SPRUJB6B November 2024 – May 2025 AM2612 , AM2612-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Device Block Diagram
- 1.3 Module Allocation and Instances
- 1.4
Device Modules
- 1.4.1 Arm Cortex-R5F Processor Sub System (R5FSS)
- 1.4.2 Programmable Real-Time Unit and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 1.4.3 Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- 1.4.4 USB 2.0
- 1.4.5 Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS)
- 1.4.6 Spinlock (SPINLOCK)
- 1.4.7 Enhanced Data Movement Architecture (EDMA)
- 1.4.8 General Purpose Input/Output Interface (GPIO)
- 1.4.9 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 1.4.10 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 1.4.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 1.4.12 3-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 1.4.13 Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 1.4.14 General Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 1.4.15 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 1.4.16 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital Interface (MMCSD)
- 1.4.17 Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 1.4.18 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 1.4.19 Timers
- 1.4.20 Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 1.5 Device Identification
- 2 Memory Map
-
3 System Interconnect
- 3.1 System Interconnect Overview
- 3.2 CORE VBUSM Interconnect
- 3.3 CORE VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.4 PERI VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.5 INFRA0 VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.6 INFRA1 VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.7 R5SS0 CONFIG SLV Interconnect
- 3.8 CONTROLSS Interconnect
- 3.9 Interconnect Safety
- 3.10 Bus Safety Errors
- 3.11 System Memory Protection Unit (MPU)/Firewalls
-
4 Module Integration
- 4.1 ADC Integration
- 4.2 DAC Integration
- 4.3 eCAP Integration
- 4.4 EPWM Integration
- 4.5 EQEP Integration
- 4.6 FSI Integration
- 4.7 SDFM Integration
- 4.8 SOC_TIMESYNC_XBAR0 Integration
- 4.9 SOC_TIMESYNC_XBAR1 Integration
- 4.10 GPIO Integration
- 4.11 I2C Integration
- 4.12 SPI Integration
- 4.13 UART Integration
- 4.14 CPSW Integration
- 4.15 Integration
- 4.16 GPMC Integration
- 4.17 ELM Integration
- 4.18 MMCSD Integration
- 4.19 OSPI0 Integration
- 4.20 OSPI1 Integration
- 4.21 MCAN Integration
- 4.22 LIN Integration
- 4.23 RTI Integration
- 4.24 WWDT Integration
- 4.25 DCC Integration
- 4.26 ESM Integration
- 4.27 ECC Aggregator Integration
- 4.28 MCRC Integration
- 4.29 PRU-ICSS XBAR INTRTR0
- 4.30 GPIO XBAR INTRTR0
-
5 Initialization
- 5.1 Initialization Overview
- 5.2 Boot Process
- 5.3 Boot Mode Pins
- 5.4 Boot Modes
- 5.5 Redundant boot support
- 5.6 PLL Configuration
- 5.7 Secure Boot Flow
- 5.8 Boot Image Format
- 5.9 Boot Memory Maps
-
6 Device
Configuration
- 6.1
Control Module
- 6.1.1 Control Overview
- 6.1.2 TOP_CTRL
- 6.1.3
MSS_CTRL
- 6.1.3.1 MSS_CTRL Integration
- 6.1.3.2
MSS_CTRL Functional Description
- 6.1.3.2.1 R5FSS CPU Global Configuration and Control
- 6.1.3.2.2 Memory Initialization
- 6.1.3.2.3 EDMA Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.4 CPSW Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.5 ICSSM Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.6 GPMC Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.7 OSPI Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.8 USB Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.9 MPU Interrupt Aggregator
- 6.1.3.2.10 MMR Access Error Interrupt Aggregator
- 6.1.3.2.11 Safety Registers
- 6.1.3.2.12 MSS_CTRL MMR Kick Protection Registers
- 6.1.3.2.13 MSS_CTRL MMR Access Error Registers
- 6.1.4 CONTROLSS_CTRL (CTRLMMR2)
- 6.1.5 IOMUX (PADCFG_CTRLMMR0)
- 6.1.6 TOPRCM (RCM_CTRLMMR0): SoC-level Clock and Reset control registers
- 6.1.7 MSS_RCM (RCM_CTRLMMR1): SoC and Peripheral-level Clock and Reset control registers
- 6.2
Power
- 6.2.1 Power Management Overview
- 6.2.2
Power Management Unit
- 6.2.2.1 PMU Reference System (REFSYS)
- 6.2.2.2
PMU Safety System (SAFETYSYS)
- 6.2.2.2.1 Power OK (POK) Modules
- 6.2.2.2.2
Thermal Manager
- 6.2.2.2.2.1 Thermal Manager Features
- 6.2.2.2.2.2 Thermal Manager Functional Description
- 6.2.2.2.2.3 Thermal FSM
- 6.2.2.2.2.4 Thermal Alert Comparator
- 6.2.2.2.2.5 Thermal Shutdown Comparators
- 6.2.2.2.2.6 Temperature Timestamp Registers
- 6.2.2.2.2.7 FIFO Management
- 6.2.2.2.2.8 ADC Values Versus Temperature
- 6.2.3 Power Control Modules
- 6.2.4 Device Power States
- 6.3 Reset
- 6.4
Clocking
- 6.4.1 Overview
- 6.4.2 Clock IO
- 6.4.3 IP Clocking
- 6.4.4 Clock Gating
- 6.4.5 Limp Mode
- 6.4.6 Clocking Registers
- 6.4.7
Programming Guide
- 6.4.7.1 PLL and Root Clocks Programming Guide
- 6.4.7.2
IP Clock Configurations
- 6.4.7.2.1 RTI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.2 WDT CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.3 OSPI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.4 MCSPI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.5 I2C CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.6 LIN_UART CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.7 ICSSM CORE CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.8 ICSSM UART CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.9 MCAN CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.10 MMCx CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.11 CPTS CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.12 HSM RTI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.13 HSM WDT CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.14 HSM RTC CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.15 HSM DMTA CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.16 HSM DMTB CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.17 GPMC CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.18 CONTROLSS PLL CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.19 CPSW_5_50_250 CLK
- 6.4.7.2.20 XTAL MMC 32K CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.21 XTAL TEMPSENSE 32K CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.22 MSS_ELM CLOCK
- 6.1
Control Module
-
7 Processors and
Accelerators
- 7.1
Arm Cortex R5F Subsystem (R5FSS)
- 7.1.1 R5FSS Overview
- 7.1.2 R5FSS Integration
- 7.1.3
R5FSS Functional Description
- 7.1.3.1 R5FSS Block Diagram
- 7.1.3.2 R5FSS Cortex-R5F Core
- 7.1.3.3 R5FSS Interfaces
- 7.1.3.4 R5FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 7.1.3.5 R5FSS Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 7.1.3.6 R5FSS ECC Support
- 7.1.3.7 R5FSS Memory View
- 7.1.3.8 R5FSS Interrupts
- 7.1.3.9 R5FSS Debug and Trace
- 7.1.3.10 R5FSS Boot Options
- 7.1.3.11 R5FSS Events
- 7.1.3.12 R5FSS TCM Address Parity Error
- 7.1.3.13
R5FSS Lockstep
Compare
- 7.1.3.13.1 Overview
- 7.1.3.13.2 Module Operation
- 7.1.3.13.3
Control Registers
- 7.1.3.13.3.1 CCM-R5F Status Register 1 (CCMSR1)
- 7.1.3.13.3.2 CCM-R5F Key Register 1 (CCMKEYR1)
- 7.1.3.13.3.3 CCM-R5F Status Register 2 (CCMSR2)
- 7.1.3.13.3.4 CCM-R5F Key Register 2 (CCMKEYR2)
- 7.1.3.13.3.5 CCM-R5F Status Register 3 (CCMSR3)
- 7.1.3.13.3.6 CCM-R5F Key Register 3 (CCMKEYR3)
- 7.1.3.13.3.7 CCM-R5F Polarity Control Register (CCMPOLCNTRL)
- 7.1.3.14 R5FSS Selftest Logic
- 7.2
Trigonometric Math Unit (TMU)
- 7.2.1 TMU Introduction
- 7.2.2 TMU Functional Operation
- 7.2.3 TMU Data Format
