JAJSKX2A August 2019 – May 2021 TPS53676
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4
Electrical Specifications
- 6.4.1 Thermal Information
- 6.4.2 Supply
- 6.4.3 DAC and Voltage Feedback
- 6.4.4 Control Loop Parameters
- 6.4.5 Dynamic VID (DVID) Tuning
- 6.4.6 Undershoot Reduction (USR) and Overshoot Reduciton (OSR)
- 6.4.7 Dynamic Phase Shedding (DPS)
- 6.4.8 Turbo Mode and Thermal Balance Management (TBM)
- 6.4.9 Overcurrent Limit (OCL)
- 6.4.10 Telemetry
- 6.4.11 Phase-Locked Loop and Closed-Loop Frequency Control
- 6.4.12 Logic Interface
- 6.4.13 Current Sensing and Current Sharing
- 6.4.14 Pin Detection Thresholds
- 6.4.15 ADDR Pinstrap Decoding
- 6.4.16 BOOT_CHA Pinstrap Decoding
- 6.4.17 Timing Specifications
- 6.4.18 Faults and Converter Protection
- 6.4.19 PMBus/AVS Interfaces
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Power-up and initialization
- 7.4
Pin connections and bevahior
- 7.4.1 Supplies: VCC and VREF
- 7.4.2 Differential remote sensing and output voltage scaling: AVSP/AVSN, BVSP/BVSN
- 7.4.3 Input current sensing: VIN_CSNIN and CSPIN
- 7.4.4 Pin-strap detection and PIN_DETECT_OVERRIDE
- 7.4.5 Enable and disable: AVR_EN and BVR_EN
- 7.4.6 System feedback: AVR_RDY and BVR_RDY
- 7.4.7 Catastrophic fault alert: VR_FAULT#
- 7.4.8 Output voltage reset: RESET#
- 7.4.9 Synchronization: SYNC
- 7.4.10 Smart power stage connections: PWM, CSP and TSEN
- 7.4.11 PMBus pins: SMB_DIO, SMB_CLK, and SMB_ALERT#
- 7.4.12 AVSBus: AVS_CLK, AVS_MDATA, AVS_SDATA, and AVS_VDDIO
- 7.5 Advanced power management functions
- 7.6
Control Loop Theory of Operation
- 7.6.1 Adaptive voltage positioning and DC load line (droop)
- 7.6.2 DCAP+ conceptual overview
- 7.6.3 Off-time control: loop compensation and transient tuning
- 7.6.4 On-time control: adaptive ton and autobalance current sharing
- 7.6.5 Load transient response
- 7.6.6 Forced minimum on-time, minimum off-time and leading-edge blanking time
- 7.6.7 Nonlinear: undershoot reduction (USR), overshoot reduction (OSR) and dynamic integration
- 7.7
Power supply fault protection
- 7.7.1 Host notification and status reporting
- 7.7.2 Fault type and response definitions
- 7.7.3 Fault behavior summary
- 7.7.4
Detailed fault descriptions
- 7.7.4.1 Overvoltage fault (OVF) and warning (OVW)
- 7.7.4.2 Undervoltage fault (UVF) and warning (UVW)
- 7.7.4.3 Maximum turn-on time exceeded (TON_MAX)
- 7.7.4.4 Output commanded out-of-bounds (VOUT_MIN_MAX)
- 7.7.4.5 Overcurrent fault (OCF), warning (OCW), and per-phase overcurrent limit (OCL)
- 7.7.4.6 Current share warning (ISHARE)
- 7.7.4.7 Overtemperature fault protection (OTF) and warning (OTW)
- 7.7.4.8 Powerstage fault (TAO_HIGH) and powerstage not ready (TAO_LOW)
- 7.7.4.9 Input overvoltage fault (VIN_OVF) and warning (VIN_OVW)
- 7.7.4.10 Input undervoltage fault (VIN_UVF), warning (VIN_UVW) and turn-on voltage (VIN_ON)
- 7.7.4.11 Input overcurrent fault (IIN_OCF) and warning (IIN_OCW)
- 7.7.4.12 Input overpower warning (PIN_OPW)
- 7.7.4.13 PMBus command, memory and logic errors (CML)
- 7.8
Programming
- 7.8.1
PMBus Interface
- 7.8.1.1 PMBus transaction types
- 7.8.1.2 PMBus data formats
- 7.8.1.3 Raw non-volatile memory programming
- 93
- 7.8.1.4
PMBus Command Descriptions
