SPRACP4A December 2019 – June 2024 AM67 , AM67A , AM68 , AM68A , AM69 , AM69A , DRA821U , DRA821U-Q1 , DRA829J , DRA829J-Q1 , DRA829V , DRA829V-Q1 , TDA4AEN-Q1 , TDA4AH-Q1 , TDA4AL-Q1 , TDA4AP-Q1 , TDA4APE-Q1 , TDA4VE-Q1 , TDA4VEN-Q1 , TDA4VH-Q1 , TDA4VL-Q1 , TDA4VM , TDA4VM-Q1 , TDA4VP-Q1 , TDA4VPE-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2High-Speed Interface Design Guidance
- 2.1 Trace Impedance
- 2.2 Trace Lengths
- 2.3 Differential Signal Length Matching
- 2.4 Signal Reference Planes
- 2.5 Differential Signal Spacing
- 2.6 Additional Differential Signal Rules
- 2.7 Symmetry in the Differential Pairs
- 2.8 Connectors and Receptacles
- 2.9 Via Discontinuity Mitigation
- 2.10 Back-Drill Via Stubs
- 2.11 Via Anti-Pad Diameter
- 2.12 Equalize Via Count
- 2.13 Surface-Mount Device Pad Discontinuity Mitigation
- 2.14 Signal Bending
- 2.15 ESD and EMI Considerations
- 2.16 ESD and EMI Layout Rules
- 3Interface-Specific Design Guidance
- 4Board Design Simulations
- 5References
- 6Revision History
2.8 Connectors and Receptacles
When implementing a through-hole receptacle (like a USB Standard-A), TI recommends making high-speed differential signal connections to the receptacle on the bottom layer of the PCB. Making these connections on the bottom layer of the PCB prevents the through-hole pin from acting as a stub in the transmission path. For surface-mount receptacles such as USB Micro-B and Micro-AB, make high-speed differential signal connections on the top layer. Making these connections on the top layer eliminates the need for vias in the transmission path. For examples of USB through-hole receptacle connections, see Figure 2-10.
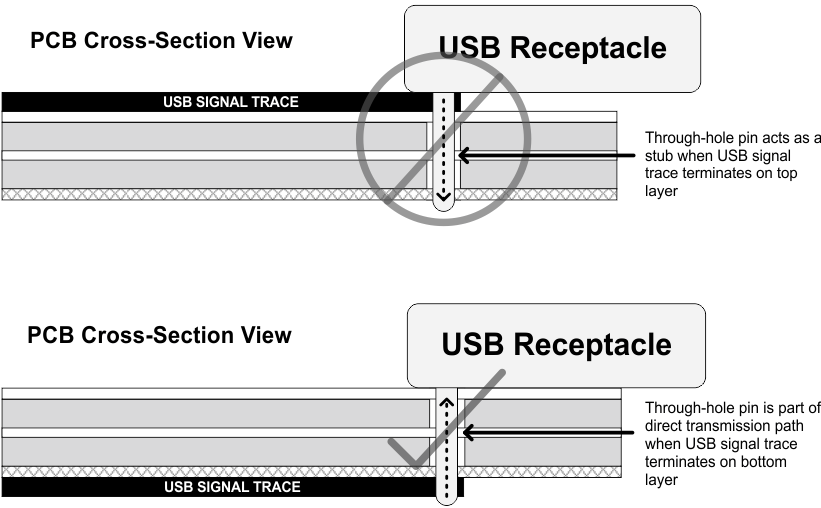 Figure 2-10 USB Through-Hole Receptacle Connection
Figure 2-10 USB Through-Hole Receptacle Connection