SPRACW5A April 2021 – December 2021 TMS320F2800132 , TMS320F2800133 , TMS320F2800135 , TMS320F2800137 , TMS320F280021 , TMS320F280021-Q1 , TMS320F280023 , TMS320F280023-Q1 , TMS320F280023C , TMS320F280025 , TMS320F280025-Q1 , TMS320F280025C , TMS320F280025C-Q1 , TMS320F280033 , TMS320F280034 , TMS320F280034-Q1 , TMS320F280036-Q1 , TMS320F280036C-Q1 , TMS320F280037 , TMS320F280037-Q1 , TMS320F280037C , TMS320F280037C-Q1 , TMS320F280038-Q1 , TMS320F280038C-Q1 , TMS320F280039 , TMS320F280039-Q1 , TMS320F280039C , TMS320F280039C-Q1 , TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28378D , TMS320F28378S , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379S , TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388S , TMS320F28P650DH , TMS320F28P650DK , TMS320F28P650SH , TMS320F28P650SK , TMS320F28P659DK-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2ACI Motor Control Benchmark Application
- 3Real-time Benchmark Data Analysis
-
4C2000 Value Proposition
- 4.1 Efficient Signal Chain Execution With Better Real-Time Response Than Higher Computational MIPS Devices
- 4.2 Excellent Real-Time Interrupt Response With Low Latency
