SLVAE30E February 2021 – March 2021 TPS1H000-Q1 , TPS1H100-Q1 , TPS1H200A-Q1 , TPS1HA08-Q1 , TPS25200-Q1 , TPS27S100 , TPS2H000-Q1 , TPS2H160-Q1 , TPS2HB16-Q1 , TPS2HB35-Q1 , TPS2HB50-Q1 , TPS2HC08-Q1 , TPS4H000-Q1 , TPS4H160-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Driving Resistive Loads
- 3Driving Capacitive Loads
- 4Driving Inductive Loads
- 5Driving LED Loads
- 6Appendix
- 7References
- 8Revision History
4.5.2 Instantaneous Power Losses During Demagnetization
During this demagnetization time, the inductor energy is absorbed within the high side switch. The instantaneous power through the switch is calculated in Equation 43 from the voltage across the switch and the load current.
Equation 43. 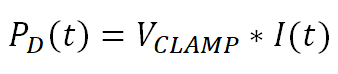
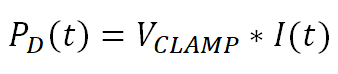
Equation 43 and Equation 38 combined give Equation 44:
Equation 44. 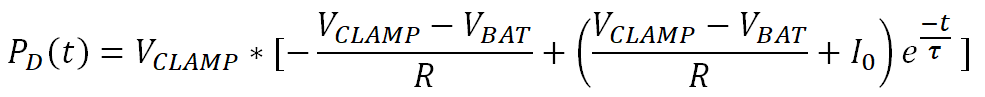
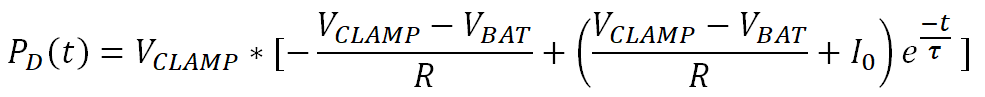
After calculating the demagnetization time in Equation 42 and the instantaneous power in Equation 44, the demagnetization energy can be calculated.