- 7.2.4 TMU Operation Pseudo Code
- 7.3
Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 7.3.1 PRU-ICSS Overview
- 7.3.2 PRU-ICSS Environment
- 7.3.3 PRU-ICSS Integration
- 7.3.4 PRU-ICSS Top Level Resources Functional Description
- 7.3.5
PRU-ICSS PRU Cores
- 7.3.5.1 PRU Cores Overview
- 7.3.5.2
PRU Cores Functional Description
- 7.3.5.2.1 PRU Constant Table
- 7.3.5.2.2
PRU Module Interface
- 7.3.5.2.2.1 Real-Time Status Interface Mapping (R31): Interrupt Events Input
- 7.3.5.2.2.2 Event Interface Mapping (R31): PRU System Events
- 7.3.5.2.2.3
General-Purpose Inputs (R31): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.1 PRU EGPIs Direct Input
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.2 PRU EGPIs 16-Bit Parallel Capture
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.3 PRU EGPIs 28-Bit Shift In
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.4 General-Purpose Outputs (R30): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.5 Sigma Delta (SD) Decimation Filtering
- 7.3.5.2.2.3.6 Three Channel Peripheral Interface
- 7.3.5.3 PRU-ICSS RAM Index Allocation
- 457
- 7.3.6
PRU-ICSS Broadside Accelerators
- 7.3.6.1 PRU-ICSS Broadside Accelerators Overview
- 7.3.6.2 PRU-ICSS Data Processing Accelerators Functional
- 7.3.6.3 PRU-ICSS Data Movement Accelerators Functional
- 484
- 7.3.7
PRU-ICSS Local INTC
- 7.3.7.1
PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.3.7.1.1 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller System Events Flow
- 7.3.7.1.2 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Disabling
- 7.3.7.2 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Basic Programming Model
- 7.3.7.3 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Requests Mapping
- 499
- 7.3.7.1
PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.3.8
PRU-ICSS
UART Module
- 7.3.8.1 PRU-ICSS UART Overview
- 7.3.8.2 PRU-ICSS UART Environment
- 7.3.8.3
PRU-ICSS UART Functional Description
- 7.3.8.3.1 PRU-ICSS UART Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3.8.3.2 PRU-ICSS UART Reset Considerations
- 7.3.8.3.3 PRU-ICSS UART Power Management
- 7.3.8.3.4 PRU-ICSS UART Interrupt Support
- 7.3.8.3.5 PRU-ICSS UART DMA Event Support
- 7.3.8.3.6 PRU-ICSS UART Operations
- 7.3.8.3.7 PRU-ICSS UART Emulation Considerations
- 7.3.8.3.8 PRU-ICSS UART Exception Processing
- 533
- 7.3.9
PRU-ICSS ECAP Module
- 7.3.9.1 PRU-ICSS eCAP Overview
- 7.3.9.2
PRU-ICSS ECAP Functional Description
- 7.3.9.2.1 PRU-ICSS Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 7.3.9.2.2
PRU-ICSS eCAP Capture Mode Description
- 7.3.9.2.2.1 PRU-ICSS eCAP Event Prescaler
- 7.3.9.2.2.2 PRU-ICSS eCAP Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 7.3.9.2.2.3 eCAP Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 7.3.9.2.2.4 PRU-ICSS eCAP 32-bit Counter and Phase Control
- 7.3.9.2.2.5 PRU-ICSS Enhanced Capture CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 7.3.9.2.2.6 PRU-ICSS eCAP Interrupt Control
- 7.3.9.2.2.7 PRU-ICSS eCAP Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 7.3.9.2.2.8 CEVT Flag Registers
- 7.3.9.2.3 PRU-ICSS eCAP Module APWM Mode Operation
- 7.3.9.2.4
Use Cases
- 7.3.9.2.4.1 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 7.3.9.2.4.2 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 7.3.9.2.4.3 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 7.3.9.2.4.4 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 7.3.9.2.4.5 Application of the APWM Mode
- 566
- 7.3.10
PRU-ICSS MII_RT
Module
- 7.3.10.1 PRU-ICSS MII_RT Introduction
- 7.3.10.2
MII_RT Functional Description
- 7.3.10.2.1 MII_RT Data Path Configuration
- 7.3.10.2.2 MII_RT Definition and Terms
- 7.3.10.2.3
RX MII Interface
- 7.3.10.2.3.1 RX MII Receive Data Latch
- 7.3.10.2.3.2 RX MII Start of Frame Detection
- 7.3.10.2.3.3 CRC Error Detection
- 7.3.10.2.3.4 RX Error Detection and Action
- 7.3.10.2.3.5 RX Data Path Options to PRU
- 7.3.10.2.3.6 RX MII Port → RX L1 FIFO → PRU
- 7.3.10.2.3.7 RX MII Port → RX L1 FIFO → RX L2 Buffer → PRU
- 7.3.10.2.4 PRU-ICSS TX MII Interface
- 7.3.10.2.5 PRU R31 Command Interface
- 7.3.10.2.6 Other Configuration Options
- 612
- 7.3.11
PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Module
- 7.3.11.1 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Overview
- 7.3.11.2 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Functional Description
- 7.3.11.3 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Receive/Transmit Frame Host Software Interface
- 625
- 7.3.12
PRU-ICSS IEP
- 7.3.12.1 PRU-ICSS IEP Overview
- 7.3.12.2
PRU-ICSS IEP Functional Description
- 7.3.12.2.1 PRU-ICSS IEP Clock Generation
- 7.3.12.2.2 PRU-ICSS IEP Timer
- 7.3.12.2.3 32-Bit Shadow Mode
- 7.3.12.2.4 PRU-ICSS IEP Timer Basic Programming Sequence
- 7.3.12.2.5 Industrial Ethernet Mapping
- 7.3.12.2.6 PRU-ICSS IEP Sync0/Sync1 Module
- 7.3.12.2.7 PRU-ICSS IEP WatchDog
- 7.3.12.2.8 PRU-ICSS IEP DIGIO
- 643
- 7.4
Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- 7.4.1 Security Features
- 7.4.2 Security Features not Supported
- 7.4.3 Security Device Types
- 7.4.4
Crypto Hardware Accelerators
- 7.4.4.1 DTHE
- 7.4.4.2 CRC Engine
- 7.4.4.3
AES Engine - Symmetric Encryption and Decryption
- 7.4.4.3.1 Functional Description
- 7.4.4.3.2 Global Control FSM and DMA I/O
- 7.4.4.3.3 Register Interface
- 7.4.4.3.4 AES Wide-bus Engine
- 7.4.4.3.5 AES Algorithm
- 7.4.4.3.6
Supported Modes of Operation
- 7.4.4.3.6.1 ECB Feedback Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.2 CBC Feedback Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.3 CTR Feedback Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.4 CFB128 Feedback Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.5 f8 Feedback Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.6 XTS Operation
- 7.4.4.3.6.7 f9 Authentication Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.8 CBC-MAC Authentication Mode
- 7.4.4.3.6.9 GCM Operation
- 7.4.4.3.6.10 CCM Operation
- 7.4.4.3.7 Extended/Combined Modes of Operations
- 7.4.4.3.8 AES Module Programming Guide
- 7.4.4.3.9 HSM_AES Memory Map
- 7.4.4.4
Asymmetric Cryptography
- 7.4.4.4.1
Public Key Engine (PKE)
- 7.4.4.4.1.1 Introduction
- 7.4.4.4.1.2
Interfaces
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.1 Clock and Reset Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.2 AHB Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.3 Interrupt Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.4 Panic/Error Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.5 Busy/Idle Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.6 Working Context SRAM Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.7 Scratchpad Register File Interface
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.8 PK Engine Register Space
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.9 PK Engine and MCG Command Register Space
- 7.4.4.4.1.2.10 Blocks and Modules
- 7.4.4.4.1.3
Supported Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1
Low-Level (MAU) Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.1 Larger Multiplier and Adjustable Pipelining
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.2 Single-Operand Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.3 Dedicated Squaring Command
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.4 Write Back and Operate
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.5 Slot-Based Addressing
