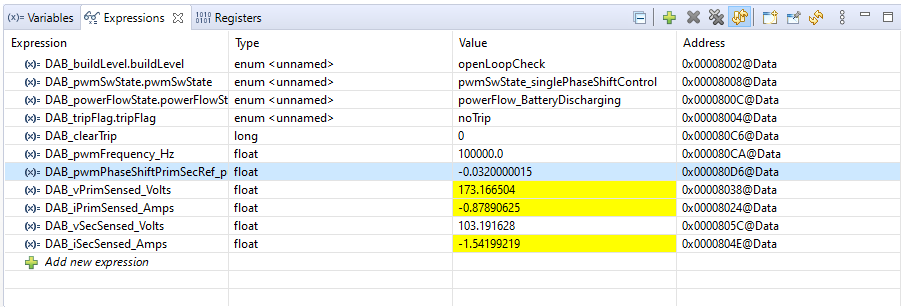 Figure 4-41 Lab 5 Watch
View
Figure 4-41 Lab 5 Watch
View - Enable PWM by writing “1” to the DAB_clearTrip variable
- Vary phase shift slowly
in steps of 0.002 pu by writing to DAB_pwmPhaseShiftPrimSec_pu and
observe the change in voltage at the output of converter. Note: The negative sign in the phase shift value is required for the reverse power flow.
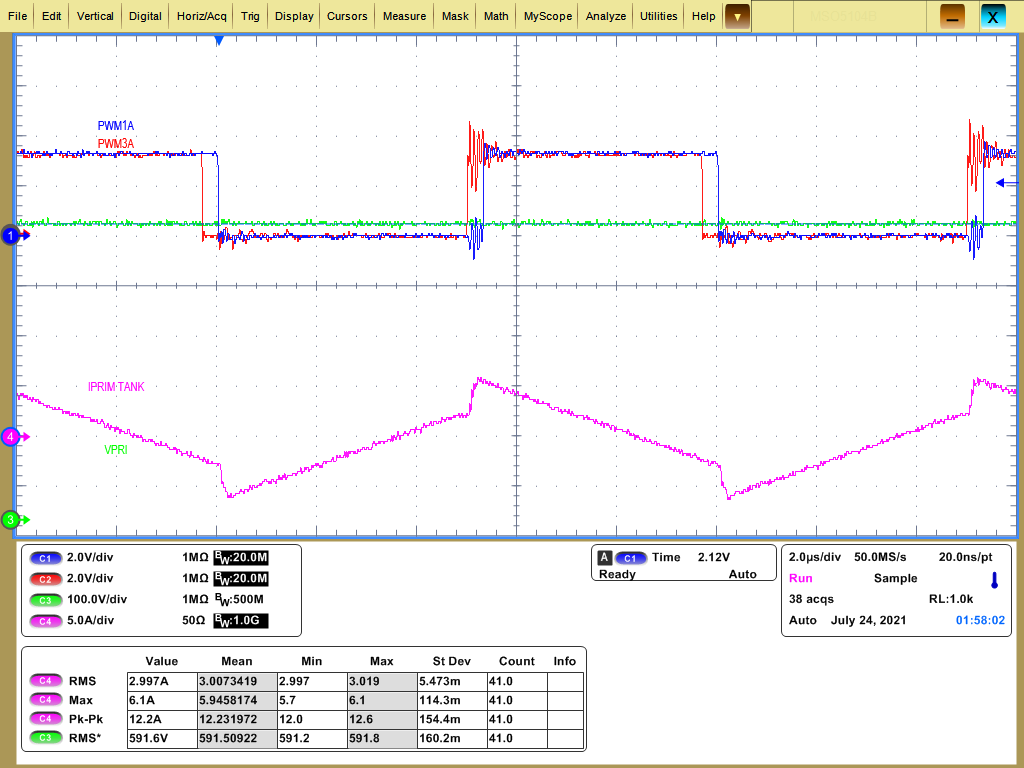 Test Conditions: VOUT = 600 VDC, Phase shift = –0.032, VIN = 330 VDC, Load = 400 ΩFigure 4-42 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow
Test Conditions: VOUT = 600 VDC, Phase shift = –0.032, VIN = 330 VDC, Load = 400 ΩFigure 4-42 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow
- Overcurrent Protections (Reverse Power Flow)
Figure 4-43 and Figure 4-44illustrate the overcurrent protections (reverse power flow).
