SPRAD28 October 2022 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434 , AM2631 , AM2631-Q1 , AM2632 , AM2632-Q1 , AM2634 , AM2634-Q1 , AM263P2-Q1 , AM263P4 , AM263P4-Q1 , AM26C31-EP , AM26C31M , AM26C32-EP , AM26C32C , AM26C32M , AM26LS31M , AM26LS32AM , AM26LS33A-SP , AM26LS33AM , AM26LV31E-EP , AM26LV32E-EP , AM26S10 , AM2732 , AM2732-Q1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Building for Debug
- 2 Code Composer Studio Stop-Mode Debugging
- 3 Debug Logging
- 4 Multi-Core Debug
- 5 Debugging Arm Cortex-R5 Exceptions
- 6 Debugging Arm Cortex-M4 Exceptions
- 7 Debugging Memory
- 8 Debugging Boot
- 9 Debugging Real-Time Control Loops
- 10E2E Support Forums
9.3.3 Add Serial Command Monitor Software
There are multiple ways to use UART0 as a debug interface. They are Debug Log and Serial Command Monitor. Debug Log is a built-in tool located at Driver Porting Layer of SDK. Like Serial Cmd Monitor, its function must be located out of interrupt callback. It is a handy tool enabling string input and output. But, input and output go through UART console only. There is no built-in GUI like Expression Window and Graph in CCS. It is recommended to disable UART0 in Debug Log at SysCfg and configure UART0 instance for Serial Command Monitor. As the name of UART in Sysconfig, "CONFIG_UART_CONSOLE", matches the handle name in "Serial_Cmd_HAL.c", it is not necessary to modify the two functions required by initialization and background loop.
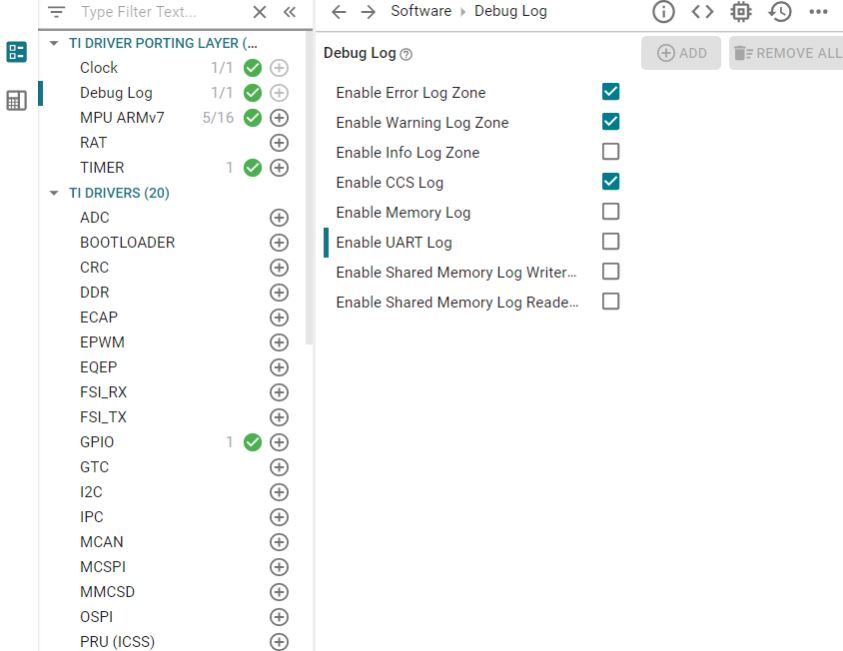 Figure 9-9 Disable UART Log in Debug
Log
Figure 9-9 Disable UART Log in Debug
Log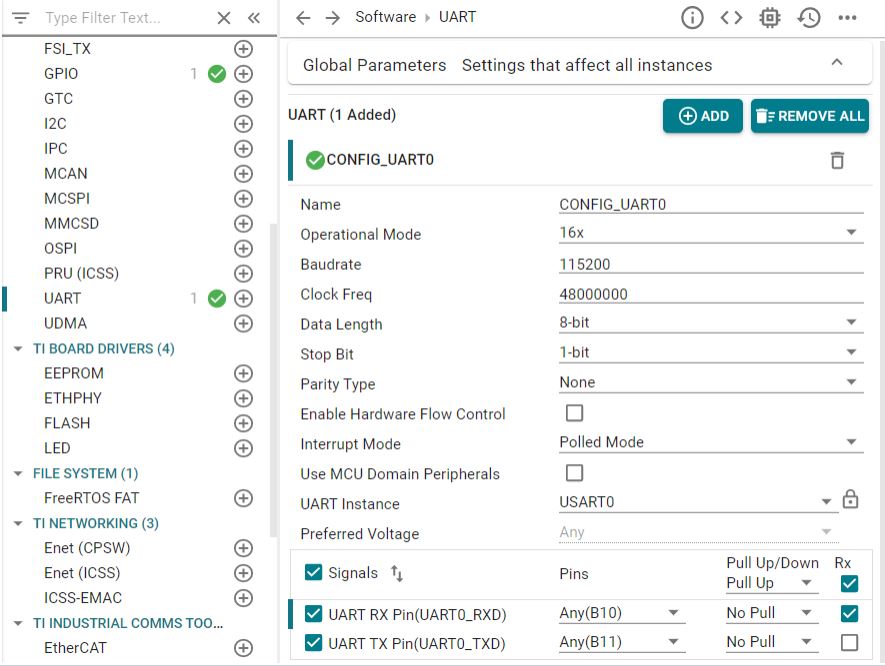 Figure 9-10 Configure UART0
Instance
Figure 9-10 Configure UART0
InstanceThen, add the serial monitor functions that were used in the benchmark demo example:
void benchmarkdemo_foc_main(void)
{
Drivers_open();
DebugP_log("\r\n START FOC benchmark\r\n");
App_statsInit(APP_ID_FOC);
SerialCmd_init();
while (1)
{
SerialCmd_read();
if (App_timerHasExpired())
{
focLoop(1);
}
App_statsUpdateUI();
}
Drivers_close();
}