- 7.8.1.4.1 (00h) PAGE
- 7.8.1.4.2 (01h) OPERATION
- 7.8.1.4.3 (02h) ON_OFF_CONFIG
- 7.8.1.4.4 (03h) CLEAR_FAULTS
- 7.8.1.4.5 (04h) PHASE
- 7.8.1.4.6 (05h) PAGE_PLUS_WRITE
- 7.8.1.4.7 (06h) PAGE_PLUS_READ
- 7.8.1.4.8 (10h) WRITE_PROTECT
- 7.8.1.4.9 (15h) STORE_USER_ALL
- 7.8.1.4.10 (16h) RESTORE_USER_ALL
- 7.8.1.4.11 (19h) CAPABILITY
- 7.8.1.4.12 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_WORD
- 7.8.1.4.13 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_VOUT
- 7.8.1.4.14 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_IOUT
- 7.8.1.4.15 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_INPUT
- 7.8.1.4.16 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_TEMPERATURE
- 7.8.1.4.17 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_CML
- 7.8.1.4.18 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_MFR
- 7.8.1.4.19 (20h) VOUT_MODE
- 7.8.1.4.20 (21h) VOUT_COMMAND
- 7.8.1.4.21 (22h) VOUT_TRIM
- 7.8.1.4.22 (24h) VOUT_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.23 (25h) VOUT_MARGIN_HIGH
- 7.8.1.4.24 (26h) VOUT_MARGIN_LOW
- 7.8.1.4.25 (27h) VOUT_TRANSITION_RATE
- 7.8.1.4.26 (28h) VOUT_DROOP
- 7.8.1.4.27 (29h) VOUT_SCALE_LOOP
- 7.8.1.4.28 (2Bh) VOUT_MIN
- 7.8.1.4.29 (33h) FREQUENCY_SWITCH
- 7.8.1.4.30 (34h) POWER_MODE
- 7.8.1.4.31 (35h) VIN_ON
- 7.8.1.4.32 (38h) IOUT_CAL_GAIN
- 7.8.1.4.33 (39h) IOUT_CAL_OFFSET
- 7.8.1.4.34 (40h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.35 (41h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.36 (42h) VOUT_OV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.37 (43h) VOUT_UV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.38 (44h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.39 (45h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.40 (46h) IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.41 (47h) IOUT_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.42 (4Ah) IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.43 (4Fh) OT_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.44 (50h) OT_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.45 (51h) OT_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.46 (55h) VIN_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.47 (56h) VIN_OV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.48 (57h) VIN_OV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.49 (58h) VIN_UV_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.50 (59h) VIN_UV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.51 (5Ah) VIN_UV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.52 (5Bh) IIN_OC_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.53 (5Ch) IIN_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.54 (5Dh) IIN_OC_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.55 (60h) TON_DELAY
- 7.8.1.4.56 (61h) TON_RISE
- 7.8.1.4.57 (62h) TON_MAX_FAULT_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.58 (63h) TON_MAX_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 7.8.1.4.59 (64h) TOFF_DELAY
- 7.8.1.4.60 (65h) TOFF_FALL
- 7.8.1.4.61 (6Bh) PIN_OP_WARN_LIMIT
- 7.8.1.4.62 (78h) STATUS_BYTE
- 7.8.1.4.63 (79h) STATUS_WORD
- 7.8.1.4.64 (7Ah) STATUS_VOUT
- 7.8.1.4.65 (7Bh) STATUS_IOUT
- 7.8.1.4.66 (7Ch) STATUS_INPUT