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.6 Non-Canonical Internal Format
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.7 Read-Only Memory
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.8 Read-Only Memory
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.9 Fault Resistance
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.10 PRNG Uses Keccak-F[200]
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.11 Compute pbar on Multiply
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.12 External Top-of-Memory and Length-of-Scratchpad Pointers
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.13 Internal Changes
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.14 Memory Map
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1.15 MAU Error Behavior
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2
MAU Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.1
Memory-Related Commands
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.1 0x1f: FLUSH: Destroy All Internal Data
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.2 0x1b: SET_RAM_SLOTS: Configure the RAM Slots
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.3 0x1c: SET_ROM_SLOTS: Configure the ROM Slots
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.4 0x01: LOAD: Load Data
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.5 0x02: STORE: Store Data
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.6 MCG_READ: Read RAM Data for MCG
- 4.4.4.1.3.2.1.7 0x1e: COPY: Copy Data
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.2 NOP: Do Nothing
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.3 Modulus Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.4 Modulo Addition and Subtraction
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.5 Modulo Multiplication
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.6 Integer Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.2.1
Memory-Related Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3
High-level (MCG) Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.1 Flushing Temporary Values on Error
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.2 High-Level Command Format
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.3 Special Primes
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.4 ROM Parameters
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.5 Point at Infinity
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.6 Interfaces
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.3.7
High-Level Command Reference
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.1 Summary of Memory Usage
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.2 0x00 ECDSA_VERIFY
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.3 0x01 ECC_KEY_BLIND
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.4 0x02: ECDSA_KEYGEN
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.5 0x03: ECDSA_SIGN and 0x0c: ECDSA_SIGN_2
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.6 0x04 and 0x05: ECDH_KEYGEN_EPH and ECDH_KEYGEN_LT
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.7 0x06 and 0x07: ECDH_SHARED_EPH and ECDH_SHARED_LT
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.8 0x08: ECC_ONCURVE
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.9 0x09: SM2DSA_KEYGEN
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.10 0x0A: ECC_ONCURVE_XONLY
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.11 0x0B: ECC_DECOMPRESS
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.12 0x0D: SM2DSA_SIGN and 0x0F: SM2DSA_SIGN_2
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.13 0x0E: SM2DSA_VERIFY
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.14 0x14 and 0x16: ECDH_MONTGOMERY_KEYGEN_EPH and ECDH_MONTGOMERY_SHARED_EPH
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.15 0x10 and 0x1A: ED448_KEYGEN and ED25519_KEYGEN
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.16 0x11 and 0x1B: ED448_SIGN_P1 and ED25519_SIGN_P1
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.17 0x12 and 0x1C: ED448_SIGN_P2 and EDDSA_SIGN_P2
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.18 0x13 and 0x1D: ED448_VERIFY and ED25519_VERIFY
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.19 0x1E: POINT_MUL_ADD
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.20 0x1F: ECC_ROM_SETUP
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.21 0x21: RSA_PUBLIC
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.22 0x22 and 0x23: RSA_SIGN and RSA_DECRYPT
- 4.4.4.1.3.3.7.23 0x24 and 0x25: MODEXP and MODEXP_MONT
- 7.4.4.4.1.3.1
Low-Level (MAU) Commands
- 7.4.4.4.1.4 Fault Countermeasures
- 7.4.4.4.1.5 Operation and usage
- 7.4.4.4.2 HSM_PKA_RAM Memory Map
- 7.4.4.4.1
Public Key Engine (PKE)
- 7.4.4.5
Hashing Function
- 7.4.4.5.1
SHA/MD5 Functional Description
- 7.4.4.5.1.1 SHA/MD5 Block Diagram
- 7.4.4.5.1.2 DMA and Interrupt Requests
- 7.4.4.5.1.3 Operation Description
- 7.4.4.5.1.4
SHA/MD5 Programming Guide
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1
Global Initialization
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1.2 Starting a New HMAC using the SHA-1 Hash Function and HMAC Key Processing
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1.3 Subsequence - Hashing a Key Bigger than 512 Bits with the SHA-1 Hash Function
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1.4 Operational Modes Configuration
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1.5 SHA/MD5 Event Servicing
- 7.4.4.5.1.4.1
Global Initialization
- 7.4.4.5.2 HSM_SHA Memory Map
- 7.4.4.5.1
SHA/MD5 Functional Description
- 7.4.4.6
Random Number Generator
- 7.4.4.6.1 True Random Number Generator (TRNG) with DRBG
- 7.4.4.6.2 HSM_TRNG Memory Map
- 7.4.5 How to Request Access for HSM Addendum
- 7.5
Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS)
- 7.5.1 Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS) Overview
- 7.5.2
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 7.5.2.1 Introduction (ADC)
- 7.5.2.2 ADC Integration
- 7.5.2.3 ADC Configurability
- 7.5.2.4 SOC Principle of Operation
- 7.5.2.5 SOC Configuration
- 7.5.2.6 Trigger Operation
- 7.5.2.7 ADC Acquisition (Sample and Hold) Window
- 7.5.2.8 ADC Input Models
- 7.5.2.9 Channel Selection
- 7.5.2.10 SOC Configuration Examples
- 7.5.2.11 ADC Conversion Priority
- 7.5.2.12 Burst Mode
- 7.5.2.13 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 7.5.2.14 Post-Processing Blocks
- 7.5.2.15 Result Safety Checker
- 7.5.2.16 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 7.5.2.17 Power-Up Sequence
- 7.5.2.18 ADC Calibration
- 7.5.2.19 ADC Timings
- 7.5.2.20 Additional Information
- 7.5.3 Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 7.5.4 Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 7.5.5
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.5.5.1 Introduction
- 7.5.5.2 EPWM Integration
- 7.5.5.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 7.5.5.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 7.5.5.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 7.5.5.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 7.5.5.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 7.5.5.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 7.5.5.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 7.5.5.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 7.5.5.4.7 Edge Detection Within a Programmable TBCTR Range
