SLUA963B June 2020 – October 2022 UCC21710-Q1 , UCC21732-Q1 , UCC5870-Q1
- HEV/EV Traction Inverter Design Guide Using Isolated IGBT and SiC Gate Drivers
- 1Introduction
- 2HEV/EV Overview
-
3Design of HEV/EV Traction Inverter Drive Stage
- 3.1 Introduction to UCC217xx-Q1
- 3.2 Designing a Traction Inverter Drive System Using UCC217xx-Q1
- 3.3 Description of Protection Features
- 3.4 Protection Features of UCC217xx-Q1
- 3.5
UCC217xx-Q1 Protection and Monitoring Features Descriptions
- 3.5.1 Primary and Secondary Side UVLO and OVLO
- 3.5.2 Over-Current (OC) and Desaturation (DESAT) Detection
- 3.5.3 2-Level and Soft Turn-Off
- 3.5.4 Power Switch Gate Voltage (VGE/VGS) Monitoring
- 3.5.5 Power Switch Anti-Shoot-Through
- 3.5.6 Integrated Internal or External Miller Clamp
- 3.5.7 Isolated Analog-to-PWM Channel
- 3.5.8 Short-Circuit Clamping
- 3.5.9 Active Pulldown
- 3.6 Introduction to UCC5870-Q1
- 3.7 Designing a Traction Inverter Drive System Using UCC5870-Q1
- 3.8 Description of Protection Features
- 3.9 Protection Features of UCC5870-Q1
- 3.10
UCC5870-Q1 Protection and Monitoring Features Descriptions
- 3.10.1 Primary and Secondary Side UVLO and OVLO
- 3.10.2 Programmable Desaturation (DESAT) Detection and Over-Current (OC)
- 3.10.3 Adjustable 2-Level or Soft Turn-Off
- 3.10.4 Active High-Voltage Clamp
- 3.10.5 Power Switch Gate Voltage (VGE/VGS) Monitoring
- 3.10.6 Gate Threshold Voltage Monitor
- 3.10.7 Power Switch Anti-Shoot-Through
- 3.10.8 Active Short Circuit (ASC)
- 3.10.9 Integrated Internal or External Miller Clamp
- 3.10.10 Isolated Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 3.10.11 Short-Circuit Clamping
- 3.10.12 Active and Passive Pulldown
- 3.10.13 Thermal Shutdown and Temperature Warning of Driver IC
- 3.10.14 Clock Monitor and CRC
- 3.10.15 SPI and Register Data Protection
- 4Isolated Bias Supply Architecture
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
3.9 Protection Features of UCC5870-Q1
The risk of latent and single-point failures can be reduced through gate driver integrated features as previously show in Table 3-1 with the UCC217xx-Q1 family. Both integrated and auxiliary circuits were outlined as ways to enable better coverage of failure modes. Table 3-2 shows the potential failure modes associated with the gate driver, the potential system impact and the UCC5870-Q1 integrated features. In this case, every key gate driver feature used to mitigate failure modes are integrated into the driver, versus externally implemented.
The system block visualization of the failure location(s) is shown in Figure 3-16 where (F1) is PMIC failure, (F2) is MCU failure, (F3) is Driver failure, and (F4) is Motor/Mechanical failure.
| System impact | Associated driver and/or inverter failures | Potential failure location(s) | UCC5870-Q1 integrated features | External circuit features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torque disturbance | Over or under voltage of driver power supply | F1 | UVLO, OVLO + interrupt signal | N/A |
| Unintended commutation | Gate driver pulse width skew | F2 or F3 | Low-delay capacitive isolation barrier and proven process Clock and data transmission monitoring ASC control of output in case of MCU failure | N/A |
| Unintended motor shutdown / Torque disturbance | Power switch short circuit | F2 or F4 | DESAT/OC detection and interrupt DESAT/OC self-test | N/A |
| Unintended motor shutdown / Torque disturbance | Gate shorted to ground or VDD | F2 or F3 | VGE monitoring and compare to PWM with interrupt | N/A |
| Unintended motor shutdown | Power switch shoot-through due to false gate signal or dv/dt-induced current | F2 | Anti-shoot-through logic and Miller clamp (internal or external) | N/A |
| Torque disturbance | Power switch over-voltage | F2 | Two-level turn-off and/or soft turn-off VCE/VDS monitoring using ADC VCE Clamp | N/A |
| Torque disturbance | Power switch over-temperature | F1, F2, or F4 | Integrated ADC with biasing current | N/A |
| Torque disturbance | Power switch gate oxide breakdown | F2 or F4 | Short circuit clamping | N/A |
| Torque disturbance | Power switch false turn-on when input power is floating | F1 or F2 | Active pulldown | N/A |
| Torque disturbance / Unintended motor shutdown | Power system DC bus over/under voltage | F1 or F4 | Integrated ADC | N/A |
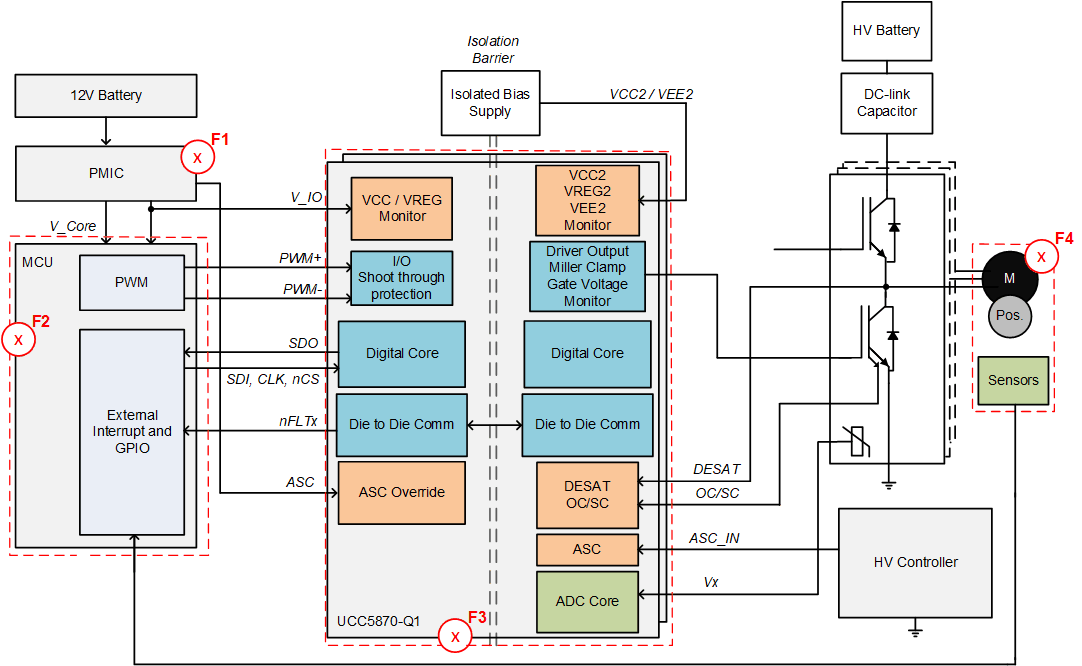 Figure 3-16 Possible Traction Inverter System-Level Failures and Prevention Circuits Using UCC5870-Q1
Figure 3-16 Possible Traction Inverter System-Level Failures and Prevention Circuits Using UCC5870-Q1