- 7.8.1.4.67 (7Dh) STATUS_TEMPERATURE
- 7.8.1.4.68 (7Eh) STATUS_CML
- 7.8.1.4.69 (80h) STATUS_MFR_SPECIFIC
- 7.8.1.4.70 (88h) READ_VIN
- 7.8.1.4.71 (89h) READ_IIN
- 7.8.1.4.72 (8Bh) READ_VOUT
- 7.8.1.4.73 (8Ch) READ_IOUT
- 7.8.1.4.74 (8Dh) READ_TEMPERATURE_1
- 7.8.1.4.75 (96h) READ_POUT
- 7.8.1.4.76 (97h) READ_PIN
- 7.8.1.4.77 (98h) PMBUS_REVISION
- 7.8.1.4.78 (99h) MFR_ID
- 7.8.1.4.79 (9Ah) MFR_MODEL
- 7.8.1.4.80 (9Bh) MFR_REVISION
- 7.8.1.4.81 (9Dh) MFR_DATE
- 7.8.1.4.82 (ADh) IC_DEVICE_ID
- 7.8.1.4.83 (AEh) IC_DEVICE_REV
- 7.8.1.4.84 (B1h) USER_DATA_01 (COMPENSATION_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.85 (B2h) USER_DATA_02 (NONLINEAR_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.86 (B3h) USER_DATA_03 (PHASE_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.87 (B4h) USER_DATA_04 (DVID_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.88 (B7h) USER_DATA_07 (PHASE_SHED_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.89 (B8h) USER_DATA_08 (AVSBUS_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.90 (BAh) USER_DATA_10 (ISHARE_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.91 (BBh) USER_DATA_11 (MFR_PROTECTION_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.92 (BDh) USER_DATA_13 (MFR_CALIBRATION_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.93 (CDh) MFR_SPECIFIC_CD (MULTIFUNCTION_PIN_CONFIG_1)
- 7.8.1.4.94 (CEh) MFR_SPECIFIC_CD (MULTIFUNCTION_PIN_CONFIG_2)
- 7.8.1.4.95 (CFh) SMBALERT_MASK_EXTENDED
- 7.8.1.4.96 (D1h) READ_VOUT_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.97 (D2h) READ_IOUT_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.98 (D3h) READ_TEMPERATURE_MIN_MAX)
- 7.8.1.4.99 (D4h) READ_MFR_VOUT
- 7.8.1.4.100 (D5h) READ_VIN_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.101 (D6h) READ_IIN_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.102 (D7h) READ_PIN_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.103 (D8h) READ_POUT_MIN_MAX
- 7.8.1.4.104 (DAh) READ_ALL
- 7.8.1.4.105 (DBh) STATUS_ALL
- 7.8.1.4.106 (DCh) STATUS_PHASES
- 7.8.1.4.107 (DDh) STATUS_EXTENDED
- 7.8.1.4.108 (E0h) AVSBUS_LOG
- 7.8.1.4.109 (E3h) MFR_SPECIFIC_E3 (VR_FAULT_CONFIG)
- 7.8.1.4.110 (E4h) SYNC_CONFIG
- 7.8.1.4.111 (EDh) MFR_SPECIFIC_ED (MISC_OPTIONS)
- 7.8.1.4.112 (EEh) MFR_SPECIFIC_EE (PIN_DETECT_OVERRIDE)
- 7.8.1.4.113 (EFh) MFR_SPECIFIC_EF (SLAVE_ADDRESS)
- 7.8.1.4.114 (F0h) MFR_SPECIFIC_F0 (NVM_CHECKSUM)
- 7.8.1.4.115 (F5h) MFR_SPECIFIC_F5 (USER_NVM_INDEX)
- 7.8.1.4.116 (F6h) MFR_SPECIFIC_F6 (USER_NVM_EXECUTE)
- 7.8.1.4.117 (FAh) NVM_LOCK
- 7.8.1.4.118 (FBh) MFR_SPECIFIC_WRITE_PROTECT
- 7.8.2 AVSBus Interface
- 7.8.1
PMBus Interface
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3 Detailed Design Procedure
The following steps illustrate the key components selection for the 0.88-V / 250-A, 1-V / 30-A ASIC application.
Inductor Selection
Smaller inductance yields better transient performance, but leads to higher ripple current and lower efficiency. Higher inductance has the opposite effect. It is common practice to limit the ripple current to between 20%-40% of maximum per-phase current for balanced performance. In this design example, 30% of the maximum per-phase current is used for channel A.