- 7.5.5.4.8 Global Load
- 7.5.5.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 7.5.5.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 7.5.5.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 7.5.5.8 Minimum Dead-Band (MINDB) + Illegal Combination Logic (ICL) Submodules
- 7.5.5.9 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 7.5.5.10 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 7.5.5.11 Diode Emulation (DE) Submodule
- 7.5.5.12 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 7.5.5.13 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 7.5.5.14 XCMP Submodule
- 7.5.5.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 7.5.5.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 7.5.5.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 7.5.5.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 7.5.5.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 7.5.5.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 7.5.5.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 7.5.5.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 7.5.5.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 7.5.5.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 7.5.5.16 ePWM Crossbar (XBAR)
- 7.5.5.17
Applications to Power Topologies
- 7.5.5.17.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 7.5.5.17.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 7.5.5.17.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 7.5.5.17.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 7.5.5.17.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 7.5.5.17.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 7.5.5.17.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 7.5.5.17.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 7.5.5.17.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 7.5.5.17.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 7.5.5.17.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 7.5.5.18 EPWM Programming Guide
- 7.5.6
Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 7.5.6.1 Introduction
- 7.5.6.2 eCAP Integration
- 7.5.6.3 Description
- 7.5.6.4
Capture Mode Description
- 7.5.6.4.1 Event Prescaler
- 7.5.6.4.2 Glitch Filter
- 7.5.6.4.3 Input Capture Signal Selection
- 7.5.6.4.4 Modulo 4 Counter
- 7.5.6.4.5 Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 7.5.6.4.6 Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 7.5.6.4.7 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 7.5.6.4.8 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 7.5.6.4.9 eCAP Synchronization
- 7.5.6.4.10 DMA Interrupt
- 7.5.6.4.11 ADC SOC Event
- 7.5.6.4.12 APWM Mode Operation
- 7.5.6.4.13 Signal Monitoring Unit
- 7.5.6.5 APWM Mode Operation
- 7.5.6.6 eCAP Synchronization and Events
- 7.5.6.7 Signal Monitoring Unit
- 7.5.6.8
Application of the eCAP Module
- 7.5.6.8.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 7.5.6.8.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 7.5.6.8.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 7.5.6.8.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 7.5.6.9 Application of the APWM Mode
- 7.5.6.10 eCAP Programming Guide
- 7.5.7
Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 7.5.7.1 Introduction
- 7.5.7.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 7.5.7.3 EQEP Integration
- 7.5.7.4 Description
- 7.5.7.5 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 7.5.7.6
Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 7.5.7.6.1
Position Counter Operating Modes
- 7.5.7.6.1.1 Position Counter Reset on Index Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 00)
- 7.5.7.6.1.2 Position Counter Reset on Maximum Position (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 01)
- 7.5.7.6.1.3 Position Counter Reset on the First Index Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 10)
- 7.5.7.6.1.4 Position Counter Reset on Unit Time-out Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 11)
- 7.5.7.6.2 Position Counter Latch
- 7.5.7.6.3 Position Counter Initialization
- 7.5.7.6.4 eQEP Position-compare Unit
- 7.5.7.6.1
Position Counter Operating Modes
- 7.5.7.7 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 7.5.7.8 eQEP Watchdog
- 7.5.7.9 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 7.5.7.10 QMA Module
- 7.5.7.11 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 7.5.7.12 EQEP Programming Guide
- 7.5.8
Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
- 7.5.8.1 Introduction
- 7.5.8.2 System-level Integration
- 7.5.8.3
FSI Functional Description
- 7.5.8.3.1 Introduction to Operation
- 7.5.8.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 7.5.8.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 7.5.8.3.3.1 Initialization
- 7.5.8.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 7.5.8.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 7.5.8.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 7.5.8.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 7.5.8.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 7.5.8.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 7.5.8.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 7.5.8.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 7.5.8.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 7.5.8.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 7.5.8.3.4 Frame Format
- 7.5.8.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 7.5.8.3.6 FSI Internal Loopback
- 7.5.8.3.7 CRC Generation
- 7.5.8.3.8 ECC Module
- 7.5.8.3.9 FSI Trigger Generation
- 7.5.8.3.10 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 7.5.8.4 FSI Programming Guide
- 7.5.9
Sigma Delta Filter Module
(SDFM)
- 7.5.9.1 Introduction
- 7.5.9.2 SDFM Integration
- 7.5.9.3 Configuring Device Pins
- 7.5.9.4 Input Qualification
- 7.5.9.5 Input Control Unit
- 7.5.9.6 SDFM Clock Control
- 7.5.9.7 Sinc Filter
- 7.5.9.8 Data (Primary) Filter Unit
- 7.5.9.9 Comparator (Secondary) Filter Unit
- 7.5.9.10 Theoretical SDFM Filter Output
- 7.5.9.11 Interrupt Unit
- 7.5.9.12 SDFM Programming Guide
- 7.5.10 Crossbar (XBAR)
- 7.6 OptiFlash
- 7.1
Arm Cortex R5F Subsystem (R5FSS)
- 8 Interprocessor Communication (IPC)
- 9 Memory Controllers
-
10Interrupts
- 10.1 Interrupt Architecture
- 10.2
Interrupt Controllers
- 10.2.1 Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 10.2.2 Other Interrupt Controllers
- 10.3 Interrupt Routers
- 10.4 Interrupt Sources
-
11Data Movement Architecture
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Definition of Terms
- 11.3
Enhanced Direct Memory
Access (EDMA)
- 11.3.1 EDMA Module Overview
- 11.3.2 EDMA Integration
- 11.3.3
EDMA Controller Functional Description
- 11.3.3.1 Block Diagram
- 11.3.3.2 Types of EDMA Controller Transfers
- 11.3.3.3
Parameter RAM (PaRAM)
- 11.3.3.3.1 PaRAM
- 11.3.3.3.2
EDMA Channel PaRAM Set Entry Fields
- 11.3.3.3.2.1 Channel Options Parameter (OPT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.2 Channel Source Address (SRC)
- 11.3.3.3.2.3 Channel Destination Address (DST)
- 11.3.3.3.2.4 Count for 1st Dimension (ACNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.5 Count for 2nd Dimension (BCNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.6 Count for 3rd Dimension (CCNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.7 BCNT Reload (BCNTRLD)