- 4.3 Tight Peripheral Integration That Scales Applications With Large Number of Peripheral Accesses
- 4.4 Best in Class Trigonometric Math Engine
- 4.5 Versatile Performance Boosting Compute Engine (CLA)
- 4.6 Deterministic Execution due to Low Execution Variance
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
4.5 Versatile Performance Boosting Compute Engine (CLA)
Many C2000 devices have a CLA (Control Law Accelerator) which runs at the same frequency as the C28x CPU and can be utilized in two different ways to achieve real-time application goals.
- CLA executing full signal chain - CLA executing independent of C28x CPU, freeing up C28x CPU for other activities and effectively doubling the available MIPS.
- C28x CPU offloading compute to CLA - parallelism resulting in better execution performance by reducing the sample to output response time.
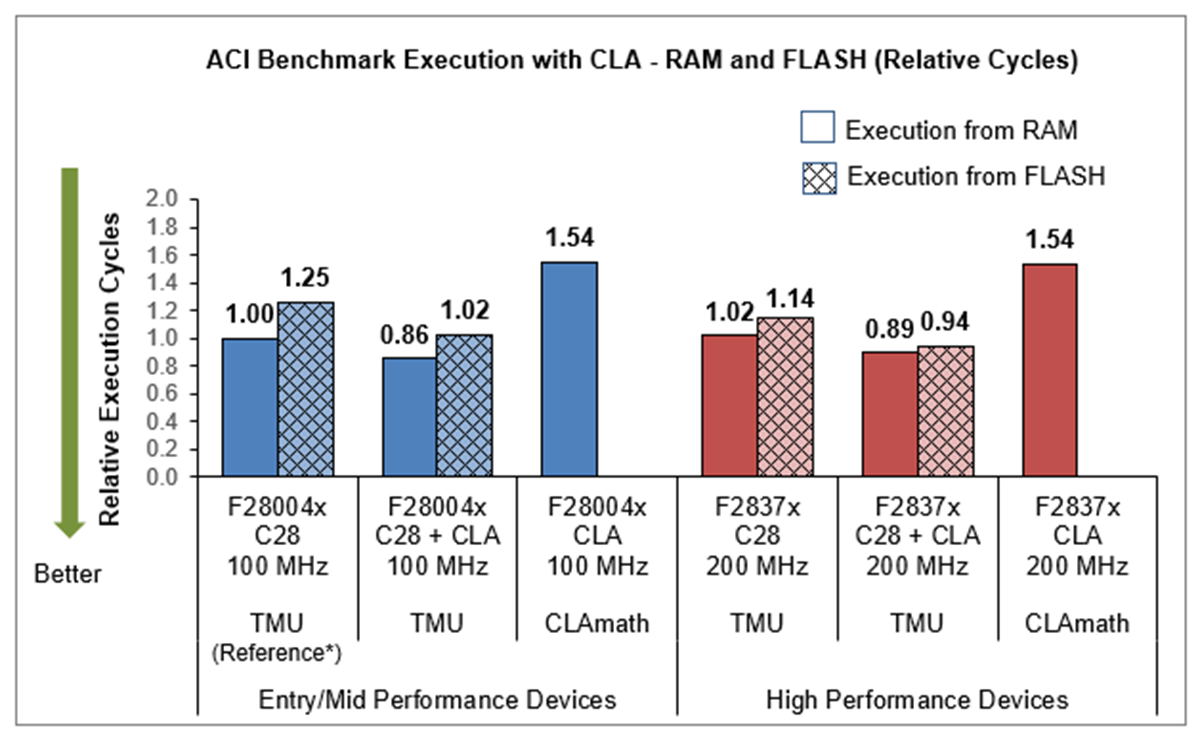
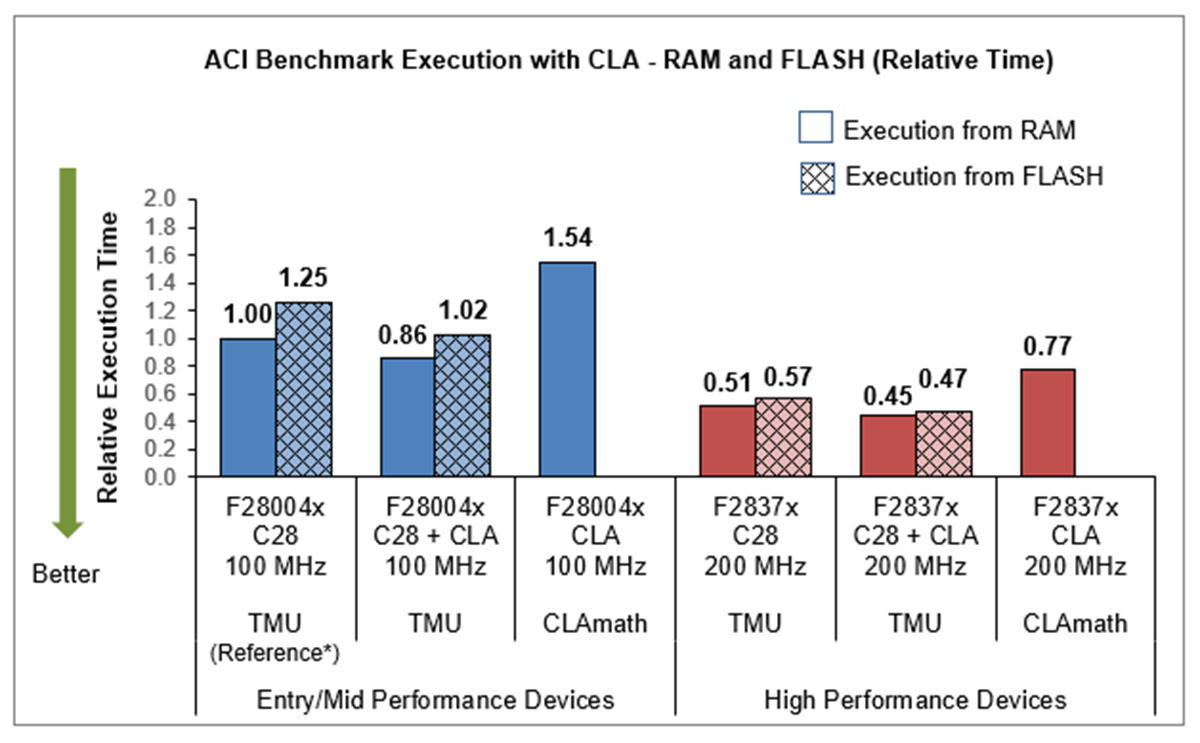
* As indicated in the Note, F28004x execution from RAM is the reference.
CLA runs from RAM only and hence does not have a Flash execution data point.
Figure 4-5 ACI Motor Control Benchmark CLA Execution (relative cycles and relative time)