SBOS558D April 2011 – April 2025 INA200-Q1 , INA201-Q1 , INA202-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application Information
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2 High-Side Switch Overcurrent Shutdown
Figure 9-7 shows the basic connection for a high-side, switch overcurrent shutdown application. The high-side PMOS switch disconnects when an overcurrent event occurs. The previous Detailed Design Procedure section describes how to apply this application example. The difference is that the current is sensed on the high side of the bus in this application, and the low side of the bus in the previous application example.
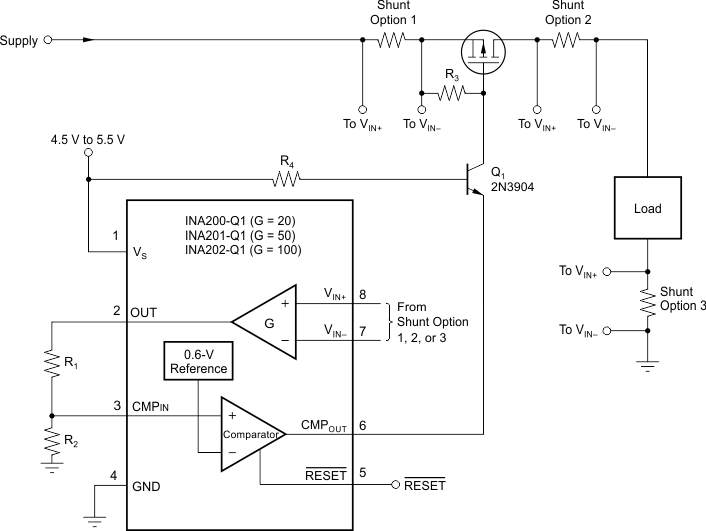
NOTE: Q cascodes the comparator output to drive a high-side FET (the 2N3904 shown is good up to 60 V). The shunt can be located in any one of the three locations shown. Use the latching capability in shutdown applications to prevent oscillation at the trip point.
Figure 9-7 High-Side Switch Overcurrent Shutdown