- 11.3.3.3.2.8 Source B Index (SBIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.9 Destination B Index (DBIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.10 Source C Index (SCIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.11 Destination C Index (DCIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.12 Link Address (LINK)
- 11.3.3.3.3 Null PaRAM Set
- 11.3.3.3.4 Dummy PaRAM Set
- 11.3.3.3.5 Dummy Versus Null Transfer Comparison
- 11.3.3.3.6 Parameter Set Updates
- 11.3.3.3.7 Linking Transfers
- 11.3.3.3.8 Constant Addressing Mode Transfers/Alignment Issues
- 11.3.3.3.9 Element Size
- 11.3.3.4 Initiating a DMA Transfer
- 11.3.3.5 Completion of a DMA Transfer
- 11.3.3.6 Event, Channel, and PaRAM Mapping
- 11.3.3.7 EDMA Channel Controller Regions
- 11.3.3.8 Chaining EDMA Channels
- 11.3.3.9 EDMA Interrupts
- 11.3.3.10 Memory Protection
- 11.3.3.11 Event Queue(s)
- 11.3.3.12 EDMA Transfer Controller (EDMA_TPTC)
- 11.3.3.13 Event Dataflow
- 11.3.3.14 EDMA Controller Prioritization
- 11.3.3.15 Emulation Considerations
- 11.3.4 EDMA Transfer Examples
- 11.3.5 EDMA Debug Checklist and Programming Tips
- 11.3.6 EDMA Event Map
- 12Time Sync
-
13Peripherals
- 13.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 13.1.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 13.1.1.1 GPIO Overview
- 13.1.1.2 GPIO Environment
- 13.1.1.3 GPIO Integration
- 13.1.1.4 GPIO Functional Description
- 13.1.2
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 13.1.2.1 I2C Overview
- 13.1.2.2
I2C Environment
- 13.1.2.2.1 I2C Typical Application
- 13.1.2.2.2
I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 13.1.2.2.2.1 I2C Serial Data Formats
- 13.1.2.2.2.2 I2C Data Validity
- 13.1.2.2.2.3 I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 13.1.2.2.2.4 I2C Addressing
- 13.1.2.2.2.5 I2C Controller Transmitter
- 13.1.2.2.2.6 I2C Controller Receiver
- 13.1.2.2.2.7 I2C Target Transmitter
- 13.1.2.2.2.8 I2C Target Receiver
- 13.1.2.2.2.9 I2C Bus Arbitration
- 13.1.2.2.2.10 I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 13.1.2.3 I2C Integration
- 13.1.2.4 I2C Functional Description
- 13.1.2.5 I2C Programming Guide
- 13.1.3
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 13.1.3.1 MCSPI Overview
- 13.1.3.2 SPI Environment
- 13.1.3.3 SPI Integration
- 13.1.3.4
MCSPI Functional Description
- 13.1.3.4.1 SPI Block Diagram
- 13.1.3.4.2 MCSPI Reset
- 13.1.3.4.3
MCSPI Controller Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.1 Controller Mode Features
- 13.1.3.4.3.2 Controller Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.3 Controller Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.4 Controller Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.5 Single-Channel Controller Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 13.1.3.4.3.8 Programmable MCSPI Clock (SPICLK)
- 13.1.3.4.4 MCSPI Peripheral Mode
- 13.1.3.4.5 MCSPI 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 13.1.3.4.6 MCSPI FIFO Buffer Management
- 13.1.3.4.7 MCSPI Interrupts
- 13.1.3.4.8 MCSPI DMA Requests
- 13.1.3.5
MCSPI Programming Guide
- 13.1.3.5.1 MCSPI Global Initialization
- 13.1.3.5.2
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 13.1.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Controller and Peripheral)
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Controller and Peripheral)
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.5 Controller Normal Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.6 Controller Turbo Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.7 Peripheral Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.9 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 13.1.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 13.1.3.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 13.1.4
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 13.1.4.1 UART Overview
- 13.1.4.2
UART Environment
- 13.1.4.2.1 UART Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.2 RS-485 Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.3 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.4 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.3 UART Integration
- 13.1.4.4
UART Functional Description
- 13.1.4.4.1 UART Block Diagram
- 13.1.4.4.2 UART Clock Configuration
- 13.1.4.4.3 UART Software Reset
- 13.1.4.4.4 UART Power Management
- 13.1.4.4.5 UART Interrupt Requests
- 13.1.4.4.6 UART FIFO Management
- 13.1.4.4.7 UART Mode Selection
- 13.1.4.4.8
UART Protocol Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.3 Multi-drop Parity Mode with Address Match
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.4 Time-guard
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.5 UART Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.2 RS-485 Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.3
IrDA Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.4 Frame Closing
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.6 Error Detection
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.9 Status FIFO
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.4 CIR Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 13.1.4.5
UART Programming Guide
- 13.1.4.5.1 UART Global Initialization
- 13.1.4.5.2 UART Mode selection
- 13.1.4.5.3 UART Submode selection
- 13.1.4.5.4 UART Load FIFO trigger and DMA mode settings
- 13.1.4.5.5 UART Protocol, Baud rate and interrupt settings
- 13.1.4.5.6 UART Hardware and Software Flow Control Configuration
- 13.1.4.5.7 IrDA Programming Model
- 13.1.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 13.2
High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 13.2.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 13.2.1.1 CPSW0 Overview
- 13.2.1.2 CPSW0 Environment
- 13.2.1.3 CPSW Integration
- 13.2.1.4
CPSW0 Functional Description
- 13.2.1.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 13.2.1.4.2 CPSW Ports
- 13.2.1.4.3 Clocking
- 13.2.1.4.4 Software IDLE
- 13.2.1.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 13.2.1.4.6
CPSW
- 13.2.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.1 Error Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.2 Bypass Operations
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.3 OUI Deny or Accept
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.4 Statistics Counting
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.5 Automotive Security Features
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.6 CPSW Switching Solutions
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.7 VLAN Routing and OAM Operations
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.8 Supervisory packets
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9
Address Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.1 Free Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.2 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.3 Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.4 Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.5 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.6 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.7 Inner VLAN Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.8 Outer VLAN Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.9 EtherType Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.10 IPv4 Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.11 IPv6 Table Entries