Considering the variation and derating of the inductance and a standard inductor value of 150nH with DCR 0.125 mΩ, is selected. Then use Equation 50 to re-calculate the actual output ripple.
With same design procedure for channel B, a standard inductor value of 150 nH with DCR 0.125 mΩ from ITG is chosen.
Output Capacitor Selection
Generally, consider output ripple and output voltage deviation during load transient when selecting output capacitors.
When available, follow the output capacitance recommendation for the load ASIC reference design. With TPS53676 device, it is possible to meet the load transient with lower output capacitance due to the high-speed nature of DCAP+ control. Output Capacitor Recommendations is the output capacitance recommendation for the above rail specification.
| Capacitor location | Channel A | Channel B |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk capacitors near power stages | 12x 470 μF / 2.5V / 3mΩ ESR | 2x 470 μF / 2.5V / 3mΩ ESR |
| Top side | 24x 220 μF / 4V / X5R/ 1206 18x 100 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 |
4x 220 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 3x 100 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 |
| Bottom side | 24x 220 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 18x 100 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 |
4x 220 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 3x 100 μF / 4V / X5R / 1206 |
| Total output capacitance | 19.8 mF | 1874 μF |
Select Per-Phase Valley Current Limit
The equation below shows the calculation of per-phase valley current limit based on maximum processor current, the operating phase number and per-phase current ripple ΔIRIPPLE(actual).
For the channel A,
Where Kmargin is the maximum operating margin factor. Choose 125% margin to avoid triggering current limit during load transient events. For this design, choose the 47A valley current limit for channel A.
The calculation above shows the minimum saturation current for inductor. Using same design procedure, the valley current limit for channel B is selected to be 26 A.
Set USR threshold to improve load transient performance
There are two levels of undershoot reduction (USR1, USR2) options. USR1 enables up to 3, 4, 5 or all normal phases and USR2 enables all available phases. To select the proper value, start with each USR threshold set to be disabled, and then systematically lower the threshold, enabling fast-phase-addition to meet the load transient requirement.
For this design, phase shedding is disabled. USR1 and USR2 are selected to be disabled for both channel A and channel B.
Input Current Sensing (Shunt/ Calculated Iin/ Inductor DCR)
TPS53676 has three input current sensing options: shunt current sensing, calculated input current sensing and inductor DCR current sensing. Either option may be chosen for precision input current reporting.
Shunt current sensing
In this design, the external shunt resistor 0.5 mΩ ± 1%, 3 W, 4026 package is selected. Once properly calibrated, Input current reporting is within the tolerance target.
Calculated input current sensing
TPS53676 includes an option to impute input current for situations in which the addition of a shunt or input inductor is prohibitive. Connect pins 46 (VIN_CSNIN) and 47 (CSPIN) together, and place a minimum 1 μF effective capacitance bypass cap from pin 46 to GND, then connect pin 46 to input supply (12 V nominally) before input inductor. Configure the calculated input current option through the NVM settings in MFR_SPECIFIC_ED (MISC OPTIONS).
Inductor DCR Current Sensing
This section describes the procedure to determine an inductor DCR thermal compensation network design. The image below shows a typical DCR sensing circuit. From the equations below, when the time constant of the RC network is equal to the L/R time constant of the inductor, the capacitor voltage VC across the CSENSE capacitor can be used to obtain the inductor current. However, inductor windings have a positive temperature coefficient of approximately 3900 ppm/°C. So an NTC thermistor is used to cancel thermal variation from the inductor DCR.
The design goal is for the DCR value to be invariant with the temperature. Therefore, the voltage across sense capacitor would be only dependent on the inductor current over the temperature range of interest.
