TIDUDS9B December 2017 – November 2022
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Design Considerations
- 2.2.1 Conditions of Use: Assumption
- 2.2.2
Diagnostics Coverage
- 2.2.2.1 Dual-Channel Monitoring
- 2.2.2.2 Checking ISO1211 Functionality With MCU (SIL1)
- 2.2.2.3 Checking TPS22919 Functionality With MCU (SIL1)
- 2.2.2.4 Checking TPS27S100 Functionality With MCU (SIL1)
- 2.2.2.5 Optional Monitoring Using RDY Pin of ISO5452, ISO5852S or UCC21750 Integrated Analog-to-PWM Isolated Sensor
- 2.2.3 Drive State
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 2.4 System Design Theory
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Getting Started Hardware
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Related Documentation
- 6About the Author
- 7Recognition
- 8Revision History
3.2.3.1 Propagation of STO2 to VCC2 of Gate Driver
The STO2 signal goes low for a period of 15 ms. As Figure 3-10 and Figure 3-11 show, the response time measured between the STO signal going low to the activation of the RDY pin is 7.4 ms. As the VCC2 goes below the UVLO threshold, the RDY pin is activated. The UVLO+ threshold for ISO5852S is 12 V. The response time is a function of the capacitance C7 at the output of the smart switch. Vary the response time by changing the value of capacitance.
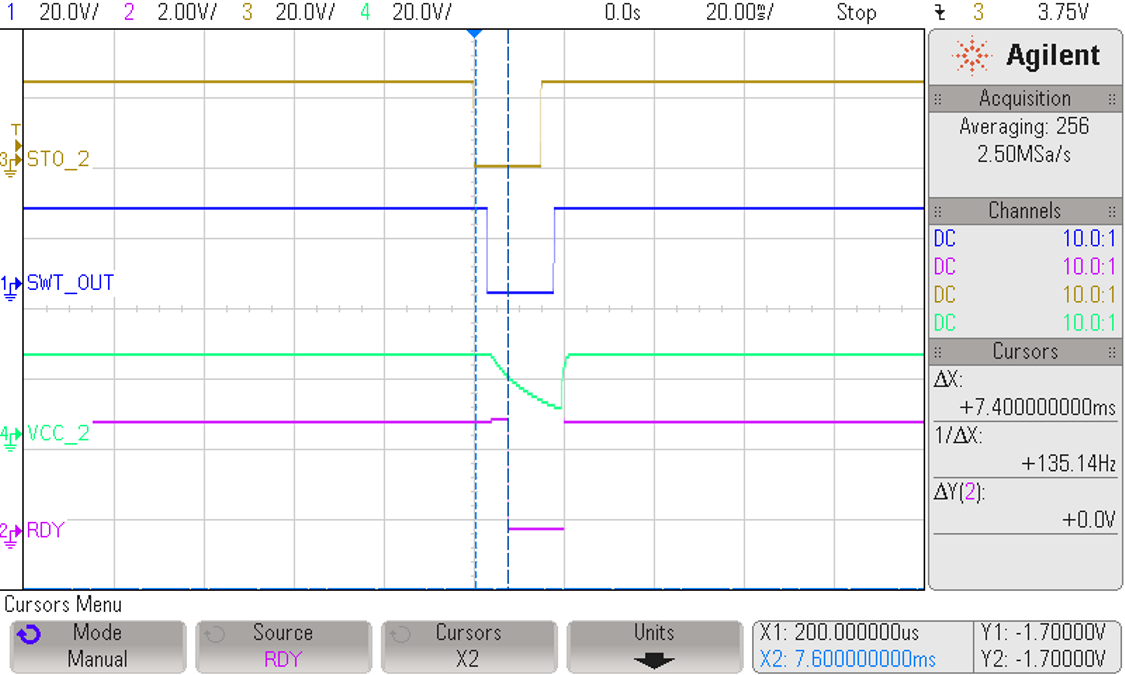 Figure 3-10 Indication of RDY Signal (Active Low) When
VCC_2 Turns OFF
Figure 3-10 Indication of RDY Signal (Active Low) When
VCC_2 Turns OFF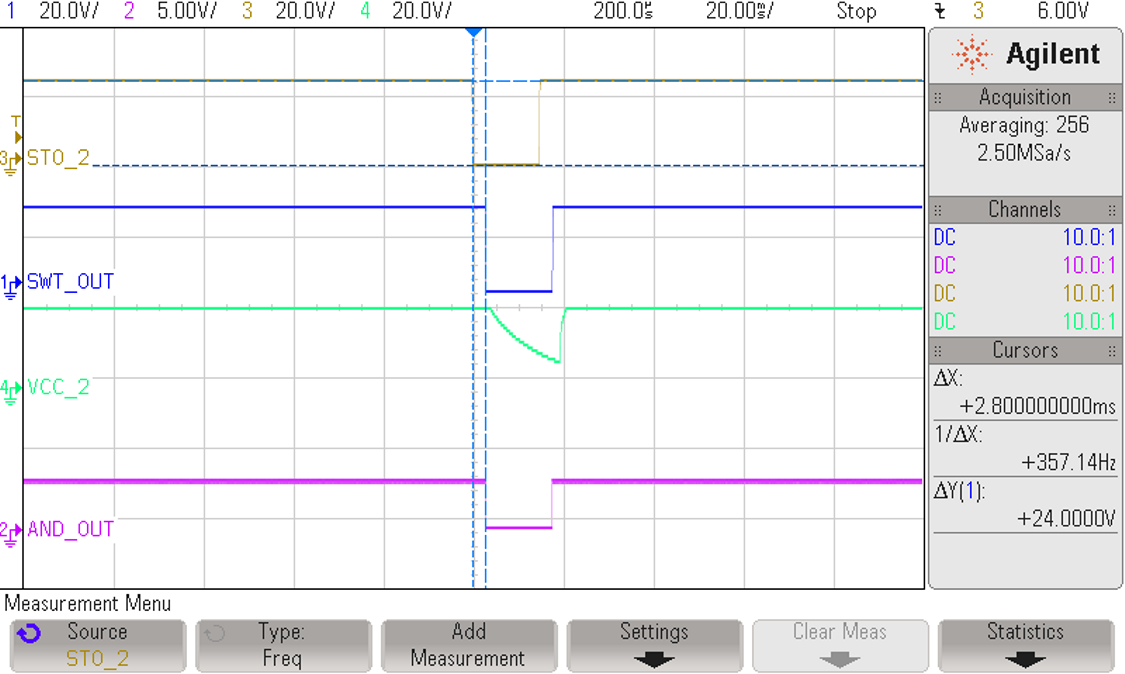 Figure 3-11 Propagation of STO2 to VCC2 of Gate
Driver
Figure 3-11 Propagation of STO2 to VCC2 of Gate
Driver