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.10 Multicast Address
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.11 Aging and Auto Aging
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.12 ALE Policing and Classification
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.13 Mirroring
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.14 Trunking
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.15 DSCP
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.16 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.17 VLAN Aware Mode
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.18 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 13.2.1.4.6.2 Packet Priority Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.3 CPPI Port Ingress
- 13.2.1.4.6.4 Packet CRC Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.5 FIFO Memory Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.6 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.7 Intersperced Express Traffic (IET – P802.3br/D2.0)
- 13.2.1.4.6.8
Enhanced Scheduled Traffic (EST – P802.1Qbv/D2.2)
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.1 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.2 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch RAM
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.3 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Interval
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.4 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch Values
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.5 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packet Fill
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.6 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Stamp
- 13.2.1.4.6.9 Audio Video Bridging
- 13.2.1.4.6.10
Ethernet MAC Sliver
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.1 CRC Insertion
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.2 MTXER
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.3 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.4 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.5 Back Off
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.6 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.7 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.2 RMII Interface
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.3 RGMII Interface
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.4 Frame Classification
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.5 Receive FIFO Architecture
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.11 Embedded Memories
- 13.2.1.4.6.12 Memory Error Detection and Correction
- 13.2.1.4.6.13 Ethernet Port Flow Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.14 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 13.2.1.4.6.15 Ethernet Switch Latency
- 13.2.1.4.6.16 MAC Emulation Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.17 MAC Command IDLE
- 13.2.1.4.6.18 FIFO Loopback
- 13.2.1.4.6.19
CPSW Network Statistics
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.1 Good Rx Frames (Offset = 3A000h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.2 Broadcast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A004h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.3 Multicast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A008h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.4 Pause Rx Frames (Offset = 3A00Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.5 Rx CRC Errors (Offset = 3A010h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.6 Rx Align/Code Errors (Offset = 3A014h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.7 Oversize Rx Frames (Offset = 3A018h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.8 Rx Jabbers (Offset = 3A01Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.9 Undersize (Short) Rx Frames (Offset = 3A020h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.10 Rx Fragments (Offset = 3A024h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.11 RX IPG Error (Offset = 3A05Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.12 ALE Drop (Offset = 3A028h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.13 ALE Overrun Drop (Offset = 3A02Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.14 Rx Octets (Offset = 3A030h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.15 Rx Bottom of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A084h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.16 Portmask Drop (Offset = 3A088h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.17 Rx Top of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A08Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.18 ALE Rate Limit Drop (Offset = 3A090h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1.19
ALE VLAN Ingress Check Drop (Offset = 3A094h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.1 ALE DA=SA Drop (Offset = 3A098h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.2 Block Address Drop (Offset = 3A09Ch)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.3 ALE Secure Drop (Offset = 3A0A0h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.4 ALE Authentication Drop (Offset = 3A0A4h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.5 ALE Unknown Unicast (Offset = 3A0A8h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.6 ALE Unknown Unicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0ACh)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.7 ALE Unknown Multicast (Offset = 3A0B0h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.8 ALE Unknown Multicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0B4h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.9 ALE Unknown Broadcast (Offset = 3A0B8h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.10 ALE Unknown Broadcast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0BCh)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.11 ALE Policer Match (Offset = 3A0C0h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.12 ALE Policer Match Red (Offset = 3A0C4h)
- 2.1.4.6.19.1.19.13 ALE Policer Match Yellow (Offset = 3A0C8h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.2 Rx Cut Thru with No Delay
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.3 Rx Cut Thru with Delay
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.4 Rx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.5 IET Receive Assembly Error (Offset = 3A140h - Port 0 or Offset = 3A340h - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.6 IET Receive Assembly OK (Offset = 3A144h - Port 0 or Offset = 3A344h - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.7 IET Receive Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A14Ch - Port 0 or Offset = 3A34Ch - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.8 IET Receive SMD Error (Offset = 3A148h - Port 0 or Offset = 3A348h - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9
