SLYY234 December 2024 AMC0106M05 , AMC0106M25 , AMC0136 , AMC0311D , AMC0311S , AMC0386 , AMC0386-Q1 , AMC1100 , AMC1106M05 , AMC1200 , AMC1200-Q1 , AMC1202 , AMC1203 , AMC1204 , AMC1211-Q1 , AMC1300 , AMC1300B-Q1 , AMC1301 , AMC1301-Q1 , AMC1302-Q1 , AMC1303M2510 , AMC1304L25 , AMC1304M25 , AMC1305M25 , AMC1305M25-Q1 , AMC1306M05 , AMC1306M25 , AMC1311 , AMC1311-Q1 , AMC131M03 , AMC1336 , AMC1336-Q1 , AMC1350 , AMC1350-Q1 , AMC23C12 , AMC3301 , AMC3330 , AMC3330-Q1
- 1
- Introduction
- Introduction to Isolated Signal Chain
- Selection Trees
-
Current Sensing
- Shunt Resistor Selection for Isolated Data Converters
- Design considerations for isolated current sensing
- Isolated Current-Sensing Circuit With ±50-mV Input and Single-Ended Output
- Isolated Current-Sensing Circuit With ±50-mV Input and Differential Output
- Isolated Current-Sensing Circuit With ±250-mV Input Range and Single-Ended Output Voltage
- Isolated current-measurement circuit with ±250-mV input and differential output
- Isolated Overcurrent Protection Circuit
- Interfacing a Differential-Output (Isolated) Amp to a Single-Ended Input ADC
- Utilizing AMC3311 to Power AMC23C11 for Isolated Sensing and Fault Detection
- Isolated Current-Sensing Circuit With Front-End Gain Stage
- Accuracy Comparison of Isolated Shunt and Closed-Loop Current Sensing
-
Voltage Sensing
- Maximizing Power Conversion and Motor Control Efficiency With Isolated Voltage Sensing
- Increased Accuracy and Performance with Integrated High Voltage Resistor Isolated Amplifiers and Modulators
- Isolated Amplifiers With Differential, Single-Ended Fixed Gain and Ratiometric Outputs for Voltage Sensing Applications
- Isolated Voltage-Measurement Circuit With ±250-mV Input and Differential Output
- Split-Tap Connection for Line-to-Line Isolated Voltage Measurement Using AMC3330
- ±12V Voltage Sensing Circuit With an Isolated Amplifier and Pseudo-Differential Input SAR ADC
- ±12-V voltage sensing circuit with an isolated amplifier and differential input SAR ADC
- Isolated Undervoltage and Overvoltage Detection Circuit
- Isolated Zero-Cross Detection Circuit
- ±480V Isolated Voltage-Sensing Circuit With Differential Output
-
EMI Performance
- Best in Class Radiated Emissions EMI Performance with Isolated Amplifiers
- Best Practices to Attenuate AMC3301 Family Radiated Emissions EMI
-
End Equipment
- Comparing Shunt- and Hall-Based Isolated Current-Sensing Solutions in HEV/EV
-
Design Considerations for Current Sensing
in DC EV Charging Applications
- Abstract
- Introduction
-
Current Sensing in AC/DC Converters
- Basic Hardware and Control Description of AC/DC
- Point A and B – AC/DC AC Phase-Current Sensing
- Point C and D – AC/DC DC Link Current Sensing
- Summary of Positives and Negatives at Point A, B, C1/2 and D1/2 and Product Suggestions
- Current Sensing in DC/DC Converters
- Conclusion
- References
-
Using isolated comparators for fault
detection in electric motor drives
- Introduction
- Introduction to electric motor drives
- Understanding fault events in electric motor drives
- Achieving reliable detection and protection in electric motor drives
- Use case No. 1: Bidirectional in-phase overcurrent detection
- Use case No. 2: DC+ overcurrent detection
- Use case No. 3: DC– overcurrent or short-circuit detection
- Use case No. 4: DC-link (DC+ to DC–) overvoltage and undervoltage detection
- Use case No. 5: IGBT module overtemperature detection
- Discrete DESAT for Opto-Compatible Isolated Gate Driver UCC23513 in Motor Drives
- Isolated voltage sensing in AC motor drives
- Achieving High-Performance Isolated Current and Voltage Sensing in Server PSUs
-
Additional Reference Designs/Circuits
- Designing a Bootstrap Charge-Pump Power Supply for an Isolated Amplifier
-
Clock Edge Delay Compensation With
Isolated Modulators Digital Interface to MCUs
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Design Challenge With Digital Interface Timing Specifications
- Design Approach With Clock Edge Delay Compensation
- Test and Validation
- Conclusion
- References
- Utilizing AMC3311 to Power AMC23C11 for Isolated Sensing and Fault Detection
Introduction
Whether you are sensing current in an industrial 3-phase servo motor system, a battery management system for an electric vehicle, or a photo voltaic inverter, it is often necessary to include some sort of safety isolation scheme. Safety-related standards define the specific isolation requirements for the end equipment associated with the particular design. Various factors come into play when determining what level of safety insulation (basic, supplemental, or reinforced) is required depending on the type of equipment, the voltage levels involved, and the environment that the equipment is to be installed.
