SBAU394B April 2022 – August 2025
2.3 Power Supplies
The PHI provides multiple power-supply options for the EVM, derived from the USB supply of the computer that is routed to the 5.5V net on the ADS1285EVM-PDK on the board.
The EEPROM on the ADS1285EVM-PDK uses a 3.3V power supply, ID_PWR, generated directly by the PHI. The 3.3V supply to the digital section of the ADC (3V3_IOVDD) is provided directly by a separate LDO on the PHI.
Figure 2-3 and Table 2-2 describe the supply generation and programmable configurations, respectively.
 Figure 2-3 ADS1285EVM-PDK AVDD1, AVDD2,
and AVSS+5V Supply Generation (Schematic)
Figure 2-3 ADS1285EVM-PDK AVDD1, AVDD2,
and AVSS+5V Supply Generation (Schematic)| VOUT (V)(2) | 3P2V | 1P6V | 0P8V | 0P4V | 0P2V | 0P1V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 | — | — | Installed(1) | — | Installed | Installed |
| 3.0 | — | Installed | — | — | — | — |
| 3.3 | — | Installed | — | — | Installed | Installed |
| 4.5 | — | Installed | Installed | Installed | Installed | Installed |
| 5.0 | Installed | — | — | Installed | — | — |
The PGA positive analog supply of the ADC, AVDD1, is supplied by the TPS7A4701 (U2). The TPS7A4701 is a low-noise, configurable-output linear regulator that uses the PHI 5.5V output voltage to generate a clean 5V supply for AVDD1 by default. Install or remove resistors R8 to R13 to change the LDO output voltage if desired. This LDO (U2) is referenced to AVSS such that AVDD1 is the same level relative to AVSS using either a unipolar or bipolar power supply.
AVDD2 is the modulator analog supply that is also used by the ADC. As with AVDD1, AVDD2 is generated by another TPS7A4701 (U3). This LDO uses the PHI 5.5V output voltage to generate a clean 3V supply for AVDD2 by default. Install or remove resistors R14 to R19 to change the LDO output voltage if desired. However, this LDO (U3) is referenced to GND such that AVDD2 is a different level relative to AVSS using a unipolar power supply compared to using a bipolar power supply. Verify that the AVDD2 voltage is within data sheet specifications when operating the EVM in either mode. Additionally, increasing or decreasing the AVDD2 voltage results in higher or lower THD performance, respectively, in unipolar mode.
AVSS+5V is used for the analog supply of the DAC1282. This pin also uses a TPS7A470x (U4) onboard the EVM, which is a low-noise linear regulator that uses the 5.5V supply on the PHI to generate a cleaner 5V output. The DAC1282 requires a 5V supply so R20 to R25 must not be modified.
The user has the option to configure the EVM for unipolar supplies (AVSS = 0V) by placing a jumper to cover pins 1 and 2 of J4 (UNIPOL), or to configure the EVM for bipolar supplies (AVSS = –2.5V) by placing the jumper to cover pins 2 and 3 of J4 (BIPOL). The TPS7A3001 (U5) is an LDO with a VIN range from –3V to –36V that provides a clean –2.5V output for the AVSS voltage. However, an external voltage is needed to supply the AVSS voltage, which can be supplied using J3. Figure 2-4 shows the supply selection and –2.5V generation circuit.
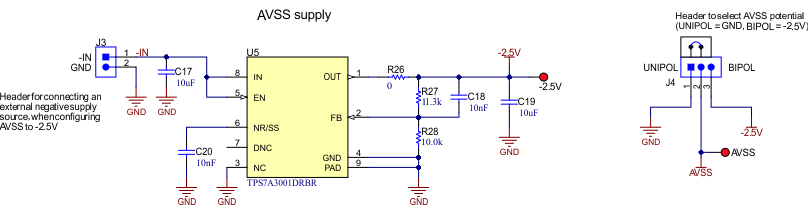 Figure 2-4 ADS1285EVM-PDK Negative LDO
and Unipolar or Bipolar Supply Selection (Schematic)
Figure 2-4 ADS1285EVM-PDK Negative LDO
and Unipolar or Bipolar Supply Selection (Schematic)AVDD1 is used as the supply for the REF6241, which is a high-precision voltage reference with an integrated high-bandwidth buffer in reference to AVSS. The voltage reference can be used to supply the positive reference, VREFP, for the ADC and DAC using resistor R38. Alternatively, remove resistors R38 and R42 to apply external positive and negative reference voltages using pins 1 and 2 of J10, respectively.
Figure 2-5 shows a schematic of the voltage reference.
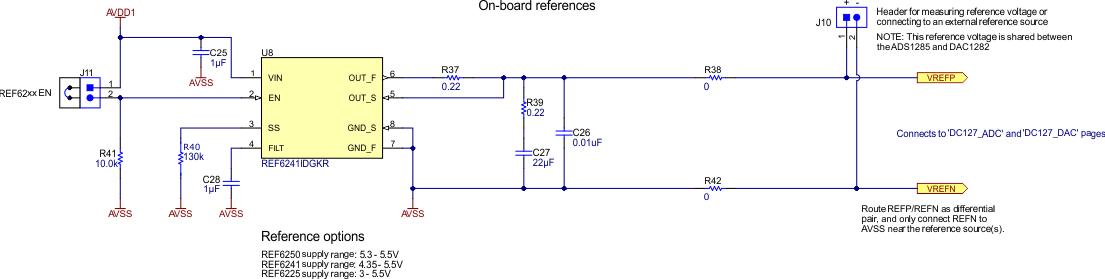 Figure 2-5 Voltage Reference
(Schematic)
Figure 2-5 Voltage Reference
(Schematic)The power supply for each active component on the EVM is bypassed with a ceramic capacitor placed close to that component. Where possible, the EVM layout uses thick traces or large copper fill areas between bypass capacitors and their loads to minimize inductance along the load current path.
As mentioned previously in Section 1, power to the EVM is supplied by the PHI through connector J5. For information about PHI pins and the power connections, see Table 2-3.
With modifications, the user can use external supplies for any voltage supplies. Using the ADC PWR header (J26), DAC PWR header (J1), and the unipolar or bipolar select (J4); the shunts can be depopulated for direct access to the AVDD1, AVDD2, AVSS+5V, DVDD, and AVSS pins.