Tx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.1 Good Tx Frames (Offset = 3A034h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.2 Broadcast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A038h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.3 Multicast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A03Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.4 Pause Tx Frames (Offset = 3A040h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.5 Deferred Tx Frames (Offset = 3A044h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.6 Collisions (Offset = 3A048h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.7 Single Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A04Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.8 Multiple Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A050h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.9 Excessive Collisions (Offset = 3A054h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.10 Late Collisions (Offset = 3A058h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.11 Carrier Sense Errors (Offset = 3A060h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.12 Tx Octets (Offset = 3A064h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.13 Transmit Priority 0-7 (Offset = 3A180h to 3A1A8h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.14 Transmit Priority 0-7 Drop (Offset = 3A1C0h to 3A1E8)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.15 Tx Memory Protect Errors (Offset = 3A17Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.16 Tx CRC Errors
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.17 Tx Cut Thru
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.9.18 Tx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.10 IET Transmit Merge Hold Count (Offset = 3A350h - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.11 IET Transmit Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A154h - Port 0 or Offset = 3A354h - Port 1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12
Rx- and Tx (Shared) Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.1 Rx + Tx 64 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A068h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.2 Rx + Tx 65–127 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A06Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.3 Rx + Tx 128–255 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A070h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.4 Rx + Tx 256–511 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A074h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.5 Rx + Tx 512–1023 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A078h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.6 Rx + Tx 1024_Up Octet Frames (Offset = 3A07Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.12.7 Net Octets (Offset = 3A080h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.13 1979
- 13.2.1.4.6.19.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 13.2.1.4.7
Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 13.2.1.4.7.1 CPSW0 CPTS Integration
- 13.2.1.4.7.2 CPTS Architecture
- 13.2.1.4.7.3 CPTS Initialization
- 13.2.1.4.7.4 32-bit Time Stamp Value
- 13.2.1.4.7.5 64-bit Time Stamp Value
- 13.2.1.4.7.6 64-Bit Timestamp Nudge
- 13.2.1.4.7.7 64-bit Timestamp PPM
- 13.2.1.4.7.8 Event FIFO
- 13.2.1.4.7.9 Timestamp Compare Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.10 Timestamp Sync Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.11 Timestamp GENFn Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.12 Timestamp ESTFn
- 13.2.1.4.7.13 Time Sync Events
- 13.2.1.4.7.14 Timestamp Compare Event
- 13.2.1.4.7.15 Host Transmit Event
- 13.2.1.4.7.16 CPTS Interrupt Handling
- 13.2.1.4.8 CPDMA Host Interface
- 13.2.1.4.9 Cut-Thru
- 13.2.1.4.10 CPPI Checksum Offload
- 13.2.1.4.11 Egress Packet Operations
- 13.2.1.4.12 MII Management Interface (MDIO)
- 13.2.1.5 CPSW0 Programming Guide
- 13.2.2 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 13.2.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 13.3
Memory Interfaces
- 13.3.1
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 13.3.1.1 GPMC Overview
- 13.3.1.2 GPMC Environment
- 13.3.1.3 GPMC Integration
- 13.3.1.4
GPMC Functional Description
- 13.3.1.4.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 13.3.1.4.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.3 GPMC Power Management
- 13.3.1.4.4 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 13.3.1.4.5 GPMC Interconnect Port Interface
- 13.3.1.4.6 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 13.3.1.4.7
GPMC Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.7.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 13.3.1.4.7.2 Access Protocol
- 13.3.1.4.7.3
External Signals
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.2 DIR Pin
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.3 Reset
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.4 Write Protect Signal (nWP)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.5 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 13.3.1.4.7.4 Error Handling
- 13.3.1.4.8
GPMC Timing Setting
- 13.3.1.4.8.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 13.3.1.4.8.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 13.3.1.4.8.6 GPMC_CLKOUT
- 13.3.1.4.8.7 GPMC Output Clock and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 13.3.1.4.8.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 13.3.1.4.9
GPMC NOR Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in non-multiplexed Mode
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.4 Page and Burst Support
- 13.3.1.4.9.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 13.3.1.4.10 GPMC pSRAM Access Specificities
- 13.3.1.4.11
GPMC NAND Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 13.3.1.4.11.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 13.3.1.4.11.3
ECC Calculator
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.1 Hamming Code
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2
BCH Code
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.1 Requirements
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 13.3.1.4.11.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 13.3.1.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.12 GPMC Memory Regions
- 13.3.1.4.13 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 13.3.1.5 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 13.3.2 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 13.3.3
Multimedia Card (MMC)
- 13.3.3.1 Introduction
- 13.3.3.2 Integration
- 13.3.3.3
Functional Description
- 13.3.3.3.1 MMC/SD/SDIO Functional Modes
- 13.3.3.3.2 Resets
- 13.3.3.3.3 Power Management
- 13.3.3.3.4 Interrupt Requests
- 13.3.3.3.5 DMA Modes
- 13.3.3.3.6 Mode Selection
- 13.3.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 13.3.3.3.8 Transfer Process
- 13.3.3.3.9 Transfer or Command Status and Error Reporting
- 13.3.3.3.10 Transfer Stop
- 13.3.3.3.11 Output Signals Generation
- 13.3.3.3.12 CE-ATA Command Completion Disable Management
- 13.3.3.3.13 Test Registers
- 13.3.3.3.14 MMC/SD/SDIO Hardware Status Features
- 13.3.3.4 Low-Level Programming Models
- 13.3.4
OptiFlash Submodules
- 13.3.4.1 RL2_OF
- 13.3.4.2
Flash Subsystem (FSS)
- 13.3.4.2.1 FSS Overview
- 13.3.4.2.2 FSS Integration
- 13.3.4.2.3 FSS Functional Description
- 13.3.4.2.4 FSS Programming Guide
- 13.3.4.2.5
Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 13.3.4.2.5.1 OSPI Overview
- 13.3.4.2.5.2 OSPI Environment
- 13.3.4.2.5.3 OSPI Integration
- 13.3.4.2.5.4
OSPI Functional Description
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.1 OSPI Block Diagram
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.2 OSPI Modes