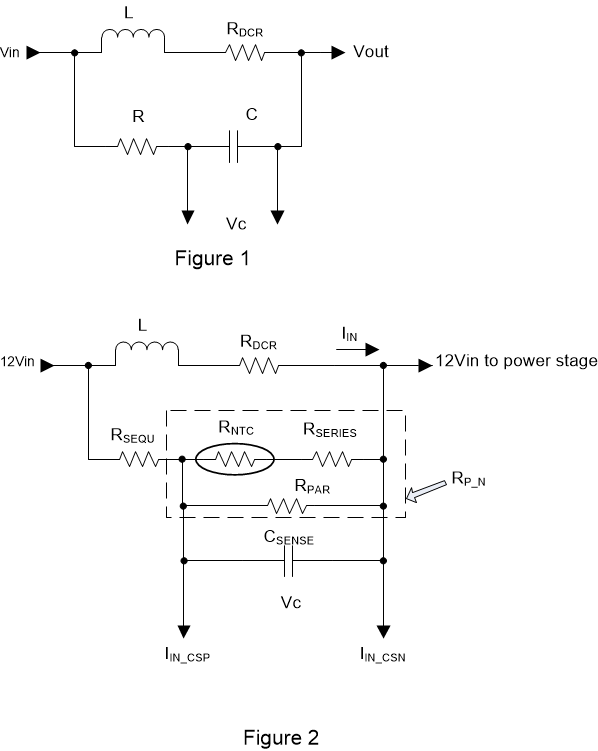 Figure 8-5 Input DCR Network
Figure 8-5 Input DCR NetworkThe equivalent resistance of the RSEQU, RNTC, RSERIES and RPAR values is given by REQ. Use the equations below to derive the values of RSEQU, RNTC, RSERIES and RPAR.
Finally the value of β, given in the equation below, represents the effective current sense gain after thermal compensation. This value can be used as the sense element resistance to derive the PMBus settings as described in Input current calibration (measured).
For this design, select thermistor RNTC as 1 kΩ, 5%, 0603, B-constant is 3650k, P/N: NCP18XQ102J03B from Murata. Select CSENSE as 1 μF X7R or better dielectric (C0G preferred).
In order to solve the value of RSEQU, RSERIES and RPAR, the β at three temperature points are set equal. set β = 0.15 mΩ equally at temperature 0 °C, 25 °C and 75 °C. With the calculation, three resistors value can be found as RSEQU = 332 Ω, RSERIES = 432 Ω, RPAR = 1.40 kΩ.
TI offers an application note and excel spreadsheet to streamline input DCR netowrk calculations. Contact your local field/sales representative to get a copy of the document.
Loop compensation design
- 5 mΩ: Typical gain from power stage current sense
- ACLL: Programmable AC load line, provides direct output voltage feedback.
- DCLL: Programmable DC load line, provides adaptive voltage positioning
- KDIV : Fixed scalar with value of 0.5
- τINT : Programmable integration time constant, adjustable from 1µs to 16 µs (scale = 1 µs)
- KINT : Programmable integration gain which can be adjustable from 0.5x, 1x, 1.5x, 2x
- KAC : Programmable AC gain which is adjustable from 0.5x, 1x, 1.5x, 2x
- VRAMP : Programmable ramp voltage which is adjustable from 80 mV to 320 mV(scale = 40 mV)
For this design, the optimal loop compensation values were derived by tuning. The final valuea are listed .
| PARAMETER | Channel A | Channel B |
|---|---|---|
| DCLL | 0.0 mΩ | 0.0 mΩ |
| ACLL | 0.2 mΩ | 0.5 mΩ |
| τINT | 1 µs | 7 µs |
| KINT | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| KAC | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| VRAMP | 320 mV | 200 mV |
Select ADDR pin resistors
Based on the design requirements of PMBus address select the upper and lower ADDR pin resistors, RHA and RLA according to ADDR pin decoding.
| PMBus address | RHA | RLA |
|---|---|---|
| 96d / C0h | 110 kΩ | 37.4 kΩ |
Select the boot voltage VBOOT for each channel
The boot voltage for channel A is determined by pinstrapping on the BOOT_CHA pin. Based on BOOT_CHA pinstrap decoding, select RHB = 20.0 kΩ and RLB = 59.0 kΩ to select 0.88 V as the channel A boot voltage.
The boot voltage for channel B is stored in NVM. Update the NVM value for VOUT_COMMAND to 1.0 V , and store the value to non-volatile memory.