Texas Instruments offers a variety of isolated current shunt amplifiers that are used in the previously-mentioned applications for voltage and current shunt sensing that meet either basic or reinforced insulation requirements. For applications requiring reinforced insulation, one such device is the AMC1301. The output of the AMC1301 is a fully differential signal centered around a common-mode voltage of 1.44 V that can be fed directly to a stand-alone analog-to-digital converter (ADC) as shown in Figure 15, or to the on-board ADC found in the MSP430 and C2000 family of microcontroller devices.
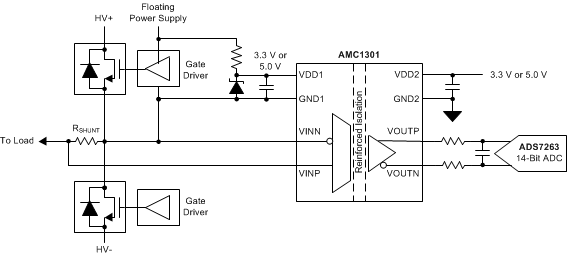 Figure 15 AMC1301
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 15 AMC1301
Functional Block DiagramEmbedded ADCs
Both the MSP430 and C2000 family of processors have embedded single-ended input ADCs so the question becomes: How do I get this differential signal into my single-ended data converter?
The simplest way to achieve this is to use only one output of the AMC1301 leaving the second output floating. The down side to this design is that only half the output voltage swing is available to the data converter, reducing the dynamic range of the measurement. The analog input range to the AMC1301 is ±250 mV. With a fixed gain of 8.2, the VOUTN and VOUTP voltages are ±1.025 V centered around the 1.44-V common-mode output as shown in Figure 16. Differentially, the output voltage is ±2.05 V.
 Figure 16 Differential Output Voltage
Figure 16 Differential Output VoltageThe addition of a differential to single-ended amplifier output stage, shown in Figure 17, allows the full output range of the AMC1301 to be provided to the ADC.
 Figure 17 Differential to Single-Ended Output
Figure 17 Differential to Single-Ended OutputAssuming a full scale sine wave of ±250 mV is applied at VIN; the internal gain of the AMC1301 provides 2.05 Vpk-pk outputs at points VOUTP and VOUTN which are 180° out of phase. The difference between these signals, VODIF, is 4.1 Vpk-pk. When R1 = R4 and R2 = R3, Equation 8 shows the transfer function of the output stage.
With equal value resistors for R1 through R4 in Equation 8 and VCM set to 2.5 V,Equation 9 reduces to:
The plots of Figure 18 show the input voltage and output voltages of the AMC1301 along with the output voltage of the final differential to single-ended output stage. Note that the differential voltage of ±2.05 V is transposed to a single-ended signal from 0.5 to 4.5 V.
 Figure 18 Single-Ended Output Voltage
Figure 18 Single-Ended Output VoltageDepending on the input voltage range of the ADC, gain or attenuation can be incorporated into the differential to single-ended stage to adjust the output swing. The output common-mode voltage can be adjusted to fit the input needs of the ADC as well.
Design Example
The ADC12 found on the MSP430 devices have an input voltage range of 0–2.5 V when using the internal voltage reference. Using the VOUTP from the AMC1301 can provide the ADC12 with an input signal ranging from 0.415 V to 2.465 V, well within the input range of the converter while only using half the input range of the AMC1301. As Figure 19 shows, using a differential to single-ended amplifier configuration with a gain of 0.5 and common mode voltage of 1.25 V, the entire voltage range of the AMC1301 can be applied to the ADC12.
 Figure 19 Scaled
Differential to Single-Ended Output
Figure 19 Scaled
Differential to Single-Ended OutputAlternative Device Recommendations
The AMC1100 or AMC1200 provide basic isolation with similar performance to the AMC1301 at a lower price point. Forthe TLV170 provides this option for applications that require a bipolar output.
| Device | Optimized Parameter | Performance Trade-Off |
|---|---|---|
| AMC1100 | Galvanic Isolation up to 4250 VPEAK | Lower Transient Immunity |
| AMC1200 | Galvanic Isolation up to 4250 VPEAK | Basic Isolation versus Reinforced |
| TLV170 | Bi-polar operation to ±18 V | Higher input bias current |
Conclusion
While it is possible to use a single output of the AMC1301 to drive a single-ended ADC, adding a differential to single-ended op-amp stage at the output ensures the target application has the largest possible dynamic range.