SLVAE57B February 2021 – October 2021 LM5050-1 , LM5050-2 , LM5051 , LM66100 , LM74202-Q1 , LM74500-Q1 , LM74610-Q1 , LM74700-Q1 , LM74720-Q1 , LM74721-Q1 , LM74722-Q1 , LM7480-Q1 , LM7481-Q1 , LM76202-Q1 , SM74611 , TPS2410 , TPS2411 , TPS2412 , TPS2413 , TPS2419
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Reverse Battery Protection
- 3 ORing Power Supplies
- 4 Reverse Battery Protection using MOSFETs
- 5 Reverse Polarity Protection vs Reverse Current Blocking
- 6 What is an Ideal Diode Controller?
- 7 Automotive Transient protection with Ideal Diode Controllers
- 8 ORing Power Supplies with Ideal Diode Controllers
- 9 Integrated Ideal Diode Solution
- 10Summary
- 11References
- 12Revision History
4.2 Input Short or supply interruption
Figure 4-4 and Figure 4-5 show the performance comparison of P-Channel MOSFET with a schottky diode during an input short or interruption. During an input short, the schottky diode is quickly reverse biased and blocks reverse current from flowing back into the shorted input. Output is isolated from the input short and hold capacitors at the output provide back-up power to the load, leading to droop in the output voltage. When the input short is removed, load is powered through the schottky diode.
In Figure 4-5, P-Channel MOSFET turns off when the gate-source voltage crosses VTH of MOSFET, close to 0 V. Output voltage sees a huge drop due to lack of reverse current blocking functionality.
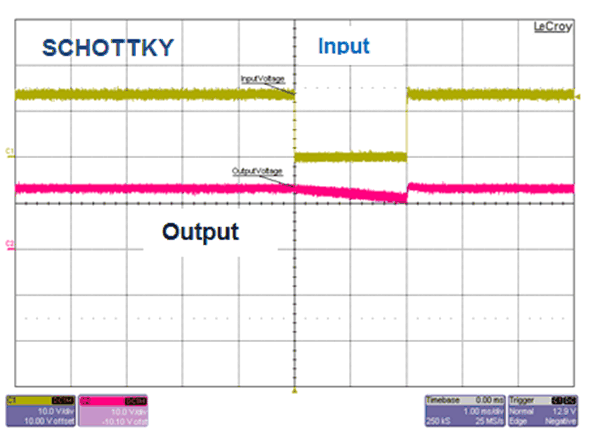 Figure 4-4 Input Short - Schottky Diode
Figure 4-4 Input Short - Schottky Diode Figure 4-5 Input Short - P-Channel
MOSFET
Figure 4-5 Input Short - P-Channel
MOSFET