SLAA334B September 2006 – August 2018 MSP430BT5190 , MSP430F1101 , MSP430F1101A , MSP430F1111A , MSP430F112 , MSP430F1121 , MSP430F1121A , MSP430F1122 , MSP430F1132 , MSP430F122 , MSP430F1222 , MSP430F123 , MSP430F1232 , MSP430F133 , MSP430F135 , MSP430F147 , MSP430F1471 , MSP430F148 , MSP430F1481 , MSP430F149 , MSP430F1491 , MSP430F155 , MSP430F156 , MSP430F157 , MSP430F1610 , MSP430F1611 , MSP430F1612 , MSP430F167 , MSP430F168 , MSP430F169 , MSP430F2001 , MSP430F2002 , MSP430F2003 , MSP430F2011 , MSP430F2012 , MSP430F2013 , MSP430F2013-EP , MSP430F2101 , MSP430F2111 , MSP430F2112 , MSP430F2121 , MSP430F2122 , MSP430F2131 , MSP430F2132 , MSP430F2232 , MSP430F2234 , MSP430F2252 , MSP430F2252-Q1 , MSP430F2254 , MSP430F2272 , MSP430F2272-Q1 , MSP430F2274 , MSP430F233 , MSP430F2330 , MSP430F235 , MSP430F2350 , MSP430F2370 , MSP430F2410 , MSP430F2416 , MSP430F2417 , MSP430F2418 , MSP430F2419 , MSP430F247 , MSP430F2471 , MSP430F248 , MSP430F2481 , MSP430F249 , MSP430F2491 , MSP430F2616 , MSP430F2617 , MSP430F2618 , MSP430F2619 , MSP430F412 , MSP430F413 , MSP430F4132 , MSP430F415 , MSP430F4152 , MSP430F417 , MSP430F423 , MSP430F423A , MSP430F425 , MSP430F4250 , MSP430F425A , MSP430F4260 , MSP430F427 , MSP430F4270 , MSP430F427A , MSP430F435 , MSP430F4351 , MSP430F436 , MSP430F4361 , MSP430F437 , MSP430F4371 , MSP430F438 , MSP430F439 , MSP430F447 , MSP430F448 , MSP430F4481 , MSP430F449 , MSP430F4491 , MSP430F4616 , MSP430F46161 , MSP430F4617 , MSP430F46171 , MSP430F4618 , MSP430F46181 , MSP430F4619 , MSP430F46191 , MSP430F47126 , MSP430F47127 , MSP430F47163 , MSP430F47166 , MSP430F47167 , MSP430F47173 , MSP430F47176 , MSP430F47177 , MSP430F47183 , MSP430F47186 , MSP430F47187 , MSP430F47193 , MSP430F47196 , MSP430F47197 , MSP430F477 , MSP430F478 , MSP430F4783 , MSP430F4784 , MSP430F479 , MSP430F4793 , MSP430F4794 , MSP430F5131 , MSP430F5132 , MSP430F5151 , MSP430F5152 , MSP430F5171 , MSP430F5172 , MSP430F5304 , MSP430F5308 , MSP430F5309 , MSP430F5310 , MSP430F5324 , MSP430F5325 , MSP430F5326 , MSP430F5327 , MSP430F5328 , MSP430F5329 , MSP430F5333 , MSP430F5336 , MSP430F5338 , MSP430F5340 , MSP430F5341 , MSP430F5342 , MSP430F5418 , MSP430F5418A , MSP430F5419 , MSP430F5419A , MSP430F5435 , MSP430F5435A , MSP430F5436 , MSP430F5436A , MSP430F5437 , MSP430F5437A , MSP430F5438 , MSP430F5438A , MSP430F5500 , MSP430F5501 , MSP430F5502 , MSP430F5503 , MSP430F5504 , MSP430F5505 , MSP430F5506 , MSP430F5507 , MSP430F5508 , MSP430F5509 , MSP430F5510 , MSP430F5630 , MSP430F5631 , MSP430F5632 , MSP430F5633 , MSP430F5634 , MSP430F5635 , MSP430F5636 , MSP430F5637 , MSP430F5638 , MSP430F6433 , MSP430F6435 , MSP430F6436 , MSP430F6438 , MSP430F6630 , MSP430F6631 , MSP430F6632 , MSP430F6633 , MSP430F6634 , MSP430F6635 , MSP430F6636 , MSP430F6637 , MSP430F6638 , MSP430FE423 , MSP430FE4232 , MSP430FE423A , MSP430FE4242 , MSP430FE425 , MSP430FE4252 , MSP430FE425A , MSP430FE427 , MSP430FE4272 , MSP430FE427A , MSP430FG4250 , MSP430FG4260 , MSP430FG4270 , MSP430FG437 , MSP430FG438 , MSP430FG439 , MSP430FG4616 , MSP430FG4617 , MSP430FG4618 , MSP430FG4619 , MSP430FG477 , MSP430FG478 , MSP430FG479 , MSP430FW423 , MSP430FW425 , MSP430FW427 , MSP430G2001 , MSP430G2101 , MSP430G2102 , MSP430G2111 , MSP430G2112 , MSP430G2121 , MSP430G2131 , MSP430G2132 , MSP430G2152 , MSP430G2201 , MSP430G2201-Q1 , MSP430G2211 , MSP430G2212 , MSP430G2221 , MSP430G2231 , MSP430G2231-Q1 , MSP430G2232 , MSP430G2252 , MSP430G2302 , MSP430G2312 , MSP430G2332 , MSP430G2352 , MSP430G2402 , MSP430G2432 , MSP430G2452 , MSP430L092
2 Simplified Flash Memory Cell
A flash memory cell is based on a transistor with a floating gate. Figure 1 shows a simplified schematic of a flash memory cell. The ultra-low-power flash memory cell of a MSP430 is slightly modified, but the basic function is the same.