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.3 OSPI Power Management
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.4 Auto HW Polling
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.5 Flash Reset
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.6 OSPI Memory Regions
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.7 OSPI Interrupt Requests
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.8 OSPI Data Interface
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.9 OSPI Direct Access Controller (DAC)
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.10 OSPI Indirect Access Controller (INDAC)
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.11 OSPI Software-Triggered Instruction Generator (STIG)
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.12 OSPI Arbitration Between Direct / Indirect Access Controller and STIG
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.13 OSPI Command Translation
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.14 Selecting the Flash Instruction Type
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.15 OSPI Data Integrity
- 13.3.4.2.5.4.16 OSPI PHY Module
- 13.3.4.2.5.5 OSPI Programming Guide
- 13.3.4.2.6 Firmware Upgrade Over the Air (FOTA) Accelerator
- 13.3.4.2.7 On the Fly Encryption and Authentication (OTFA)
- 13.3.4.2.8 Error Correction Code (ECC) and Safety
- 13.3.5 Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI1)
- 13.3.1
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 13.4
Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 13.4.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 13.4.1.1 MCAN Overview
- 13.4.1.2 MCAN Environment
- 13.4.1.3 MCAN Integration
- 13.4.1.4
MCAN Functional Description
- 13.4.1.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 13.4.1.4.2 Interrupt and DMA Requests
- 13.4.1.4.3
Operating Modes
- 13.4.1.4.3.1 Software Initialization
- 13.4.1.4.3.2 Normal Operation
- 13.4.1.4.3.3 CAN FD Operation
- 13.4.1.4.3.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 13.4.1.4.3.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.8 Power Down (Sleep Mode)
- 13.4.1.4.3.9 Test Modes
- 13.4.1.4.4 Timestamp Generation
- 13.4.1.4.5 Timeout Counter
- 13.4.1.4.6 ECC Support
- 13.4.1.4.7 Rx Handling
- 13.4.1.4.8 Tx Handling
- 13.4.1.4.9 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 13.4.1.4.10 Message RAM
- 13.4.2
Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 13.4.2.1 LIN Overview
- 13.4.2.2 LIN Integration
- 13.4.2.3 Serial Communications Interface Module
- 13.4.2.4
Local Interconnect Network Module
- 13.4.2.4.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 13.4.2.4.1.1 LIN Standards
- 13.4.2.4.1.2 Message Frame
- 13.4.2.4.1.3 Synchronizer
- 13.4.2.4.1.4 Baud Rate
- 13.4.2.4.1.5 Header Generation
- 13.4.2.4.1.6 Extended Frames Handling
- 13.4.2.4.1.7 Timeout Control
- 13.4.2.4.1.8 TXRX Error Detector (TED)
- 13.4.2.4.1.9 Message Filtering and Validation
- 13.4.2.4.1.10 Receive Buffers
- 13.4.2.4.1.11 Transmit Buffers
- 13.4.2.4.2 LIN Interrupts
- 13.4.2.4.3 Servicing LIN Interrupts
- 13.4.2.4.4 LIN Configurations
- 13.4.2.4.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 13.4.2.5 Low-Power Mode
- 13.4.2.6 Emulation Mode
- 13.4.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 13.5 Timer Modules
- 13.6
Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 13.6.1 Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 13.6.2 ECC Aggregator
- 13.6.3
Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 13.6.3.1 ESM Overview
- 13.6.3.2 ESM Features
- 13.6.3.3 ESM Integration
- 13.6.3.4
ESM Functional Description
- 13.6.3.4.1 ESM Functional Operation
- 13.6.3.4.2 Error Event Inputs
- 13.6.3.4.3 Error Interrupt Outputs
- 13.6.3.4.4 ESM Error Pin Output
- 13.6.3.4.5 Error Pin Behavior During Reset
- 13.6.3.4.6 PWM Mode
- 13.6.3.4.7 Minimum Time Interval
- 13.6.3.4.8 Safety Protection for MMRs
- 13.6.3.4.9 ESM Interrupts
- 13.6.3.4.10 Programming Guide
- 13.6.4
Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) Controller
- 13.6.4.1 MCRC Overview
- 13.6.4.2 MCRC Integration
- 13.6.4.3
MCRC Functional Description
- 13.6.4.3.1 MCRC Block Diagram
- 13.6.4.3.2 MCRC General Operation
- 13.6.4.3.3 MCRC Modes of Operation
- 13.6.4.3.4 PSA Signature Register
- 13.6.4.3.5 PSA Sector Signature Register
- 13.6.4.3.6 CRC Value Register
- 13.6.4.3.7 Raw Data Register
- 13.6.4.3.8 Example DMA Controller Setup
- 13.6.4.3.9 Pattern Count Register
- 13.6.4.3.10 Sector Count Register/Current Sector Register
- 13.6.4.3.11 Interrupts
- 13.6.4.3.12 Power Down Mode
- 13.6.4.3.13 Emulation
- 13.6.4.4 MCRC Programming Examples
- 13.6.5
Self-Test Controller (STC)
- 13.6.5.1 STC Overview
- 13.6.5.2 Block Diagram
- 13.6.5.3
Module Description
- 13.6.5.3.1 ROM Interface
- 13.6.5.3.2 FSM and Sequence Control
- 13.6.5.3.3 Register Block
- 13.6.5.3.4 VBUSP Interface
- 13.6.5.3.5 STC Flow
- 13.6.5.3.6 Programming Sequence
- 13.6.5.3.7
ROM Organization
- 13.6.5.3.7.1 TR_T: Transition Delay Methodology Type
- 13.6.5.3.7.2 FT: Fault Model for the BIST Run
- 13.6.5.3.7.3 SEG_ID[1:0]
- 13.6.5.3.7.4 Pattern Count ( patt_count[9:0] )
- 13.6.5.3.7.5 MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.6 LP_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Low Power Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.7 INV_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Inverse Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.8 LP_INV_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Low Power Inverse Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.9 Pn_SDm[7:0] (n - no. of patterns, m - scan chain length): OP-MISR Scan Data
- 13.6.6 Programmable Built-In Self-Test (PBIST) Module
- 13.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
-
14On-Chip Debug
- 14.1
On-Chip Debug
- 14.1.1 On-Chip Debug Overview
- 14.1.2 On-Chip Debug Features
- 14.1.3 On-Chip Debug Functional Description
- 14.1.4 Arm Debug Links
- 14.1
On-Chip Debug
- AM261x TRM Revision History
11.3.3.2.1 A-Synchronized Transfers
In an A-synchronized transfer, each EDMA sync event initiates the transfer of the 1st dimension of EDMA_TPCC_ABCNT_n[15:0] ACNT bytes, or one array of ACNT bytes. Each event/TR packet conveys the transfer information for one array only. Thus, BCNT × CCNT events are needed to completely service a PaRAM set.
Arrays are always separated by EDMA_TPCC_BIDX_n[15:0]SBIDX and EDMA_TPCC_BIDX_n[31:16] DBIDX, as shown in Figure 11-6, where the start address of Array N is equal to the start address of Array N – 1 plus source (SRC) or destination (DST) in EDMA_TPCC_BIDX_n register.
Frames are always separated by EDMA_TPCC_CIDX_n[15:0] SCIDX and EDMA_TPCC_CIDX_n[31:16] DCIDX. For A-synchronized transfers, after the frame is exhausted, the address is updated by adding SRCCIDX/DSTCIDX to the beginning address of the last array in the frame. As in Figure 11-6, SRCCIDX / DSTCIDX is the difference between the start of Frame 0 Array 3 to the start of Frame 1 Array 0.
Figure 11-6 shows an A-synchronized transfer of 3 (CCNT) frames of 4 (BCNT) arrays of n (ACNT) bytes. In this example, a total of 12 sync events (BCNT × CCNT) exhaust a PaRAM set. See Figure 11-6 for details on parameter set updates.
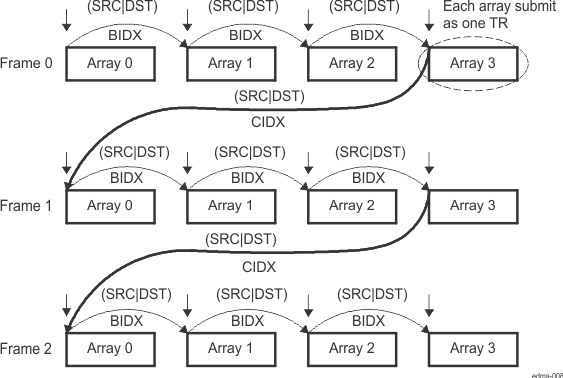 Figure 11-6 A-Synchronized Transfers (ACNT = n, BCNT = 4, CCNT = 3)
Figure 11-6 A-Synchronized Transfers (ACNT = n, BCNT = 4, CCNT = 3)