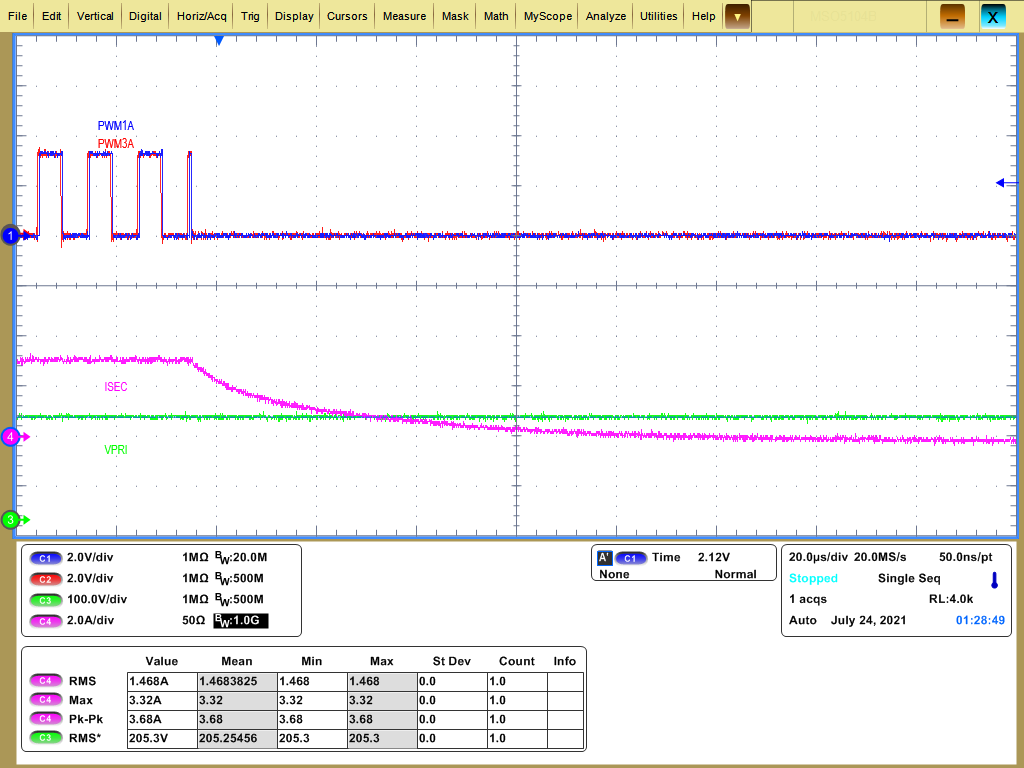 Figure 4-43 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow Trip on Secondary (Source), Limit Set = 4 A
Figure 4-43 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow Trip on Secondary (Source), Limit Set = 4 A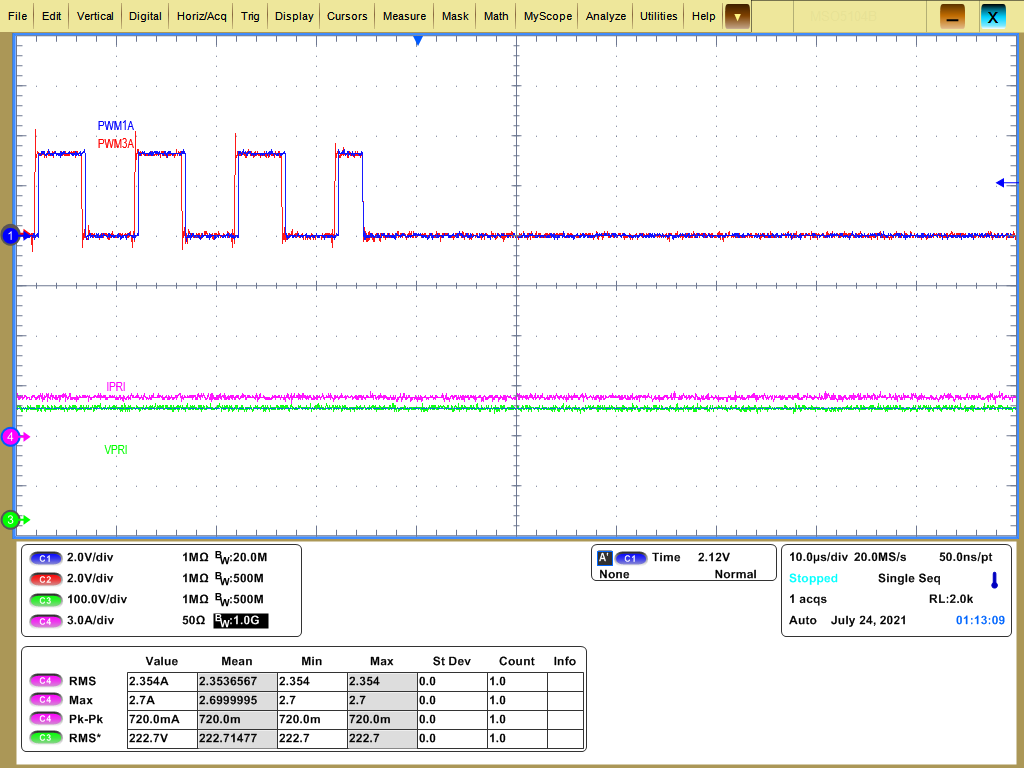 Figure 4-44 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow Trip on Primary (Resistive Load), Limit Set = 2.5 A
Figure 4-44 Lab 5 Reverse Power Flow Trip on Primary (Resistive Load), Limit Set = 2.5 A