SLVA787 September 2016 LM8330 , LM8335 , P82B715 , P82B96 , PCA6107 , PCA9306 , PCA9306-Q1 , PCA9515A , PCA9515B , PCA9518 , PCA9534 , PCA9534A , PCA9535 , PCA9536 , PCA9538 , PCA9539 , PCA9543A , PCA9544A , PCA9545A , PCA9546A , PCA9548A , PCA9554 , PCA9554A , PCA9555 , PCA9557 , PCF8574 , PCF8574A , PCF8575 , PCF8575C , TCA4311A , TCA6408A , TCA6416A , TCA6418E , TCA6424A , TCA9509 , TCA9517 , TCA9517A , TCA9534 , TCA9534A , TCA9535 , TCA9538 , TCA9539 , TCA9539-Q1 , TCA9543A , TCA9544A , TCA9545A , TCA9546A , TCA9548A , TCA9554 , TCA9554A , TCA9555 , TCA9617A , TCA9617B , TCA9800 , TCA9801 , TCA9802 , TCA9803
2.4 Level Shifting
Some devices in the I/O expander family feature level shifting/voltage translation, which allows the I2C bus voltage to be at a different voltage level than the GPIO ports. A common example of I/O level shifting is for situations where the output of the I/O expander must be at 5 V to drive logic devices or LEDs, but the I2C bus is at 3.3 V.
When choosing from the I/O expander portfolio, the selection chart shown in Figure 3 allows quick selection of the appropriate device, based on specific parameters/features. For example, an I/O expander with 8 channels, no RESET pin, and internal pull-up resistors would narrow the search down to TCA9554/A.
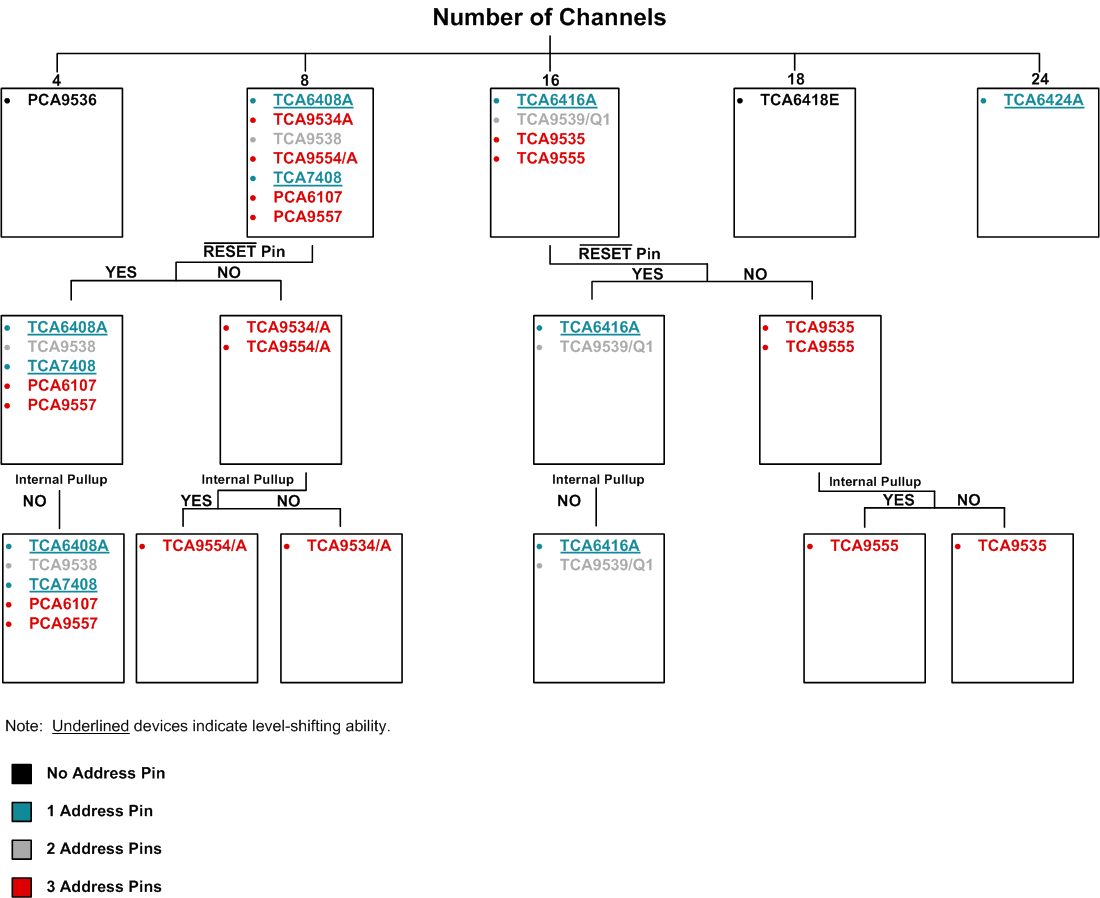 Figure 3. Selection Chart for TI I/O Expanders and their Key Features
Figure 3. Selection Chart for TI I/O Expanders and their Key Features