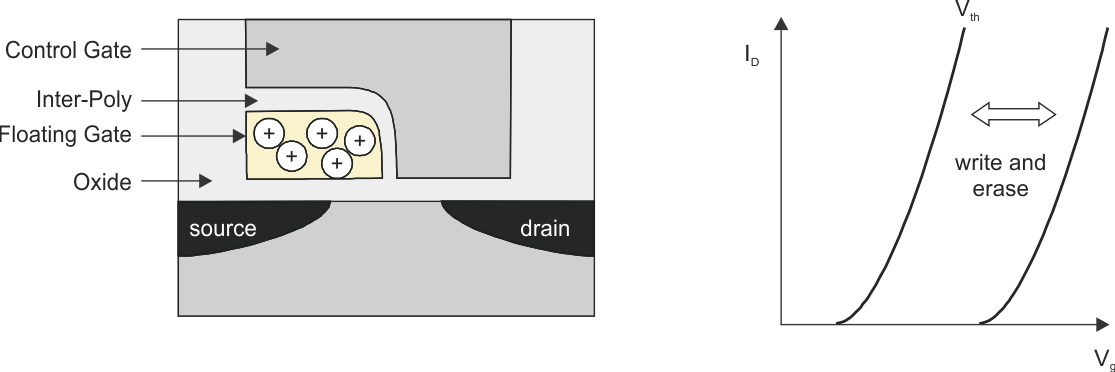 Figure 1. Flash Memory Cell
Figure 1. Flash Memory Cell Underneath the control gate is an additional floating gate. This floating gate is either fully charged or discharged. Charging and discharging this floating gate is done with high energy through the oxide. The amount of charge in the floating gate influences the threshold of the transistor, which generates a logical 1 or 0 when this flash cell is read.
Erasing a flash cell, as shown in Figure 2, is positive charging the floating gate. A positive-charged floating gate results in reading a logical 1 from this erased memory cell. Negatively charging the floating cell, as shown in Figure 3, means programming this cell. The CPU reads from a programmed cell the logical value 0. For erasing and programming, high energy is needed to transport the charge through the oxide by FN tunneling for erasure or channel hot electron (CHE) injection for programming.
.gif) Figure 2. Erasure of Flash Memory Cell (Erased Cell Is on the Right)
Figure 2. Erasure of Flash Memory Cell (Erased Cell Is on the Right) .gif) Figure 3. Programming a Flash Memory Cell (Programmed Cell Is on the Right)
Figure 3. Programming a Flash Memory Cell (Programmed Cell Is on the Right) The smallest unit that can be erased in a flash memory is a complete flash segment. Erasing flash means generating logical 1s in the memory. The MSP430 main flash memory has a segment size of 512 bytes. All MSP430 devices also have some smaller 64-byte or 128-byte flash segments. This area of the flash is called the information memory. In most applications, the main memory stores program code and constant data values, and the information memory is used for calibration data, serial numbers, etc. Except for the segment size, there is no difference between the main and the information memory. Hence, both can store program code or constant data values or both.
Programming flash memory generates logical 0 values in the flash memory cell. Programming can be performed bit, byte, or word wise. Flash segment size has no influence on programming of flash cells.
Only logical 0 can be written as single bits, bytes, or words. Because writing logical 1 in flash memory is only possible with erasing the memory, 1s can only be written segment-wise.
A high voltage is needed to program and erase flash memory. All MSP430 devices have an integrated charge pump and automatically generate this high voltage, when necessary. Also, a flash timing generator for automatic generation of erase and programming sequences is integrated in every MSP430. Hence, MSP430 flash programming is done without any external components. For programming and erasure, it only is important to keep the supply voltage VCC within the data sheet limits and to program the input clock frequency of the flash timing generator according to data sheet requirements.