TIDA029A july 2019 – june 2023 CC2640R2F-Q1 , CC2642R , CC2642R-Q1
- 1
- Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) Antenna Design
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Angle of Arrival Antenna Design Considerations
- 3Dipole Antenna Array
- 4Calculating AoA From IQ Measurements
- 5References
- 6Revision History
4.2 Dipole Antenna Array Compensated AoA Results
In this section, gain and offset compensation is added to the base calculated AoA values in Section 4.1 (excluding the PCB + RF absorbing material hardware setup) to reduce the AoA error from the actual angle Phi. The compensation is applied as Equation 5 shows.
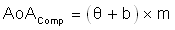
where
- θ equals the calculated AoA
- b equals the offset
- m equals the gain
For all hardware setups except the setup with the metal stand, the offset value was selected to make sure that when Phi equals zero, the calculated average AoA also equals zero. This offset was adjusted for each individual frequency as all frequencies require a slightly different offset value. To calculate the gain, the best fit line method was used for each frequency in the most linear range ( that is, –65° to 65°) after adding the required offset. However, there is much smaller variance of gain values over frequency as the majority of frequencies require the same gain or similar gain values.